Brief introduction of Goods and Services Tax in India (GST) What is GST in India?
GST stands for Goods and Services Tax which came into effect on 1st July 2017. This is indirect taxation, which an end consumer usually pays. GST replaced many other indirect taxes such as excise duty, VAT, service tax, entry tax and luxury tax. In brief, this tax is levied on the supply of goods and services. It is calculated on the value added to any goods. Goods and Services Tax in India is a comprehensive, destination-based and multi-stage tax added on every value addition.
Comprehensive
- GST covers every aspect of sale and purchase. It replaced various other taxes. It is called comprehensive because it encompasses every aspect of commercial life.
Destination-based
- GST is levied in a state where the product is sold rather than the state where it was manufactured. For example, if these goods were produced in West Bengal and sold in Andhra Pradesh, the GST will be levied and collected in Andhra Pradesh
Multi-stage
- In the production of any goods or services, there are usually plenty of stages. These stages include the procurement of raw materials, production or manufacture, warehousing, selling to wholesalers, retailers and finally, the end consumers. At every stage, GST is levied. This makes it a multi-valued tax.
Value addition
- For example in textile production, first, raw materials such as cotton or silk are taken and made into cloth. This increases the value of the raw materials. Then the fabric is designed into clothes which further enhance their value. After the dresses are made, they are branded and sold to retailers who advertise and market them, thereby increasing their value. GST is levied on each of these stages where value is added to the product.
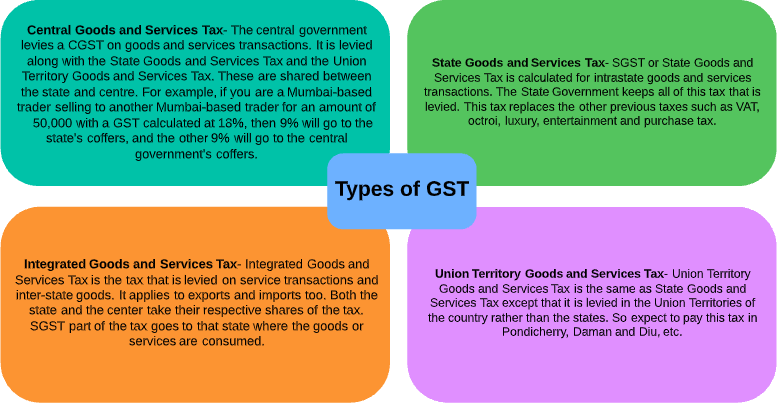
What are the types of GST in India?
There is a four-fold break-up of goods and services tax in India. It oversees the levy of tax for central government GST, GST for states, union territories, and the integrated goods and services tax.
What are the different GST rates on goods and services?
There are four types of GST slab rates. These are 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%. The GST council revises these rates to ensure efficient pricing of these products. Here are the different slabs of GST and the various goods and services that fall under these categories.
The goods and services available at 5% GST
- Edible oil, spices, tea, coffee, and sugar
- Coa
- Matting, coir mats, and floor covering
- Wind-based Atta Chakki or Pawan Chakki
- Fertilizers
- Natural cork
- Appliances for differently-abled individuals, such as Braille paper, Braille watches, hearing aids, etc.
- Marble rubble
- Indian sweets or Mithai
- Different accessories or carriage parts for differently-abled individuals
- Fly-ash blocks
- Biogas
- Incense sticks and kites
- Life-saving drugs and medicines, like insulin
- Numismatic coins
- Ice and snow
- Walking sticks
- Cashew nuts
- First-day covers revenue stamps
- Stamp postmarks
- Renting a motor car without paying for fuel
Goods and services available at 12% GST
- Frozen meat
- Fruit juices
- Diagnostic kits and reagents
- Sewing machines
- Handmade matches
- Dairy products
- Notebooks and exercise books
- Jewellery box
- Plastic beads
- Two-way radios
- Fixed Speed Diesel Engines
- Sauces, bottles of ketchup, condiments
- Real estate construction
- Hotel accommodation within 1001 and 7500 per day
Goods and services available at 18% GST
- Food or drinks at those places with AC and liquor license
- Party arrangement with shamianas and food supplies
- Movie tickets prices above 100
- Household products
- Non-leather school bags and satchels
- Shopping bags and handbags made of cotton, jute, artificial plastic, and other materials but excluding basket work or wickerwork
- Precast concrete pipes
- Outdoor catering
- Works contract supply
- Dental wax
- Electrical transformer
- Headgear and its parts
- All devices for length measuring by hand, like measuring tapes, callipers, etc.
- Staplers, pencil-sharpening devices
- Rear tractor wheel rims, tractor housing transmissions, tractor center housing, tractor support front axle
- Transformers and industrial electronics
- Plastic tarpaulin
- Pencil sticks for Kajal
- Aluminium foil
Goods and services available at 28% GST
- Caffeinated beverages
- Food or drinks at 5-star hotels
- Gambling
- Go-karting
- Ballet
- State-owned and state-authorized lotteries
- Cars and two-wheelers
- Dishwashing machines
- Aerated beverages
- Tobacco products, such as cigarettes
- Racing club services
- Washing machines
- Cement
- Paint
- Air conditioners
- Yachts
What is GST registration?
Every business with a turnover that exceeds 40 lakhs or 10 lakhs for the North East and hill states must register as a normal taxable person. This process is called GST registration. GST registration usually takes between 3-6 days and can be quite a tedious process.
How to register for GST?
Every individual or business has to register for GST. You will have to apply with the Goods and Services Network (GSTN). Once you have registered, you will receive a Goods and Services Tax Identification Number. This is a 15 digit number that is issued state-wise once you have completed the registration.
Documents for GST registration process online
Some of the documents that you will require while registering for GST are:
- An applicant’s PAN card
- Pan, Voter, or Adhaar card of the promoters and partners
- A business address proof in the form of a lease agreement, rent, or other utility bills
- Account statement of the firm, or individual or company
- Partnership deed or incorporation certificate
How to apply for GST registration online?
PART A of registration:
Follow these steps to apply for GST registration online
- Go to the GST portal https://www.gst.gov.in/.
- Select the "Services" tab.
- Choose "Registration" and then select "New Registration."
- Under the drop-down menu for "I am a," select "Taxpayer."
- Fill the form GST REG-01 for the new registration, and enter the details of your business, state, email address, mobile number and PAN card.
- A one-time password will be sent to your mobile. Enter that password and select "Proceed."
- When you complete this level, you will have to go to another process called part B.
- You will receive a Temporary Reference Number (TRN) after verification.
This is how you complete the application for the GST number.
PART B of the registration:
- To start the registration under PART B, you need to login with the TRN.
- Enter the Captcha code.
- Complete the OTP verification with the OTPs sent to the email id and the registered mobile number.
- Then you will be redirected to the GST registration page.
- Next, the details of your business need to be given, such as the name of your Business or Company.
- Add other information such as PAN number and the state where your business is to be set up.
- If you have any existing registrations, mention them and the date when the business will commence.
- In the next step, the names and details of up to ten business partners or promoters need to be mentioned.
- In case of a sole proprietorship, the PAN, Aadhar, DIN (Director Identification Number) and personal details have to be provided.
- In case someone else is filing your GST returns, their details have to be furnished.
- The address of the premises, official contact information and nature of the property need to be filled in.
- The company's bank account details, details of the services and details of any other places of the same business have to be filled in.
- The "type of business" needs to be specified. All these details are to be entered under the correct heading.
- Click on the "Save and continue" button. After it is submitted, you will need to provide your digital signature.
- Click on "Submit."
- You will now receive your ARN (Application Reference Number) by email or SMS to confirm the registration of your application.
How to calculate the GST amount?
The following formulae are needed for calculating the GST before the application of GST and after the removal of GST. Here's how GST is calculated.
Formulae for adding GST
GST Amount = (Original Cost x GST %) /100
Net Price = Original Cost + GST Amount
Formulae for removing GST
GST Amount = Original Cost – [Original Cost x {100/(100+GST%)}]
Net Price = Original Cost – GST Amount
You can also find several GST tax calculators online.
What are the benefits of GST?
There are many benefits of GST registration; few of them are listed below:
- The benefit of GST to the government
One of the chief benefits of the GST to the government is bringing all the nation's markets under one tax system. This creates confidence in the international market for Indian products and increases foreign investment. This boost to foreign investment will help Indian products reach a global venue and increase the export and import market. - The benefit of GST to the common man
The benefits of GST to the consumer are manifold. Consumers will have to pay much less than before when they had to pay VAT. GST is a one-time tax, so it is charged at just one stage. For example, food items have become cheaper and packaged goods such as shampoos, toothpaste and soaps have become more affordable.
- With GST, the cascading effect to tax has been eliminated, which is the "tax on tax" system.
- There is now a higher threshold for a business person to register under GST (The business has to have a turnover of 40 lakh or more. It sets smaller companies free from having to pay GST.
- GST has come up with a "composition scheme" that is responsible for helping small businesses pay lesser tax and also reduces compliance.
- There is one simple and easy procedure to pay the GST tax. You can do it online by getting your registration number.
- The number of compliances is fewer. There is just one return to be filed. The GSTR-1 will be manually populated, and the other forms are auto-populated.
- There is a clear-cut definition for the e-commerce sector where companies like Amazon and Flipkart are treated the same in all the states, and there is no notable difference in identifying them.
- The unorganized sector has been largely regulated with the arrival of GST. The new regulations have benefited the construction and textile industry.
What is GST return?
All businesses have to file monthly, quarterly, or annual GST returns. You can file the GST returns online. A GST return is a document that contains the sales, purchase, expense, or income of every business or person with a GSTIN. This document is used by tax authorities to calculate the net tax liability. There are different GST return charges. You can do the GST return filing online.
GST helpline number and official details
1) You can call the GST Helpline Numbers, which are given below and contact the government authorities to help with GST filing.
| Helpdesk Name | Phone Number(s) |
| GST Help Desk | 0120-4888-999 |
| Saksham Seva | 1800-266-2232, 1800-121-4560 |
| CBEC Mitra | 1800-1200-232 |
| ICEGATE Help Desk | 1800-3010-1000 |
2) Here are some of the key email contacts that you can contact for the filing of your GST.
| Helpdesk Name | Email ID |
| GST Help Desk | helpdesk@gst.gov.in |
| Saksham Seva | saksham.seva@icegate.gov.in |
| CBEC Mitra | cbecmitra.helpdesk@icegate.gov.in |
| ICEGATE Help Desk | icegatehelpdesk@icegate.gov.in |
3) GST Self Service Portal
Under the Services → User Services section of the official GST portal https://www.gst.gov.in/, you can fill out the grievances in the form along with your details and complaint, which will then be addressed.
In conclusion, GST is the tax change that has united the country under One Nation, One Tax. It has made the taxation system much simpler and has joined the country irrespective of the state into one tax regime that makes business easier and more manageable for day-to-day transactions.
What is a GST exemption?
Understanding the taxability of goods and services also includes knowing whether a good or service is exempted from GST registration. Upon knowing this, applicants can get clarity on several other factors. Essentially, the GST exemption limit for businesses depends on their annual aggregate turnover. Previously, businesses with an annual turnover of up to 20 lakhs did not need to register for GST. The amount was 10 lakhs for North-eastern or hilly states like Meghalaya, Sikkim, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Assam, Tripura, Uttarakhand, and Jammu & Kashmir. However, as per the GST council meeting on 10th January 2019, the values doubled for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in both cases. In addition to this, certain supplies of goods and services fall under the GST registration exemption list. Let’s understand this better by referring to the following section.
What is an exempt supply under GST?
There are three types of supplies that can enjoy exemption under GST. They are as follows:
- Supplies taxable at 0% tax or nil tax rates.
- Whole or partial exemption of supplies under CGST or SGST.
- Supplies under Section 2(78).
Note: One cannot utilize the input tax credit applicable to these supplies.
In addition to this, one must follow the list mentioned below to understand the differences between nil-rated, zero-rated, exempt and non-GST supplies.
| Supplies | Meaning |
| Nil-rated | Supplies that have 0% tax rate. Example: Salt. |
| Non-GST | Ones that do not come under the purview of GST law include alcohol for human consumption. |
| Zero-rated | Export supplies to SEZ (Special Economic Zone) developers. |
| Exempt | Taxable supplies that do not attract GST. Curd, fruits are among some of the supplies. |
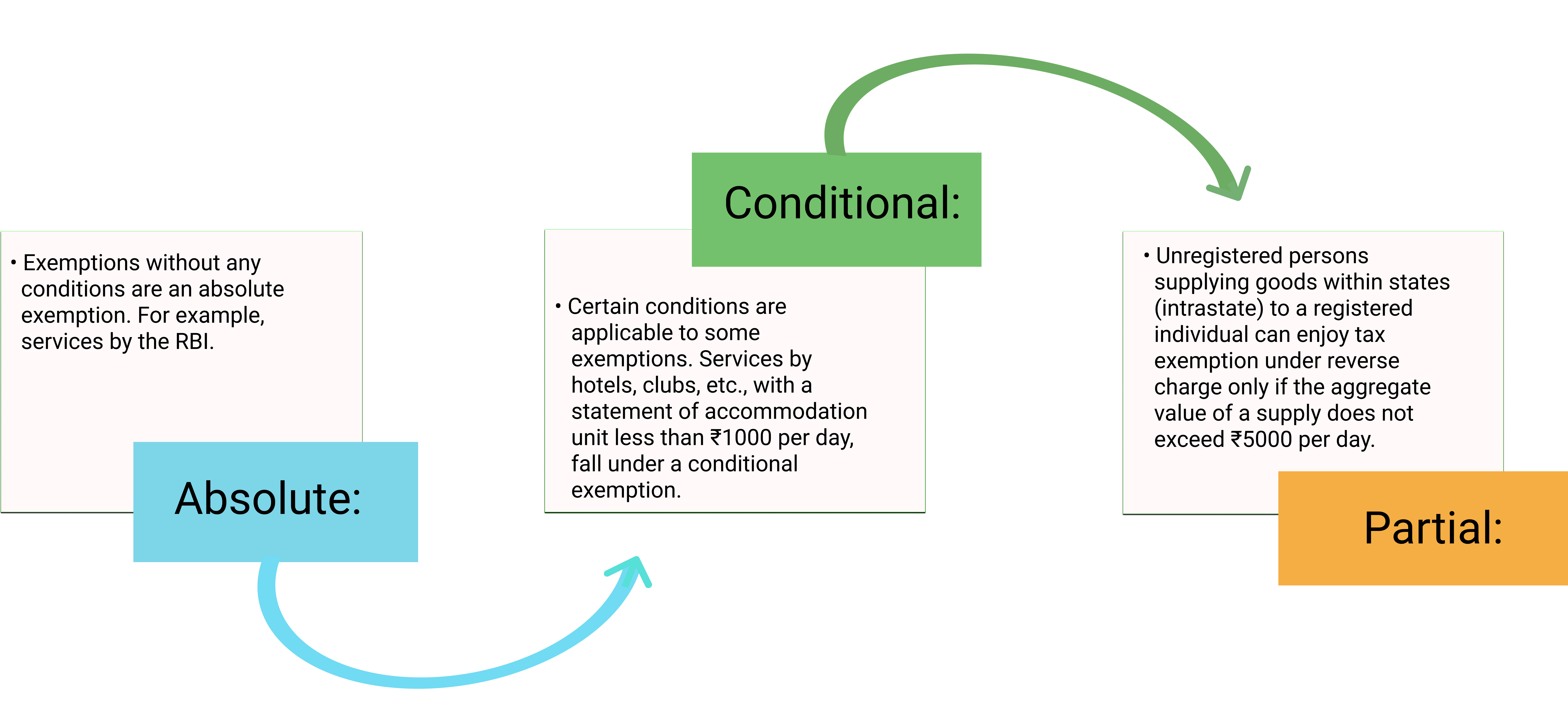
Furthermore, there are different types of GST exemptions one needs to know about.
Types of exemption in GST
Given below are the three types of exemptions in GST:
List of GST exemption
Goods, services, supplies, businesses, and individuals must register for GST provided they fulfill certain conditions. However, there are few exceptions to this. In the following section, you will find a list mentioning all the items, businesses, and taxpayers who can avail of tax exemption under the Goods and Services Tax regime.
GST exemption from registration
The following category of taxpayers need not register for GST:
- Individuals belonging to the threshold exemption limit.
- Exempt suppliers of goods and services.
- A person supplying non-GST goods and services.
- Taxpayers engaging in activities other than the supply of goods or services.
- Agriculturists.
- Ones supplying goods covered under reverse charge.
Therefore, if you belong to the above list, you can enjoy a full GST exemption.
GST exemption for start-ups and small businesses
Individuals aspiring to start a business can benefit greatly from the latest regulations of the GST scheme. Here are a few pointers to keep in mind regarding GST exemption for start-ups.
- Any business with a turnover of less than 40 lakhs is recognized as a GST-exempt business.
- Businesses that have a lower annual aggregate turnover than 1.5 crores can avail of a composition scheme under GST. The scheme allows individuals to pay taxes at a fixed rate depending on the turnover amount. The rate may vary between 1-6%.
- Also, small businesses are exempted from e-invoicing under GST. However, businesses with a turnover of more than 50 crores have to apply for e-invoicing mandatorily.
- Small businesses with an income below 5 crores can opt for a quarterly filing system.
Hence, it is evident that small businesses can accrue several benefits under this new tax scheme.
Exempted goods under GST
In the following section, you will find a list of the GST exempted goods in India:
- Fresh and dry vegetables like potatoes, onions, and other leguminous vegetables.
- Non-GST goods include fish, egg, fresh milk, etc.
- Grapes, melons, ginger, garlic, unroasted coffee beans, green tea leaves that are not processed, and more.
- Food items that are not put into branded containers like rice, hulled cereal grains, wheat, corn, etc.
- Components like human blood.
- Unspun jute fibres, raw silk, khadi fibre, etc.
- Hearing aid manufacturing parts, chalks, slates, handloom, etc.
Note: Certain non-GST items, once processed, will attract a GST.
Exempted services under GST
A number of services qualify for GST exemption. Here is a GST exemption list of services for your reference:
- Agricultural services, including harvesting, packaging, warehouse, cultivation, supply, leasing of machinery, are essentially GST exempt services. An exception to these exempted services includes the rearing of horses.
- Public transportation services, auto-rickshaws, metered cabs, metro, etc.
- Transportation of agricultural products and goods outside of India.
- Labor supply for farms.
- Goods transportation where the charges are less than 1500.
- Services like retail packing, pre-conditioning, waxing, etc.
- Foreign diplomatic and government services.
- Healthcare and educational services like mid-day meal catering, VET clinics, paramedics, etc. Ambulance and charity services also qualify for exemption under GST.
- Services offered by RBI, IRDAI, Central and State Government, NPS and more.
- Banking services like Basic Saving Bank Deposit (BSBD) account operable under the Pradhan Mantri JanDhan Yojana (PMJDY).
In addition to this, services related to religious ceremonies, sports organization, tour guides, and libraries are exempted under GST.
Reasons for exemption under GST
The government decides on exempting goods from registering under GST in the following cases:
- In case the GST council recommends the exemption.
- The government might find certain exemptions from GST registration to be beneficial for the public.
- Under exceptional or unforeseen situations, the government might grant exemption by special order.
- Upon providing official notification, one can supply specific goods under a full exemption.
Therefore, from the points mentioned above, it is evident that several sectors can qualify for a GST exemption provided they fulfill some prerequisites. Knowing those criteria in detail will help a taxpayer to register under GST without any hassle.
What is the GST invoice?
Implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) is probably one of the most significant tax reforms our country has seen, and there have been many discussions on the topic ever since. Some of the prominent queries here can be surrounding the GST invoice bill – the building block of this tax system. A GST-compliance purchase invoice contains the details of the parties involved in the mentioned transaction and lists all goods and services sold, with their prices. This bill also displays the percentage of discounts and taxes charged on each item, besides other details.
Do all businesses need to issue GST invoices?
A GST invoice must be issued without fail by businesses that hold a GST registration. Other enterprises, however, do not need to issue these particular invoices.
Mandatory fields in GST invoice
Here is a list of particulars that must be present in a GST tax invoice specified under Rule 54 of the CGST Act of 2017.
- Name, GSTIN, and address of the supplier
- Invoice number
- Date of issuance
- Invoice type
- Shipping and billing address
- Name of the customer
- GSTIN of the customer if registered
- Details of products and services provided, including description, quantity, etc.
- SAC code or HSN code
- Rate of CGST, IGST, UTGST, and SGST charged
- Total tax amount and discounts, if any
- Reverse charge
- Signature of the invoice issuer
GST tax invoice rules
When following the above guidelines in terms of invoice contents, issuers need to consider certain rules that specify the “what” and “how” of these details.
GST invoice serial number rules
Following are the mandates that issuers need to follow as per Rule 46 (b).
- The invoice numbers must be sequential or consecutive.
- They must be unique for a financial year, containing an alphanumeric combination.
- A serial number must not exceed 16 characters.
- GST should be split into CGST, SGST, and IGST. It must not be charged as a whole.
- In the case of any transactions made outside the issuer’s state, a separate tax called IGST has to be charged. On the other hand, SGST and CGST should be charged against sales within the same state.
GST invoice signature rules
The CGST rules make the issuer's signature one of the mandatory fields in a GST invoice. Specifications of a valid signature are as follows.
- The bill can be signed by hand or digitally, provided it is affixed as per the mandates of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- The GST invoice bill must be signed by the supplier or his/her authorized representative
- As per section 116 (2), his/her ‘authorized representative’ can be a company secretary, a practicing advocate, a chartered accountant, a retired officer of the Commercial Tax Department, or a regular employee appearing on the supplier’s behalf.
GST invoice payment rules
Another mandate under the CGST Act concerns a scenario where a GST-registered individual makes purchases from a seller who is not registered. There can be 2 cases here.
- If the registered individual buys from an unregistered entity, the former has to issue a tax invoice.
- If the registered individual receives supplies exempted from GST, he/she needs to issue a bill of supply instead of an invoice bill.
Now, you might be wondering that it might get difficult to always issue an invoice following such extensive guidelines right upon purchase every time.To ease this process, the Indian government has also provided outlines regarding the time of issue of invoice under GST.
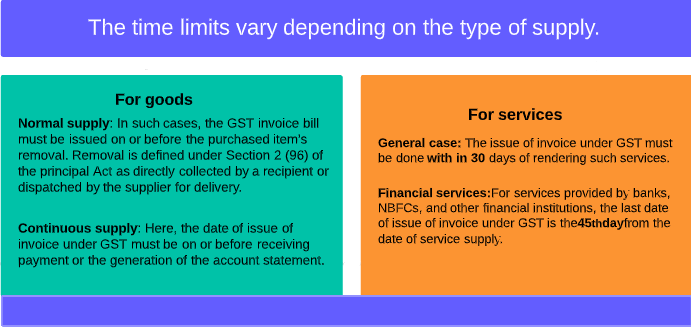
When to issue a GST invoice?
What are other types of invoices under GST?
Here is a list of the other types of GST invoices besides a tax invoice.
Bill of supply
The only difference between a bill of supply and a tax invoice is that a 0% or no GST is charged in the former. Therefore, this type of invoice can be issued in 2 cases.
- When a GST-registered supplier has chosen the composition scheme.
- When a GST-registered supplier is dealing in exempted services and goods.
As a result, the recipient does not have the provision to claim an input tax credit based on this document. Also, a registered entity can issue an all-encompassing invoice-cum-bill of supply as per the Notification No. 45/2017 of Central Tax if it deals in both exempt and taxable services/goods.
Aggregate invoice
If a seller issues multiple invoices to an unregistered buyer, each less than 200, he/she can issue a single invoice, summing up all the amounts. This is called a bulk or aggregate invoice.
Debit and credit note
Such commercial documents are issued when there is any discrepancy found in a previously issued tax invoice for a product or service.
A debit note is issued when any of these 2 conditions arise.
- The formerly issued tax invoice displays a lower taxable value than the correct amount.
- The amount of tax charged in this tax invoice is lower than the actual value.
On the other hand, a credit note is issued for the opposite reasons.
- The taxable amount or tax charged in the invoice is higher than the correct figures.
- There is a discrepancy in services or products provided, and the buyer returns them and asks for a refund.
Besides the above types of invoices in GST, there are several other documents and vouchers relating to such transactions, depending on several conditions.
Revising invoices issued before GST
There can be several instances of getting a wrong GST invoice bill issued. As a solution, there is a provision for revising such tax invoices before. All sellers need to apply for provisional registration before they get the permanent certificate. Any tax invoice issued from the date of GST implementation till the date on which permanent registration certificate is issued must have a revised invoice under GST issued against them. This must be done within 1 month from the date of issue of the registration certificate. This revised tax invoice under GST must have “Revised Invoice” mentioned on it, along with all the mandatory details of a tax invoice as already discussed.
How many copies of invoices should a supplier issue?
Since proof of transaction should remain with all parties involved, there are a specific number of invoice copies issued depending on the type of supply.
1. For goods
The dealer must produce 3 copies of the GST invoice bill issued.
- Original copy: Received by the buyer
- Duplicate copy: Received by individuals delivering the products from the supplier’s end to the recipient’s end
- Triplicate copy: Must be kept with the dealer
2. For services
In the case of services, the issuer needs to arrange 2 copies of the invoice.
- Original copy: Sent to the buyer
- Duplicate copy: Remains with the supplier for later reference.
These are the relevant details regarding a GST invoice bill. If you are a registered dealer, ensure issuing such documents to avail Input Tax Credit (ITC). If you are not GST-registered yet, consider getting a certificate to help your business benefit from such provisions.
All about GST Registration Online in India
GSTIN or GST identification number is a unique 15-digit PAN-based number assigned to every individual registered under GST. Therefore, GST registration is necessary to obtain this number. There may be multiple GSTIN for a single person. In such a scenario, when the applicant reaches a threshold limit for GST registration online, the person must acquire GSTIN.
How to register for GST?
The new tax regime rolled out on 1st July 2017. Since then, it is vital for all business entities to apply for GST to benefit from this regime. After successful registration, one can obtain a GST number and enjoy tax benefits. However, one needs to follow certain steps to apply for a GSTIN. Here is the process for GST registration.
How to apply for GST registration?
For the procedure of GST application online, follow these steps:
- Visit the GST portal online.
- From the “Taxpayers” tab, click on “Register Now” for registration.
- By selecting the “New Registration” option, you will land on a page where you need to provide details like name, permanent account number, state, district, etc.
- After filling up the details precisely, click on “Proceed.”
- You will receive an OTP in your registered email ID and mobile number. Enter it in the required field.
- A ‘Temporary Reference Number’ will be assigned to you. Make a note of this number.
- Upon revisiting the portal, you need to follow the same steps. Instead of “New Registration,” select “Temporary Reference Number” and enter captcha details to proceed to the next step.
- Again, you will receive an OTP in your registered number and email ID. Enter it.
- On the next page, you will find the application status shown as drafts. You may click on the edit icon.
- Finally, select your category and submit documents for the place of business, authorized signatory, and more to proceed to verification.
Upon completion of verification, you will receive an ‘Application Reference Number’ on your mobile number. This concludes the process to apply for a GST number. These are the basic steps one needs to follow for new registration. After this, one needs to present a list of documents required for GST registration. We have discussed the same in the following sections.
Who should register for GST?
To successfully obtain a GST number, an individual needs to meet the following eligibility for GST registration.
- Individuals who are still classified under the pre-GST law (VAT, Service Tax, etc.)
- Business turnover above 40 lakhs (The same amount is 10 lakhs for north-eastern states, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Jammu & Kashmir)
- A taxable person who is a non-resident
- Input service distributor and supplier agent
- Individuals who are paying tax under reverse charge mechanism
- Person supplying through an e-commerce aggregator
- E-commerce aggregators
- Individuals who supply online information or database access or retrieval services from a foreign country to a resident in India are not registered taxable
Furthermore, according to the category of a person, there are different types of registration under GST.
What are the types of registration in GST?
Here are the types of GST registration in India:
- Normal taxpayer: This category includes any person whose business turnover is more than 40 lakhs. An individual whose aggregate turnover in the previous year did not surpass 75 lakhs should register under this scheme. Additionally, taxpayers from service industries, GSTR3B, and GSTR1 need to opt for Goods and Services Tax registration.
- Composition scheme: Any taxpayer whose annual turnover is less than 1.5 crores can register for GST under this scheme. This is a simple and easy scheme availing which small taxpayers can avoid inconvenient GST formalities and pay tax at a fixed rate.
- Casual taxable person: An individual without a fixed place of business supplying goods or services in a territory where GST is applicable is treated as a casual taxable person under GST
- Input service distributor: This is an office of goods or services supplier that receives tax invoices on input services receipt. Such tax invoices are issued for the distribution of credits on the same services to a facility with the same PAN.
- Non-resident taxable person: A person outside of India supplying goods or services where GST is applicable is a non-resident taxable person under GST.
- Non-resident online service distributor: Individuals supplying online services outside India other than a registered person must register for GST.
- UN Body/Embassy/other notified individuals: The Ministry of External Affairs issued a Unique Identification Number to the UN bodies and embassies. This number allows them to receive the supply of goods and services from registered individuals. These categories can apply for GST from its online portal.
- Special Economic Zone unit or developer: SEZ developers and units must initiate a new registration for GST by submitting the necessary certificate and documents.
- TDS/TCS: Candidates paying more than 2.5 lakhs to suppliers need to register under GST as a tax deducted at source. The individuals can directly apply for the registration from the website.
Furthermore, there are some vital documents required for GST registration
Which documents are required for GST registration?
For registration under GST, one needs to carry the following documents:
- PAN card
- Aadhaar
- Business registration proof or incorporation certificate
- ID and address proofs of promoters or directors with passport size photographs
- Supporting address proof of the place of business
- Bank account statements
- Digital signature
- Letter of authorization for authorized signatory
After successfully presenting the scanned copies of the above documents, one can complete the procedure for GST registration. Additionally, it takes 2-6 days to complete the registration process. One can apply for GST by visiting the online GST portal and following the steps mentioned above. However, an individual may visit the GST Seva Kendra set up by the Government of India to apply for GST offline. All you need to do is fill up the form, present the necessary documents, and submit them to the authority.
What are the fees for GST registration?
Taxpayers should note that GST registration charges are free. Therefore, you need not pay anything for registration under GST. However, defaulting tax payments or making short payments will incur a GST penalty. The penalty under GST stands at 10% of the tax amount only if the amount is a minimum of 10,000. In case of deliberate tax evasion, the penalty will be 100% of the tax amount.
How to check GST application status?
Candidates can check GST status with or without logging in to the portal. Here are the steps to follow if you wish to check GST registration status without logging in:
- Upon visiting the GST portal, you need to select “Services” and “Registration.”
- Now click on the “Track Application Status” and enter your ARN.
- You will find any one of the statuses out of - pending for processing, site verification assigned, site verification completed, pending for clarification, clarification filed- pending for order, clarification not filed- pending for order, approved, or rejected.
Additionally, one can track GST application status after logging in to the portal by following these steps:
- Login to the GST portal.
- Choose the “Services” and “Track Application Status” options.
- You need to select “Registration” from the module drop-down.
- Either by providing your ARN or SRN (Service Request Number) or submission date, you can check your status for GST registration.
You can download the acknowledgement slip by clicking on the “Download” hyperlink. Therefore, after making a note of all this crucial information, one can proceed with GST registration in a hassle-free and convenient manner. This will allow the individuals to avail of tax benefits under the regime.
Types of GST in India
Goods and Services tax and types: An overview
On 1st July 2017, the government announced a new indirect tax regime under Goods and Services tax to replace several other indirect taxes like state VAT, customs duties, central excise duty, and entertainment tax. In simple words, GST is a tax applicable to the value added to goods and services at each stage in the supply chain. There are four types of GST, namely, CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST. Each type features different taxation rates applicable at the buyer’s end.
Types of GST in India
To understand the types of tax under GST, firstly, you need to understand the main motive behind this unified tax system’s introduction. The primary reason is to make the Central and State Governments independent of each other.
The different tax heads under GST are as follows:
- Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST): The central government is responsible for collecting this tax.
- Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST): This form of GST is collected by the Union Territory government
- State Goods and Services Tax (SGST): This tax is applicable when transactions take place within a state. Such taxes are collected by the individual state governments.
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST): If transactions are made between 2 different states, then IGST is collected by the Central government instead of SGST.
What is CGST?
CGST stands for Central Goods and Services tax. It replaced all the previous taxes under the Central Government.Some examples of such taxes are central surcharges & cess and central excise duty. CGST is levied on the movement of goods within a state. For example, if a manufacturer produces a good in West Bengal, and sells it intra-state (within the state), both SGST and CGST will be levied where the former will go to the West Bengal State Government, whereas the latter will reach the Central Government. In most cases, the tax is divided equally between the State and Central Governments as per the GST council mandate.
| Goods | CGST Percentage |
| Household items like tea, coffee, edible oil, sugar, and spices, life-saving medicines, Indian sweets, and coal | 2.5 |
| Computer products and processed foods | 6 |
| Capital products, hair oils, toothpaste, soaps, and industrial goods | 9 |
| ACs, motorcycles, refrigerators, luxury items | 14 |
Hence, we can see that the maximum rate of CGST is 14%, as per data from October 1, 2019.
What is SGST?
The GST collected by the State Government is known as SGST, which is applicable on transactions within its geographical boundaries. Under the new tax regime, previous state taxes like entertainment tax, VAT, and State Sales tax became non-functional. SGST stands for State Goods and Services tax, a single tax levied on intrastate supplies of goods and services, except for alcoholic liquor. It can be charged solely on a product’s transactional value – an amount the buyer needs to pay. SGST features might vary state-wise since each State Government has individual acts. However, specific characteristics like taxable events, valuation, classification of goods and services, and measures are similar across the nation.
Thus, this tax embodies the objective of this new tax regime: one tax, one nation.
| Products | SGST Percentage |
| Household amenities like tea, sugar, etc. Medicines, coal, and Indian sweets | 2.5 |
| Processed food items like cheese and bread. Computers and laptops also fall under this group. | 6 |
| Capital goods, soaps, toothpaste | 9 |
| Air conditioners, refrigerators, high-end vehicles. | 14 |
What is IGST?
IGST stands for Integrated Goods and Services tax. It is generally applicable during interstate transactions, i.e., transactions between two different states. Among the types of GST, it’s levied on supplies of products and services between two states and even on exports and imports (IGST + customs). The Central Government is responsible for its collection as per the IGST Act. Let’s simplify this with the help of an example. Suppose a manufacturer from West Bengal sells goods to a customer in Maharashtra. In this case, IGST will apply to the transaction value. The Central Government will collect this sum. Later, this amount will be divided between the consumer state – in this case, Maharashtra – and the Central Government.
The tax goes to the consumer state and not the manufacturing state because the buyer incurs the tax.
| Products | IGST Percentage |
| Household products like tea, sugar, etc. Indian sweets and life-saving drugs | 5 |
| Cheese, bread, other processed food items, desktops, laptops, et al. | 12 |
| Hair oil, toothpaste, soaps, capital goods | 18 |
| Luxury items like ACs and refrigerators | 28 |
What is UTGST?
UTGST stands for Union Territory Goods and Services tax, applicable to the transaction of goods and services in the Union Territories. It is levied on the supply of products in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Daman Diu, Chandigarh, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli. Note that UTGST is only applicable on Union Territories without a legislature. Hence, Delhi, Puducherry, and even the newly formed UTs of Jammu & Kashmir are not liable for UTGST but SGST. Simply understanding the UTGST meaning is not sufficient. You must also know the applicable rates. This tax is collected by the Central Government and is a substitute for the State Goods and Services tax in UTs. Thus,the UTGST percentage is similar to that of SGST, which are 2.5%, 6%, 9%, and 14%. Furthermore, after understanding the types of GST and rates associated with them, it is vital to know that some products are taxed at 0%. Meat from mammals, birds and fish do not draw such a tax. Additionally, sanitary napkins, bananas, apples, and grapes are other tax-free products.
Benefits of GST
- Before the GST era, multiple taxes were levied by the State and Central Government. Therefore, regulation of these taxes was quite a hassle.
- GST is a convenient and easy-to-follow tax regime.
- It minimizes the chances of tax mix-up between the Central and State Governments.
- It brought uniformity to the taxation system.
Persons with GST-registered businesses at any location in India are liable to incur taxes under this regime, whether it’s under the forward charge or reverse charge mechanism. It includes e-commerce operators as well. GST calculators are used in calculating the costs of GST applicable on a certain product. These are available on various third-party websites.
Online GST Calculator
Ever since the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017, calculating the final price of a product/service has been the responsibility of a customer. GST is a multi-level all-inclusive tax covering all the previously fragmented indirect taxes.
What is a GST calculator?
An online GST tax calculator is a quick and easy way to determine the total GST payable for a period or against a product/service. This online tool comes with 3 modes of operation, each for a buyer, manufacturer, and retailer/wholesaler. Each of these variants comes with different input options.
- The calculator for buyers needs inputs for product price and GST rate.
- Manufacturers need to enter their product cost, percentage of profit, and GST rate.
- Wholesalers or retailers need to input the total cost of goods, profits ratio, and GST rate.
Each of these users will get the results for the final price, including tax, total tax, and this tax’s breakdown into CGST and SGST/IGST.
Why should you use an online GST calculator?
Here is how you can benefit from an online GST calculator tool.
- It is easy to use and saves time by providing instant results.
- An online calculator curbs the inaccuracies of manual calculation and provides precise results.
- Taxpayers can determine the individual amounts for CGST, SGST, and IGST accurately, which cannot be manually calculated using the GST tax calculation formula.
- You can also estimate the gross price for your selected item.
How to calculate GST amount using an online GST calculator?
The process of calculating the GST online is extremely easy. However, before going ahead with the calculation process, you must have an idea of the GST rates applicable for products/services of different categories.
The GST rate slabs under the new tax structure are 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. Once you know the rate applicable for your product, follow these steps as a buyer.
Step 1: Enter the net price of goods/services you want.
Step 2: Enter a suitable GST rate corresponding to the category that your concerned product/service belongs. You can also find the applicable GST rate using an HSN or SAC code.
Step 3: Click on “Calculate.”
An online GST calculator will help you gain a clear perspective regarding the tax charged at different stages of a product until it reaches you.
What is the formula to calculate GST?
If you wish to cross-check the output provided by this online tool on your own, here is a mathematical formula to calculate GST. Now, there can be 2 instances.
1. Where you know the net price and want to compute the GST-included price:
Here, you will first need to calculate the GST amount, say A, using this formula: A = (P x r) / 100
Where P stands for net price and r indicates the GST rate.
Now you can calculate the final or gross price G as follows.
G = P + A
2. Where the GST-included price is given, and you want to compute the original price:
First, you need to derive the total GST amount A from the given gross price G as follows.
A = G - [G x {100 / (100 + r)}]
Now you can calculate the original or net price P as well.
P = G – A
From the above instances, you can clearly understand that manual calculation using these formulae can only give you the total GST amount.
You cannot get the tax break-up of CGST and SGST/IGST. This is something that only an online GST calculator can provide, which brings us to the next section
What is GST interest?
If you file your GST returns after the given due date, you will need to pay a late penalty along with interest on your net GST liability. This interest is calculated from the day immediately succeeding the due date.
Now, you might be wondering if this applies to you if you have had no sales on supplies in the concerned period. Yes, even then, you need to file your NIL GST returns.
If you have missed the deadline and want to know your probable interest payment, here is the GST interest calculation formula for your convenience.
I = P x (r/100) x (n/365)
Where I stands for interest payable, P indicates the net GST liability, r is the annual interest rate, and n is the number of days of delay since the due date. You can also find a GST interest calculator online, which can help you determine such amounts faster. To avoid such unnecessary charges, make sure to note the last date for filing GST returns in a month or quarter. Also, know your tax liability with the help of an online GST calculator and don’t remain in the dark! Hence a GST calculator can be used by every individual involved in the payment or collection of GST, including buyers, wholesalers, and manufacturers.
To utilize this tool, a buyer must first enter the net cost of a product before GST is added. Next, enter the GST rate. The calculator will automatically compute the total taxes, CGST, and SGST, along with the cost of production. Due to the integrated algorithm, these online tools do not make mistakes, provided you enter the parameters and details correctly. Thus, unlike in manual calculations, a GST calculator ensures minimal errors.
Understanding the Impact of GST in India
One nation, one market, one tax' was the motto with which GST was applied in its full capacity on 1st July 2017. This move has brought 1.3 million citizens of our nation into a unified indirect taxation system.
Impact of GST on our economy
GST is levied on every stage of manufacturing and sales of goods and services across India. This tax is levied when the goods or services are consumed. With this brief idea, let's go through the impacts of GST on the Indian economy -
- Simpler tax structure
With GST, the taxation system of our country has become simpler. It is a single tax, ensuring easier calculation. With this tax, the buyer gets a clear idea of the amount paid as tax when purchasing certain products. This is crucial when considering GST and its impact on the GDP. - More funds for production
Another effect of GST on the Indian economy has been the reduction in the total taxable amount. This saved fund can again be invested back into the production cycle to foster production. - Support for small and medium enterprises
Based on the size of your organization, the amount of GST depends on your firm's annual turnover, provided you have been registered under the Composition Scheme introduced by GST. Enterprises with a yearly turnover of 50 lakhs have to pay 6% GST whereas enterprises with 1.5 crores worth of turnover have to pay 1% GST. - Increased volume of export
When considering GST and its impact on the Indian economy, customs duty on exporting goods has reduced. So now production units save money while producing goods and also while shipping them. This two-way savings has lured many production units to export their goods, increasing the export quantity. - Enhanced operations throughout India
With a unified taxation system, transporting goods around India has now become easy, boosting operations throughout the country. - No more cascading effect
With GST, taxes of the State and Central Government have been merged. This has removed the cascading effect of taxes, reducing the burden on the buyer and the seller. So even if it may look like one big chunk of tax to be paid, you pay lesser hidden taxes.
- How did the introduction of GST impact real estate
Real estate contributes to almost 8% of our nation's total GDP. Before the onset of GST, buying an underconstruction property meant you were subject to VAT, service tax, stamp duty, and registration charges. However, purchasing a completed property meant only the application of stamp duty and registration charges. The application of GST will reduce the amount of buying a house, especially if booked before construction. Now developers too shall enjoy input credits on GST paid on goods and services delivered by them as that liability shall be passed on to potential buyers.
Taxes levied over real estate have also become simpler as the government has removed stamp duty after the application of GST, thereby making the impact of GST on the real estate sector more prominent. All underconstruction properties will total to 5% of GST without the input tax credit. There is no GST applicable for ready-to-move-in properties. If you are looking to purchase a house, consider these effects of GST on properties.
Suppose the carpet area of a particular property is up to 60 sq. meters, and in a non-metro, it is up to 90 sq. meters. In that case, that property can be included in the affordable housing scheme. This affordable house will accrue 1% GST if its value is below 45%; otherwise, 5% GST is applicable. These are some of the important effects of GST on the real estate sector. Builders have to pay a higher tax amount in the 4-tier taxation, but they also avail input credits later. However, the burden for potential buyers has risen, as they will have to bear GST apart from those who are a part of the CLSS Scheme. Thus, one can easily notice how GST benefits the Indian economy.
- The impact of GST on the common man’s pocket
If you see the short-term impacts, customers now shall need to pay more taxes on goods and services they purchase. A majority of essential consumables will input either the same or a higher amount of tax. The benefits of GST to the common man are plentiful. Small-scale trades also have to bear the cost of compliance, which may raise the prices of their produce, affecting the consumer.
Nevertheless, in the long term, GST also promises several benefits. With the decrease of payable taxes for producers of consumer goods like FMCG, the automotive sector will have to reduce the prices of their commodities. This will allow the consumer to pay less while trying to avail of these services. A drop in prices will show an immediate surge in demands, boosting the production cycle bringing in more profits. With this, both the buyer and the seller get to save a fair share of money eventually, and the economy, too, shall be boosted.
A boost in production shall also pave the way for expansion, leading to more employment and increased income. This not only creates a better scope for the common man but also strengthens the economy.
The implementation of GST also implies raising an invoice for the purchase of any goods and services. With a proper billing system, the prospect of black money and corruption shall also go down. These have been troubling aspects for the common man in India. - How does GST affect the other sectors?
Till now, we discussed the small, medium, and large scale manufacturers and the real estate sector; let’s now take a look at the impact of GST on businesses other than real estate
- Logistics
In a country as big as ours, logistics plays a key contribution to the economy. A well-organized and structured logistics industry can grow exponentially, especially under the Make in India banner. - E-commerce
E-commerce has high growth potential. However, e-commerce companies shall have to bear with tax collected at source factor for GST. - Haridwar 2 Nights Tour Package
The pharma and healthcare sector shall have a positive impact on GST with its simplified tax structure. It will also be availing a tax respite in lieu of making healthcare cheaper and accessible to people of all income groups. - Telecom
A drop in prices can be expected in the telecom sector, as costs like warehousing, logistics, etc., will reduce. - Textile
Indian textile is one of the largest employers of skilled and unskilled labor. With the textile industry also making 10% of total exports in India, the numbers are likely to increase with the removal of customs duties. GST shall also affect the value of cotton, a material on which most small-scale textile industries depend. These are some of the impacts of GST on small traders. - Agriculture and farming
Agriculture is the biggest contributor to India's GDP, covering more than 16%. With the ease of logistics, transportation costs of agricultural produce will also go down. Thus, the impact of GST on wholesalers has been greatly positive.
- FMCG
With GST eliminating the need for multiple sales depots, FMCG shall save a lot on logistics and distribution costs. - Automobile
Under the previous taxation system, several taxes like excise, VAT, sales tax, road tax, motor vehicle tax, registration duty were applicable, which has now been replaced by GST. Automobile prices are likely to drop as the producers are saving more in the form of taxes now. - Startups
GST has tremendously benefitted Indian startups with perks like a DIY compliance model, increased limits for registration, a free flow of goods and services and tax credit on purchases. It has also become easier for companies with a pan India presence to calculate taxes, especially if belonging to the ecommerce sector. Understand the impact of GST on small-scale industries if you are a part of this sector - Self-employed individuals
Self-employment or freelancing is a young industry in our country, but filing for taxes has become easier as they fall under service providers with GST implementation. Understanding the impact of GST on micro small and medium enterprises is important for such individuals. Entrepreneurs engaged in the hospitality sector should also check out the impacts of GST on the hospitality industry.
GST comes with its set of pros and cons, affecting both buyers and sellers. One must be aware of GST’s negative impact on the GDP as well. So one side, when taxes have become simplified, they have also led to a rise in compliance costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can all taxpayers use the ‘communication between taxpayers’ facility?
-
All taxpayers registered under GST can use this functionality except those registered as TDS, TCS and NRTP.
- 2. Does a supplier/recipient receive an alert when the notification sent is received by the counterparty?
-
The counterparty will receive an alert. However, the sender of notification can see the notifications sent in his outbox.
- 3. How many notifications can be sent to the same GSTIN in a financial year?
-
A maximum of 100 notifications can be sent to the same GSTIN in a financial year with the same tax period.
- 4. Can a taxpayer upload/download the documents in CSV format while sending notifications?
-
This functionality is not available as of now.
- 5. How many documents can be manually added through UI or screen for a particular notification?
-
50 documents can be manually added through UI or screen for a particular notification.
- 6. Who is not required to file GSTR-4?
-
Below mentioned persons are not required to file Form GSTR-4 (annual return):
- Non-resident taxable person
- Regular taxpayer
- OIDAR
- Input service distributor
- Casual Taxable Person
- Person deducting TDS under section 51
- Person collecting TCS under section 52
- UIN holder
- 7. Is a taxpayer required to login to the GST portal to download form GSTR-4 (Annual Return) offline utility?
-
No, it can be downloaded from the downloads section of the portal without logging into the portal.
- 8. Is a taxpayer required to login to GST portal to download the generated JSON file using Form GSTR-4 (annual return) offline utility?
-
Yes, one must log in to download the generated JSON file using the form GSTR-4 offline utility.
- 9. Does the offline utility validate all the errors in the excel utility?
-
The offline tool validates only limited errors as it does not have a connection with the GST portal. For example, GSTIN structure, computation of tax and duplicate entries.
- 10. Can a taxpayer enter negative/decimal values in the offline utility?
-
Yes, a taxpayer can enter negative or decimal values wherever required.
- 11. Will the downloaded JSON error file contain all entries updated at the time of upload on the GST portal?
-
Only erroneous entries are reflected here. Entries with no errors can be viewed on the GST portal.
- 12. What is GST ITC-01?
-
A registered taxpayer who is entitled to claim ITC under section 18(1) of the CGST Act, can claim ITC by filing Form GST ITC-01. The credit can be taken on inputs, inputs held in semi-finished/finished goods as below:
- A day immediately preceding the date on which his registration was granted for claim under clause (a) or clause (b) of sub-section (1) of section 18; once in the lifetime of a taxpayer.
- One day immediately preceding the date from which the person becomes liable to pay tax under section 9 for claim under clause (c) of sub-section (1) of section 18; once in a financial year.
- One day immediately preceding the date from which the supplies made by the registered taxpayer becomes taxable for claim under clause (d) of sub-section (1) of section 18, once in a month.
- 13. What are the features of Form GST ITC-01?
-
The key features are:
- It can be prepared offline.
- Most of the data entry and business validations are built-in, which minimizes the chances of errors on upload to GST portal.
- 14. What is the precondition to filing form GST ITC-01?
-
- In case of new registration:
(i). The applicant has filed for registration within 30 days of becoming liable to pay GST and has been granted registration.
(ii). The applicant has details of ITC on purchases on or after the appointed day but before registration and stock as on the day immediately preceding the day from which he becomes liable to pay GST. - In case of opting out from composition scheme and where the exempt supply of goods/services or both becomes taxable:
A registered person has the details of ITC on inputs/capital goods as on the day immediately preceding the day in which he opts out from composition scheme. - In case of voluntary registration:
A registered person has the details of ITC on inputs/capital goods as on the day before the date of grant of registration.
- In case of new registration:
- 15. Is the offline tool of GST ITC-01 mobile compatible?
-
No. Currently, the GST ITC-01 offline tool is only available for use on desktops and laptops.
- 16. When should GSTR-11 be filed?
-
Form GSTR-11 is a prerequisite for claiming a refund. A UIN holder can request a refund of taxes paid on inward supplies by applying Form GST RFD-10 once in each quarter.
- 17. What are the features of the Form GSTR-11 offline utility?
-
The key features of GSTR-11 offline tool are:
- It can be prepared offline.
- The data entry and business validations are built-in, thereby reducing the chances of errors on upload to the GST portal.
- 18. What are the details required to be filed in GSTR-11?
-
The invoice details of the inward supply of goods or services or both are required to be filed in GSTR-11.
- 19. Is the offline tool of GSTR-11 mobile compatible?
-
No. Currently, the GSTR-11 offline tool is only available for use on desktops and laptops.
- 20. My GST registration got cancelled in the financial year. Should I still file GSTR-4 (Annual return)?
-
Yes, it is compulsory to file GSTR-4 (Annual) if:
- You were a composition taxpayer anytime during a part of the financial year, or
- Your GST registration got cancelled anytime during the financial year, or
- You voluntarily opted out of the composition scheme during that financial year.
- 21. What is a Nil GSTR-4 (Annual return)?
-
A Nil GSTR-4 (Annual Return) can be filed for a financial year if the following conditions are met:
- No record of outward supply.
- The taxpayer did not receive any goods or services.
- 22. Will tax fields be auto-populated based on the values entered in taxable value?
-
Yes, however, cess must be manually fed.
- 23. What to do if I get a warning message that record are under processing or processed with errors while filing GSTR-4 (Annual return)?
-
In case you receive such a warning message, kindly wait for the processing to complete at the back end. In case of errors, return to the Form GSTR-4 (Annual Return) dashboard and take action on the relevant records.
- 24. What are the recommended system configurations to use the offline tool for Form GSTR-3B?
-
The required system configuration is Windows 7 or above Operating System with Internet Explorer 10+ and MS Excel 2007 onwards.
- 25. Is it possible to sign and file returns using the offline tool for Form GSTR-3B?
-
No, the offline tool is only for entering data into the Form GSTR-3B. The form will ultimately have to be signed and filed on the GST common portal itself.
- 26. Can the offline utility of GSTR-3B run on mobile?
-
No. At present, the offline utility is not compatible with mobile devices.
- 27. Is the TRAN-2 offline tool mobile compatible?
-
Currently, the TRAN-1 offline tool is not available for mobile phones and can be only used on desktops.
- 28. Can stocks, which are not supported by evidence of duty and taxes paid, be declared while filing the July month TRAN-2, if the same has not been reported in TRAN-1?
-
No, you will not be able to claim credit in TRAN-2 if you have not declared that stock in TRAN 1.
- 29. From where can a taxpayer download GSTR-8 offline utility without login to the portal?
-
A taxpayer can download the offline utility by clicking on this linkhttps://www.gst.gov.in/download/gstr8.
- 30. How many rows for TCS details can be added in the offline utility?
-
A maximum of 15,000 rows can be added in the utility.
- 31. If one of the suppliers of an e-commerce operator has made supplies to four different customers then is the e-commerce operator required to report all the four cases separately in the offline utility?
-
No, rows with duplicate GSTINs are not allowed in the utility. An ecommerce operator can add up all the supplies made through that particular supplier and enter one single consolidated amount in the “gross value of supplies made” column.
- 32. If the net amount liable for TCS gets negative, will it be accepted on the portal?
-
Yes, if the value of goods returned is more than the current month’s supply, then the utility will auto-calculate the net amount liable for TCS as negative. The IGST, CGST and SGST amounts for these columns will automatically become zero.
- 33. If a taxpayer has by mistake entered rows with the same GSTIN, can he use the delete option from the action column to delete such rows?
-
Add or delete option in the action column can be used to add/delete data on the GST portal. The incorrect data in a particular row can be deleted by using the delete button on the keyboard.
- 34. Can GSTR-7 be filed offline?
-
No, filing of return can be done only online through GST portal. Only the details in table 3 and table 4 can be updated using the offline tool. Payment and filing functionalities are available only on the GST portal.
- 35. Can the offline utility populate the name of the taxpayer based on GSTIN?
-
No, the offline utility cannot populate the name of the taxpayer on the basis of GSTIN as the database is not available to get the details.
- 36. How many rows can be added under the TDS details of the suppliers in the offline utility?
-
Maximum 10,000 rows can be added under the TDS details section.
- 37. If a taxpayer has made payment for 2 different products to the supplier then is he required to show the payments in two different rows?
-
No, the whole amount paid to the supplier should be reported in a single row. Rows with duplicate GSTINs are not allowed.
- 38. What should a taxpayer do if he has entered the same GSTINs in multiple rows?
-
One can delete the incorrect data by using the delete button on the keyboard.
- 39. Does the downloaded JSON error file contain all entries updated at the time of upload on the GST portal?
-
No, it only contains the erroneous entries.
- 40. Can the offline utility validate all the errors in the excel utility?
-
No, only limited validations are available on the excel utility as it does not have a connection with the GST portal. It can validate errors such as GSTIN structure, computation of tax and duplicate entries.
- 41. What are the basic system requirements to use the offline utility for GSTR-10?
-
The offline utility for GSTR-10 will need Windows 7 or above and MS Excel 2007 or above.
- 42. Can the offline utility be used on mobile for GSTR-10?
-
The offline utility for GSTR-No, at present there is no way to use the offline utility on the mobile. GSTR-10 will need Windows 7 or above and MS Excel 2007 or above.
- 43. Will the name be auto-populated once GSTIN is entered for GSTR-10?
-
The offline utility for GSTR-10 will No, since this is an offline utility, there is no access to the GSTIN database to extract such information. Windows 7 or above and MS Excel 2007 or above.
- 44. I have entered incorrect details in the rows. Should I use the ‘Delete’ option under the drop-down list provided in the ‘Action’ column?
-
The ‘Add’ or ‘Delete’ option provided in the drop-down list under the ‘Action’ column is to be used for deleting data in the GST portal. For mistakes made while inputting data into the rows of the utility, simply press the ‘Delete’ button on your keyboard to clear the cell.
- 45. After clicking on the ‘Validate Sheet’ button, the utility only highlights the cells in red and the ‘Sheet validation’ column only shows ‘Error in row’. How do I know what exactly is the problem in my data?
-
To get a description of the error, either move your cursor over the redhighlighted cells or go to the ‘Review’ ribbon and select ‘Show All Comments’.
- 46. I am re-uploading the GSTR-10 JSON file after making the requisite corrections. What will happen to the data that I have previously uploaded?
-
The previous data will be updated with the new details and if there are any new entries, the same will be added.
- 47. Can a taxpayer file Form GSTR-9C if he has not filed his annual return?
-
No, the form GSTR-9C can be filed only after filing GSTR-9.
- 48. Is login to the GST portal required for downloading GSTR-9C offline utility?
-
No, it can be downloaded from the link below, without logging in to the GST portal. https://www.gst.gov.in/download/gstr9c
- 49. Which fields will be pre-filled in Form GSTR-9C tables derived from Form GSTR-9?
-
The following tables in Form GSTR-9C will be pre-filled:
- Turnover as declared in GSTR-9
- Taxable turnover as declared in GSTR-9
- Total amount of tax paid as per GSTR-9
- ITC claimed in GSTR-9
- 50. Can a taxpayer send the system generated filed Form GSTR9 and Form GSTR-9C tables derived from GSTR-9 to the auditor from the GST portal?
-
No, the PDFs cannot be sent through the portal. However, the same can be sent offline (via USB/hard copy) or via email.
- 51. Is login to the GST portal required for uploading the generated JSON file using GSTR-9C offline utility?
-
Yes, log in to the GST portal is required for upload of generated JSON.
- 52. Can a taxpayer file complete Form GSTR-6 using offline utility?
-
No, filing can be done only online through the GST portal. Using offline utility a taxpayer can only prepare tables such as: Table 3.ITC Received 5, 8 Distribution of ITC 6B CDN, 6A ITC received (B2BA) 6C CDNA and 9 Amendment of distribution of ITC Filing will have to be done on the GST portal.
- 53. Is login to the portal essential for download of GSTR-6 offline utility?
-
No, it can be downloaded from the downloads section of the GST portal without logging in. However, to upload the JSON file generated using GSTR-6 offline utility, you will need to login to the portal.
- 54. Does the offline utility auto-populate the name of the taxpayer based on GSTIN?
-
No, the offline utility cannot auto-populate the name of the taxpayer on the basis of GSTIN details entered in the home tab. But, it can validate the structure of GSTIN entered.
- 55. Can negative or decimal values be updated in offline utility?
-
Negative values cannot be entered. However, one can enter decimal values in the offline utility.
- 56. Can a taxpayer generate JSON files without entering any details in the offline utility for GSTR-6?
-
No, a NIL JSON file cannot be generated.
- 57. What are the features of GSTR-9A offline utility?
-
GSTR-9A has the following features:
- A taxpayer can update the details of Table 6 to Table 16 offline.
- Validation check option is available in the offline utility, thus reducing the chances of errors on upload to the GST portal.
- No, a taxpayer needs to login to the GST portal to file GSTR-9A.
- 58. Is the GSTR-9A offline utility mobile compatible?
-
No, it can be used only on desktops/laptops.
- 59. What things need to be kept in mind while making entries in utility?
-
- Enter a valid GSTIN. Verify the same by going home>search>taxpayer>search GSTIN/UIN to make sure that the registration is active.
- A taxpayer can use copy/paste functionalities but cannot use cut/paste functionalities for entering data in the utility.
- A taxpayer can change the file name and location of the generated JSON file, but should not change the extension of the generated JSON file.
- 60. Is it possible to file the annual return (Form GSTR-9) using the Offline Utility?
-
No, it is not possible to file the annual return using the offline utility. The purpose of the offline utility is only to generate the JSON file for uploading online. The filing process will happen on the GST portal itself.
- 61. Is it compulsory to use the offline utility in GSTR-9?
-
No, you can alternatively enter data on the GST portal itself. However, where more than 500 records are to be entered in Table 17 and Table 18, the offline utility must be used.
- 62. What data can be entered in the offline utility in GSTR-9?
-
Data in Table 4 to Table 18 of Form GSTR-9 can be entered using the offline utility.
- 63. Is it compulsory to download the JSON file from the portal and import the same on to the offline utility in GSTR-9?
-
Yes, it is compulsory to do so since doing so would update specific fields in the utility that were extracted from previously filed Form GSTR-1 and Form GSTR-3B of the same financial year.
- 64. Does the ‘Validate Sheet’ button to ensure that there are no errors in the data entered?
-
No, the offline utility can only detect errors to a limited extent; for example, the utility can only check if the GSTIN entered is in the correct format. Whether the GSTIN exists and belongs to the taxpayer or not can only be verified after processing done by the GST portal.
- 65. Can negative values or decimal amounts be entered in the offline utility in GSTR-9?
-
Yes, negative and decimal values can be entered in the offline utility.
- 66. Can 2-digit HSN codes be entered in the offline utility?
-
The 2-digit HSN codes can be entered in the offline utility. For HSN codes starting with 99, a Unique Quantity Code (UQC) and quantity details are not required.
- 67. What are the system prerequisites for filing GSTR-9C?
-
Below are the system prerequisites for filing Form GSTR-9C: -Windows Operating System should be of version 7 and above -Microsoft Excel should be of 2007 version and above -Internet Explorer to be 10+ -Java should be 1.6 or above -Use the latest offline utility of the Form.
- 68. What is the time limit to file GSTR-9C and should Form GSTR-9 and Form GSTR-9C be filed separately?
-
As per Section 44(2), GSTR-9C should be filed along with the Annual Return GSTR-9. Also, as per Section 44(1), the due date to file Annual Return is on or before 31st December following the end of the financial year for which the return is prepared. Thus, it can be inferred that the due date of filing GSTR-9C is on or before 31st December following the end of the financial year for which the return is prepared.
- 69. What are the documents to be enclosed with Form GSTR9C?
-
The following documents are required to be enclosed along with Form GSTR-9C:
- A copy of the audited financial statements as per Section 35(5)
- A copy of the audit report where the audit of the entity is carried out by another person under a statute other than the GST Act.
- 70. What are the steps for creating a JSON file of Form GSTR9C?
-
Here is a detailed guide to preparing Form GSTR-9C and generating the JSON file using the offline tool.
- 71. Can GSTR-9C be revised?
-
Currently, there is no provision to revise Form GSTR-9C. Hence, taxpayers are requested to take the utmost care when reporting details in Form GSTR-9C and filing the same.
- 72. Can an internal auditor of an entity certify Form GSTR-9C?
-
No, as per instructions issued by the ICAI, an internal auditor cannot certify Form GSTR-9C.
- 73. Should Form GSTR-9C be filed for state-wise for every registration under the same PAN?
-
Yes, Form GSTR-9C should be filed for every registration in each state. Once the PAN-based aggregate turnover exceeds 2 crore, every registered GSTIN having the same PAN is required to get its accounts audited and file Form GSTR-9C.
- 74. Should a CA be registered as a GST practitioner for certifying Form GSTR-9C?
-
The GST Act does not vest a GST practitioner with the power to audit under section 35(5). It is granted only to a Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant. Thus, to certify Form GSTR-9C, a CA need not be registered as a GST Practitioner.
- 75. How should an auditor provide his Membership Number?
-
Auditors prefixing ‘0’ in their membership number should refrain from doing so. If the membership number is ‘020’, then an auditor should enter ‘20’ on the aforesaid part in the membership number field & not ‘020’.
- 76. Can GSTR-9C be filed without filing Annual GST Return (GSTR-9)?
-
No, GSTR-9C can be filed only after filing GSTR-9.
- 77. Which fields are auto-populated from GSTR-9 in Form GSTR9C?
-
Below are the fields which will be auto-populated:
- The turnover details as per GSTR-9
- Liability as per GSTR-9
- Total tax paid as mentioned GSTR-9
- Input Tax Credit availed in GSTR-9
- 79. Does aggregate turnover include stock transfers/cross charges between branches located in the same state to determine the threshold limits?
-
Branches having the same GSTIN: If both the branches have the same GSTIN, then such stock transfers will not be included in aggregate turnover for determining the threshold limit.
Branches having different GSTIN: If both the branches have different GSTIN’s, then such stock transfers will be included in aggregate turnover for determining the threshold limit. - 80. Is the supply of alcohol for human consumption included in determining the threshold limit of ₹ 2 crores by a registered person?
-
The term aggregate turnover includes exempt turnover. As per CGST Act, exempt turnover means supply of any goods or services or both which attracts nil rate of tax or which may be wholly exempt from tax under section 11, or under section 6 of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act and includes non-taxable supply.
Non-taxable supply is a supply of goods or services which is not chargeable to tax under either the CGST Act or the IGST Act. Section 9(1) of CGST/ SGST Act and Section 7(1) and 5(1) of UTGST and IGST Act specifically excludes alcoholic liquor for human consumption from the levy/charge of GST. Thus, on a combined reading of all the sections it can be inferred that alcoholic liquor for human consumption falls under exempt turnover and as exempt turnover is part of the aggregate turnover, the same should be included in computing the threshold limit of 2 crores.
- 81. Does a registered person exclusively deal in exempted supplies exceeding ₹ 2 crores, required to file GSTR-9C?
-
Yes, because the definition of aggregate turnover includes exempted supplies.
- 82. What are the late fees for failure in submitting Annual Return and not getting the accounts audited?
-
If a taxpayer fails to file both Annual Return and Form GSTR-9C, then he is liable to a fee of 200/- per day during which the default continues ( 100 under CGST law + 100/- under State / Union Territory GST law) *Capped to a maximum amount of 0.50% (0.25% under the CGST Law + 0.25% under the SGST / UTGST Law) of turnover in the State/UT. These provisions apply to the filing of GSTR9; however, no specific provisions apply to GSTR-9C, and hence the filing of GSTR-9 and non-filing of GSTR-9C could be subject to a general penalty of 25,000.
- 83. Can the late fee be waived off in genuine cases?
-
The Government may do so by way of issue of notification specifying the circumstances but, no such notification has been issued yet.
- 84. Which details are to be provided in table 5B of Form GSTR9C?
-
Table 5B requires reporting of addition to unbilled revenue at the beginning of the Financial Year. Thus, in simple words, this clause requires reporting of any unbilled revenue, which was recorded in the books of the previous financial year, but the invoice was issued in the current year under the GST law.
- 85. Should a taxable person disclose details of notice pay recovery from employees in GSTR-9C? If yes, where should it be reported?
-
If the notice pay recovered from employees is considered a taxable supply, but the same is not disclosed as an income in the Profit and Loss account, then it should be reported under Sl.No.5O of GSTR-9C.
- 86. Where should the ineligible ITC identified by an auditor which are claimed as eligible by the dealer in GSTR 3B and in Form GSTR 9 be reported in Form GSTR 9C?
-
Total ITC availed by the dealer- This is reported in column 3 Part IV of Sl.14 of Form GSTR 9C. Eligible ITC as determined by the auditor- This is reported in column 4 Part IV of Sl.14 of Form GSTR 9C. Thus, the difference between the two is ineligible ITC. The auditor should disclose such ineligible ITC in the Certificate issued by him.
- 87. Does the submission of the Form GSTR 9C lead to the understanding that the Commissioner or any officer authorized by him will not undertake an audit under Section 65 of the CGST Act?
-
No, there are two separate provisions for Departmental Audit and the one done by CA. Section 65 deals with departmental audit, whereas section 35(5) is for Audit to be performed by CA. Audit under section 35(5) is required when aggregate turnover is greater than 2 crores; on the other hand, there is no such condition for audit under section 65.Thus, submission of Form GSTR 9C does not restrict the right of the department to conduct an audit.
- 88. Are all the OIDAR service providers required to file GSTR 5A?
-
No, only the OIDAR service providers who are non-resident and are providing services to unregistered persons or government are required to file GSTR 5A.
- 89. Is registration necessary for these non-resident OIDAR service providers?
-
Yes, as without the registration, they will not have a GSTIN and without a GSTIN, the filing of GSTR 5A is not possible.
- 90. Can Input tax credit be availed in Form GSTR 5A?
-
No, there is no provision to avail the input tax credit in GSTR 5A. As it is also evident from the format above where there is no field or table to enter the details of ITC available.
- 91. How can the service providers make use of Authorized representatives in India to file returns?
-
The authorized representatives of the non- resident OIDAR service providers can act as their agent and file GSTR 5A on their behalf. They can also assist in making the payment of the taxes due.
- 92. Should I file GSTR-1 even if there are no sales in a month?
-
Yes, filing GSTR 1 is mandatory. If your total sales for a year is less than 5 crore you have the option to file the return on a quarterly basis. With this, there is also an Invoice furnishing facility available to upload sales invoices on a monthly basis (for the first two months of the
- 93. Can I upload an invoice only while filing the return?
-
You can upload invoices anytime. It is highly advised that you upload invoices at regular intervals during the month to avoid bulk upload at the time of filing return. This is because bulk upload takes a lot of time.
- 94. Can I change a bill uploaded on the GST Network?
-
After uploading bills you can make changes multiple times. There is no restriction on changing invoices after uploading them. But you can change an invoice only before submitting a return. Once submitted, the numbers are frozen.
- 95. Can I file GSTR-1 even after filing GSTR-3B?
-
GSTR-3B is a simple summarized return to be filed by taxpayers on a monthly basis (or quarterly basis if QRMP scheme is chosen). With effect from 1st January 2021, GSTR-1 has to be filed before filing the GSTR-3B return. Prior to this date, a quarterly GSTR-1 filer would have filed his quarterly GSTR-1 end of the month succeeding the quarter, which would have been after filing GSTR-3B.
- 96. I have opted for the composition scheme. Should I file GSTR-1?
-
GSTR-1 should not be filed by you. Form CMP-08 must be used to make tax payments on a quarterly basis by such taxpayers opting for the composition scheme.
- 97. Should I make a GST payment after filing GSTR-1?
-
GSTR-1 is a return where details of sales are filed with the government. No tax has to be paid after filing this return. The tax has to be paid at the time of filing GSTR-3B.
- 98. I have been filing GSTR-1 on a quarterly basis so far. My annual sales are below ₹1.5 lakh. What happens if I choose the QRMP scheme now in December 2020?
-
You need to continue filing GSTR-1 on a quarterly basis and the GSTR3B will also need to be filed on a quarterly basis with monthly tax payments. For more information about the QRMP scheme, read our article on “All about the QRMP scheme.”
- 99. Can amendments be made to details already filed in GSTR1? If yes, then what will be the filing period to make amendments?
-
Yes, you can make amendments to an already filed GSTR-1 of a particular tax period by declaring the amended details in the return For example, Mr. X of Kerala has sold goods to Mr. Y of Karnataka for 1,00,000 on 30th August 2020 and declared in the GSTR-1 of August 2020. Now he realized that he made a mistake in the date of the invoice, so he can make an amended invoice with the correct invoice date i.e., 16th August 2020. This amended invoice can be shown in the GSTR-1 of September 2020.
- 100. What should the ‘Revised date’ be in the amended invoice?
-
The ‘Revised date’ to be mentioned in an amended invoice must be not later than the last date of the original invoice tax period. For example, if an original invoice dated 12th July 2020 is being amended in August then the revised invoice date cannot be later than 31st July 2020.
- 101. What are the amendments not admissible or not allowed?
-
The following details cannot be amended at Invoice level:
- The Customer GSTIN
- Changing a tax invoice to a bill of supply
- The following with respect to Export Invoices cannot be amended:
(a). Shipping Bill Date/Bill of Export Date
(b). Type of Export- With/Without payment
- The following with respect to Credit Debit Notes cannot be amended:
(i). Receiver/Customer GSTIN. However you may amend & link any other invoice for the same GSTIN.
(ii). Place of Supply
(iii). Reverse charge applicable Reason: Since the above details are based on the original Invoice which it Is linked to, Hence these details must match with the details of the linked Invoice.
If the receiver of goods has taken action on the invoices i.e. accepted or modified and the supplier accepts such modifications in GSTR-1A, he will not be allowed to amend those invoices. The reason is that those invoices will automatically get reflected in the GSTR-1 of the supplier in the month of such acceptance under the relevant amendments table. The following details cannot be amended at a summary level
- Nil Rated
- HSN summary of Outward supplies
- Cannot add a new place of supply
Note: However, you can replace the existing place of supply with another place of supply with some limitations.
- 102. What are the amendments allowable with respect to the Place of supply?
-
With respect to Place of Supply, note the following:
- You can amend the original place of supply for a transaction.
- You cannot add any new place of supply to a transaction.
Let us understand the above with the following scenarios:
Nature Place of supply Rate of Tax Taxable Value Amendment Original Kerala 18% 10000 Allowed Amended To Karnataka 18% 10000 Original Kerala 28% 50000 Allowed Amended To Karnataka 18% 50000 Original Karnataka 5% 10000 Allowed 12% 20000 Amended To Karnataka 18% 30000 Original Kerala 18% 60000 Allowed Amended To Karnataka 28% 20000 Karnataka 12% 40000 Original Kerala 18% 60000 Not Allowed 12% 40000 Amended To Karnataka 28% 50000 Kerala 28% 50000 We can see that in all those cases where the original place of supply was amended from Kerala to Karnataka (whether or not there was a change in tax rates or invoicing), the amendment is allowed.
But in the last case where in addition to Kerala, Karnataka is also added as a place of supply (irrespective of change in tax rates or invoicing) amendment does not hold good.
- 103. Where to show the amended invoices in GSTR-1?
-
Declare the amended invoices or details in the tax period in which the amendment takes place as follows:
Sl.no. Type of Amendment Explanation 1. B2B Amendments (9A) Amendments made in the invoices already issued earlier must be reported here. These are the invoices for taxable supplies made to registered taxpayers including supplies made to SEZ/ SEZ Developers with or without payment of taxes and deemed exports. 2. B2C Large Amendments (9A) Amendments in the original invoices already issued must be mentioned here These reflect original invoices issued for taxable outward supplies made to unregistered taxpayers where 1. Supply is made interstate and 2. Total invoice value is more than Rs 2,50,000/- 3. Credit/Debit Notes (Registered) Amendments(9C) Credit or debit note amended against already issued Credit or debit note reported under B2B (i.e. where supply is made to registered taxpayer), will be reported here. 4. Credit Debit Note (Unregistered) Amendments(9C) Amended Credit or debit note issued against original Credit or debit note reported under B2C Large and Export Invoices section, will be reported here. 5. Export Invoices Amendments(9A) Amended invoices issued against already issued original invoices must be reported here. Export invoices includes - Export under bond/LUT-If you are exporting under bond or letter of undertaking and not paying IGST.
- 2. Export with IGST-If you are exporting without furnishing bond/letter of supply and paying IGST on such supply (It excludes deemed exports & supply to SEZ)
6. B2C Others Amendments (10) Amendments made in the invoices already issued earlier must be reported here. These are all those invoices not covered under 1. B2B 2. B2C Large 3. Exports 7. Advances Received (Tax Liability) Amendments (11(2)) Any amendments made to the advances received in previous tax periods has to be declared here. 8. Adjustment of Advances Amendments (11(2)) Any amendments made to the advances adjusted in previous tax periods have to be declared here. - 104. For taxpayers who files returns on a quarterly basis, what are the types of regular returns that should be used?
-
For taxpayers who have an aggregate turnover of up to crore in the previous year, the regular returns that are to be used are either -Sugam, Sahaj, or normal (quarterly) returns.
- 105. For what reasons can we file Form RET-1 through the SMS mode?
-
Form RET-1 can be filed through SMS in the case of Nil returns, where supplies have not been made or received.
- 106. If documents are left pending by recipients, can amendments be made in the documents by the supplier?
-
Suppliers can only make amendments in the documents if the document has been rejected by the recipient, and not if they have been left pending.
- 107. Can the period of filing of returns be changed by the taxpayer?
-
Yes, the period of filing can be changed by the taxpayer once. This can only be done at the time that the first return of the financial year is filed.
- 108. In form ANX-1, if the document details are entered into the wrong table, can it be corrected?
-
The facility to shift such documents to the correct table is available but is provided only once the documents are rejected by the recipient.
- 109. How to file GST Returns Online?
-
All taxpayers have to file their tax returns with the GST department every year. Fortunately, the new GST regime has automated the complete process. The taxes can now be filed online through the app and software provided by the Goods and Service Tax Network (GSTN). Below we have explained the steps on how to file your GST returns online:
- Visit the GST portal, i.e., www.gst.gov.in.
- Based on your state code and PAN number, 15-digit GST identification will be issued on the portal.
- You must then upload all your invoices on the GST portal or the software. The system will generate an invoice reference number for each invoice.
- Once you upload the invoices, outward return, inward return, you must file the cumulative monthly return online. In case you make any errors, you can correct them by refilling the returns.
- You should file the outward supply returns in GSTR-1 form through the information section located on the GST Common Portal (GSTN). This filing must be completed on or before the 10th of the following month.
- The recipient can access the details on outward supplies furnished by the supplier through the GSTR-2A.
- The details on outward supply have to be verified, validated, and modified by the recipient. Also, details on credit and debit notes should be duly filled in.
- The GSTR-2 form must also carry details on the inward supplies of taxable goods and services.
- The modifications on the details of inward supply made in the GSTR - 1A may either be accepted or rejected.
- 110. How to Download GST Returns?
-
The GST returns can be easily downloaded through the official GST portal using the following steps:
- Log in to the GST portal, i.e., www.gst.gov.in.
- Click on the ‘Services’ tab that is located on the top menu.
- Next, click on the ‘Returns Dashboard’ that is located under the ‘Returns’ option.
- Select the financial year and the return filing period from the respective drop-down boxes on the next page.
- Click on the ‘Search’ tab before selecting the GTR that you wish to download.
- Click on the ‘Prepare Offline’ button under the selected GSTR.
- Next, click on the ‘Generate File’ option under ‘Download’.
- In general, the request for the generation of the file takes around 20 minutes.
- A download link will be generated once your file is prepared. Click on the ‘Click Here’ option and download the ZIP file to view your GST Returns.
- 111. How to File GST Returns with GSTN?
-
The Goods and Service Tax Network (GSTN) stores information about all GST registered sellers and buyers to ensure a streamlined and simple process. The data is then combined and maintained for future reference. Business entities can simply download the excel workbook that is available on the common GST portal free of charge. The template can be used to collate all the necessary information offline smoothly. Once done, the file must be uploaded to the GST portal.
- 112. Who is liable for GST in India?
-
The supplier of the goods or services is liable to pay the GST. This is, however, charged to the end consumer but is paid over to the government by the supplier. However, there are cases where the tax is to be paid by the recipient under the reverse charge mechanism.
- 113. Which taxes have been subsumed into GST?
-
Excise duty, service tax, countervailing duty, special additional duty of customs, luxury tax, octroi tax, entry and entertainment tax, VAT, tax on lottery, betting and gambling at the state and central level have been combined into GST.
- 114. What is the minimum amount for GST?
-
The minimum amount for a business to file for GST since April 2019 is 40 lakhs. Any company that has an annual turnover of this amount needs to file for GST. They can do so online using the GST portal.
- 115. Can I do business without GST?
-
No, you can't do business without following the GST guideline. You need to get your business registered under the guidelines, and failure to do so can result in the payment of penalties.
- 116. Does GSTR-1 need to be filed even if there is no business activity in the period?
-
Yes, a GSTR-1 needs to be filed even if there has been no business activity in the period. So it needs to be mentioned that there were no returns in the GST returns.
- 117. Who is not required to file the GSTR-1?
-
The following persons are not required to file a GSTR-1. These are:
- taxpayers under a composition scheme,
- non-resident foreign taxpayers,
- Input Service Distributors, and
- e-commerce operators deducting TCS.
- 118. What can a taxpayer do to auto-populate information in GSTR-2?
-
GSTR-2 is an auto-populated form from the invoices that are uploaded. Hence a taxpayer can accept, reject or modify any of this information provided by a supplier if it is incorrect, or he can keep the transactions pending if the goods or services have not been received.
- 119. Who all can utilize the GST calculator?
-
A GST calculator can be used by every individual involved in the payment or collection of GST, including buyers, wholesalers, and manufacturers.
- 120. What is the process for a buyer to use a GST calculator?
-
To utilize this tool, a buyer must first enter the net cost of a product before GST is added. Next, enter the GST rate. The calculator will automatically compute the total taxes, CGST, and SGST, along with the cost of production.
- 121. How likely are errors when computing taxes in a GST calculator?
-
Due to the integrated algorithm, these online tools do not make mistakes, provided you enter the parameters and details correctly. Thus, unlike in manual calculations, a GST calculator ensures minimal errors.
- 122. Is it mandatory to register under GST?
-
If your business turnover exceeds the threshold value as mentioned, you must register under GST for additional tax benefits.
- 123. Can I apply for multiple GST registrations within the state?
-
Yes, you can apply for multiple registrations if you own the same businesses within a state. Different business verticals need not apply for registration.
- 124. Can I get a GSTIN without registering?
-
No, you need to register under GST, submit the forms, and obtain a GSTIN.
- 125. What are the specifications for the issuer’s signature in the case of e-invoicing?
-
When issuing a GST invoice online, a supplier must upload the invoice’s JSON on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). Now, the Invoice Registration Number is generated by IRP, and it will digitally sign the JSON using its private key. Once signed, it will become a valid e-invoice, and the IRP will send this document to the e-way bill system and GSTIN.
- 126. Can I issue a GST invoice bill before the date of providing services?
-
Yes, you can issue a tax invoice before the services are rendered. The only mandate is that the date of issue must not cross the deadline succeeding the date of service supply.
- 127. Which sectors are considered special cases when it comes to GST invoicing?
-
Banking, goods, transport agencies, and passenger transport are three of the sectors where the government allows certain relaxations when it comes to GST invoicing. Relaxations differ in each of these sectors
- 128. Under which conditions is a supplementary invoice issued?
-
A supplementary invoice needs to be issued when:
- There is a change in taxable amounts or tax rates.
- The buyer returns the products due to low quality.
- The buyer claims a refund for the returned items.
- 129. How does the invoice date differ from the due date?
-
While invoice date is the date on which this document is created, the due date refers to the deadline within which the amount on this invoice must be paid.
- 130. Will an individual dealing with tax-exempt supplies need to register under GST if his annual turnover exceeds ₹20 lakhs?
-
No, dealing with any tax-exempt supplies will not attract a GST. It is considered non-taxable.
- 131. Is it mandatory to issue a tax invoice if I sell exempt goods to a single person?
-
No, it is not necessary to issue a tax invoice. However, you have to issue a bill of supply for your supplies.
- 132. What is the treatment of ITC in the case of exempt supply?
-
The amount of credit applicable to exempt supplies will be reversed.
- 133. Who are the taxable persons under GST?
-
Persons with GST-registered businesses at any location in India are liable to incur taxes under this regime, whether it’s under the forward charge or reverse charge mechanism. It includes e-commerce operators as well.
- 134. What is the use of a GST calculator?
-
GST calculators are used in calculating the costs of GST applicable on a certain product. These are available on various third-party websites.
- 135. What is a GSTIN?
-
Every business is appointed with a unique GST Identification Number known as GSTIN. It is a 15-digit number signifying the state, PAN, and the number of registered enterprises within the state.