Key Relaxation to Small Companies- Introduction
Small Company – Meaning and Explanation under Companies Act, 2013
The Finance Minister proposed a revised definition of a small company while presenting the Union Budget 2021. The purpose behind the revised definition was to provide ease of doing business and reduce the compliance burden for many companies.
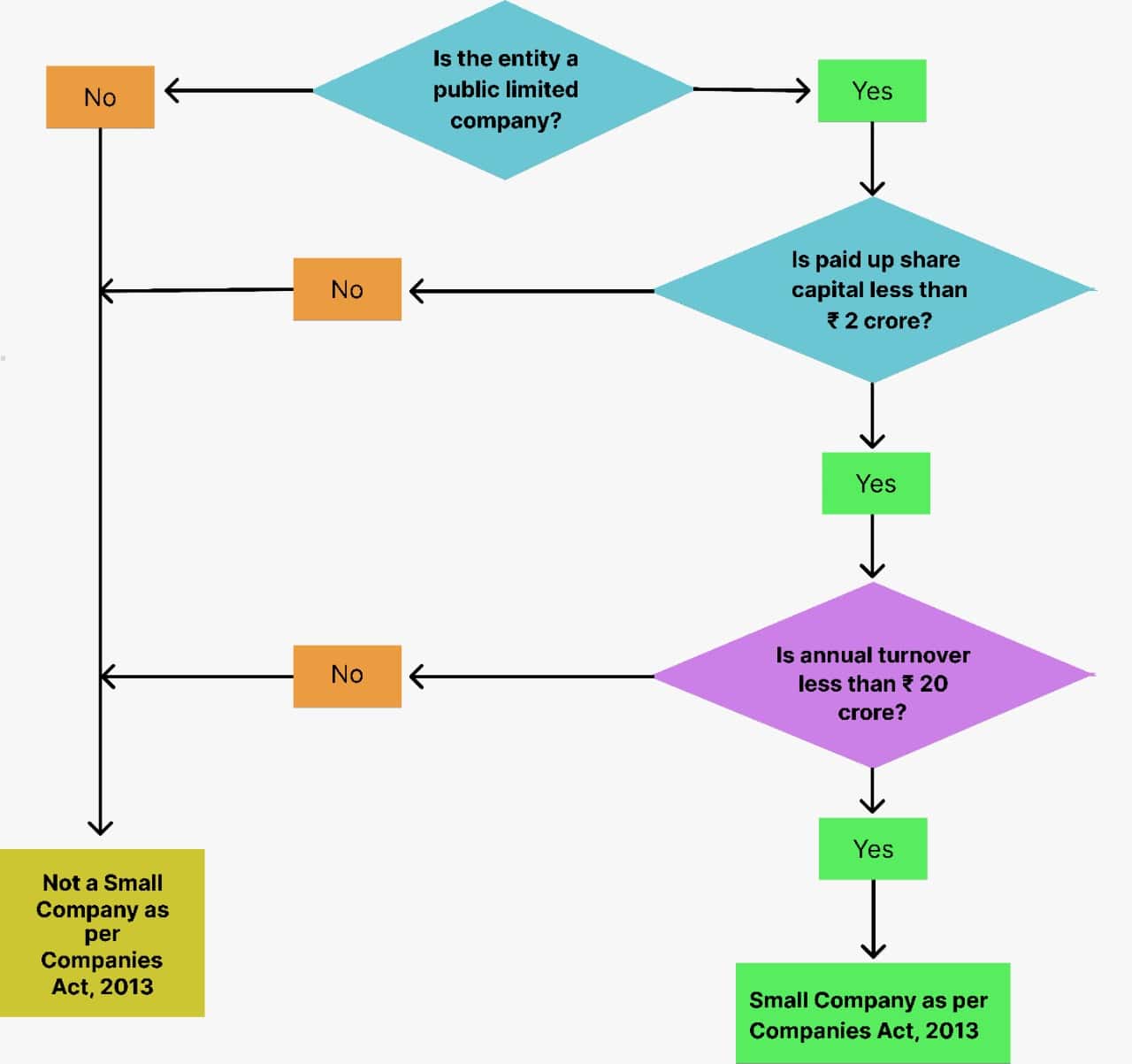
Accordingly, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) notified the Companies (Specification of Definitions Details) Amendment Rules, 2021, to amend the old definition of a small company. The new definition proposed in the Budget 2021 is effective from 1 April 2021.The new amended definition of a small company is provided under Section 2(85) of the Companies Act, 2013. The Act defines a small company as a company that is not a public company and has:
- A paid-up share capital equal to or below 2 crore or such a higher amount specified not exceeding more than 10 crores.
- A turnover equal to or below 20 crore or such a higher amount specified not exceeding more than 100 crore.
However, the concept of small companies does not apply to the following companies:
- A holding or a subsidiary company.
- A company registered under section 8.
- A body corporate or company governed by any special act.
Most startups in India are classified as small companies as they will not have a paid-up capital of more than 10 crores and an annual sales turnover of more than 20 crores.The Companies Act, 2013 (‘Act’) introduced the concept of small companies to provide advantages for small businesses operating as private limited companies. Small companies have less annual revenue compared to regular-sized companies. In a developing country like India, small companies play a significant role in generating profits and boosting employment. Thus, they are the backbone of the economy.
Small companies do not have any separate procedure to obtain registration under the Act. It is registered as a private limited company. But the Act differentiates a private company as a small company based on its fewer amounts of investment and turnover.
However, the status of a small company can change every year depending upon its paid-up capital and turnover limits. When a company crosses the thresholds provided in the new definition either for paid-up capital or turnover, the benefits available during a financial year will be removed in the following year. The small company will lose its status as a small company and be treated as a private limited company not classified as a small company.
Most Startups will be Small Company. Since most of the startups will have a paid-up capital of fewer than 50 lakhs and also an annual sales turnover of less than 200 lakhs, they will be classified as a small company.
A small company is not registered specifically or recognized. A small company is formed due to the status it has obtained and based on the turnover and paid-up capital. A private limited company may be called a small company also, immediately after its incorporation subject to conditions provided above. The promoters and directors are mostly unaware of this special status and the benefits. Hence, it is necessary for them to be aware of such provisions to claim such beneficial position.
Small company is a special status given to companies registered under Indian Companies Act, 2013 due to its scope of business, measured in terms of capital and turnover. The companies enjoying the status of small company enjoy certain benefits in form of exemption from applicability of provisions. To claim the status of the small company, it does not need to register a company in India; rather a company already registered and fulfilling provided conditions is known as a small company.
Section 2(85) – Small Company under Companies Act, 2013
The Companies Act, 2013 introduced a new concept of ‘small company’. The concept of a small company was introduced in Companies Act 2013 to provide certain advantages for small businesses operating as a private limited company. Small businesses are the backbone of any economy and it the procedure for starting and managing a small business must be made simple to boost employment and the economy. Therefore, the classification of “small company” in the Companies Act, 2013 goes a long way in promoting the small business in India.
It is simply a Private Company but with less capital and turnover size. Only a Private Company can be classified as a Small As per the new definition and threshold limits, companies with a paid-up capital of 2 crore or less, and turnover of 20 crore or less come are defined as small companies. The Companies Act, 2013 provides for certain exemptions and grants certain privileges to a Small Company.
Small Companies are basically the companies with limited amount of investment and having the privilege of special status under the Companies Act, 2013.
The concept of “small company” has been introduced for the first time by the Companies Act, 2013. The Act identifies some companies as small companies based on their capital and turnover for the purpose of providing certain relief and / or exemptions to these companies. Most of the exemptions provided to a small company are same as that provided to a One Person Company (OPC).
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has notified an amendment in the Companies (Specification of Definitions Details) Rules, 2014 that came into force on 1st April 2021. The MCA (Ministry of Corporate Affairs) has effected this amendment in accordance with the proposal of the Honorable Finance Minister to revise the definition of Small companies in India by increasing the paid-up capital limit from 50 Lacs to 2 Crores in the Union Budget 2021 while the turnover threshold by enhancing from 2 crores to 20 crores.
Currently, almost 13.2 lacs of companies are active, out of which more than 12 lacs companies are classified as small companies as per the official statement. Recently in Budget 2021, there has been a development that helped more companies as the definition has been changed with the purpose of giving the benefit of the liberalized regime. Before the said change was introduced nearly 8 lacs companies fell under the purview of small companies. But after the change in the norms of the paid-up share capital and turnover threshold have helped an additional 2 lakhs companies avail themselves the relief.
A small company is a private limited company that satisfies both the following conditions:
- Paid-up share capital does not exceed 2 crores or such higher prescribed amount which shall not be more than 10 crores, and
- Turnover of the preceding financial year does not exceed 20 crores or such higher prescribed amount which shall not be more than 100 crores.
Note-
There is no need to file any form or company any process to convert small company into non small Company. Once a company fall in limits given under definition of small Company it shall be consider as Small Company, if company cross the limits given in definition shall be consider as non-small company itself.
The status of a company as “Small Company” may change from year to year. Thus the benefits which are available during a particular year may stand withdrawn in the next year and become available again in the subsequent year.
Know whether your company falls into Small Companies
Comparison of Small Company New Definition with Old Definition
The amendment proposed in the Budget 2021 to the definition of a small company increased the maximum limit of paid-up capital and turnover. The limits were increased so that more companies could be covered within the ambit of a small company, making them eligible to get the benefits of a small company provided under the Companies Act 2013.
The comparison of the old and new definitions of a small company is provided below:
| Particulars | Old Definition Criteria | New Definition Criteria |
| Paid-up share capital | Maximum paid-up share capital of 50 lakh | Maximum paid-up share capital of 2 crore |
| Turnover | Maximum turnover of 2 crore | Maximum turnover of 20 crore |
| Should not exceed | Share capital- 5 crore Turnover - 20 crore | Share capital- 10 crore Turnover- 100 crore |
Thus, both the criteria specified in the definition must be fulfilled for a company to fall into the category of small company. However, these limits may be raised but not exceeding rupees ten crores in case of paid up capital and rupees one hundred crore in case of turnover.
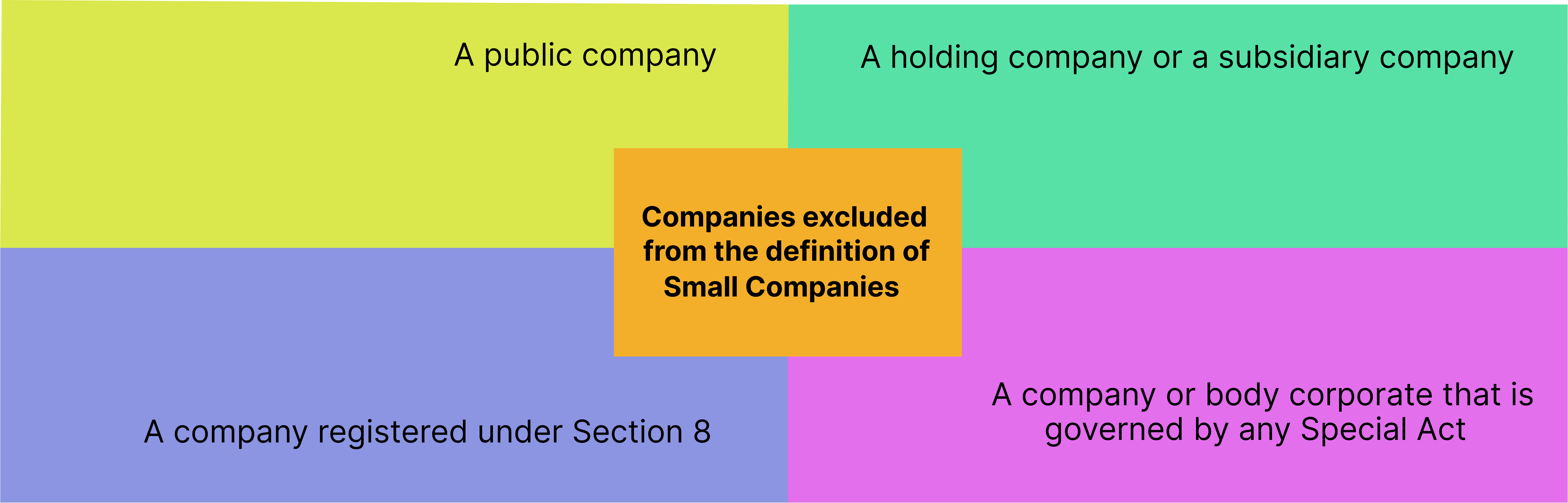
Further, the following companies do not fall under the purview of small company and the exemptions or reliefs to small companies are not available to them:
Exceptions:
The above definition of a small company is not applicable to the following (i.e., a small company cannot be the below ones):
- A public company
- A holding company or a subsidiary company
- A company registered under Section 8
- A company or body corporate that is governed by any Special Act like Banking Companies, Electricity Companies, Insurance companies, NBFC etc. will not be 'small company'.
Thus, even though the above-mentioned companies satisfy the capital and turnover requirements, they would nevertheless fall beyond the purview of ‘small company’ and, consequently, the advantages applicable to a small company cannot be extended to them.
The Issues regarding Small Company
Issue 1: Both limits to cross
The first issue is whether for being a small company, the company should be below threshold limit in both sub-clauses i.e. share-capital and turnover or it will be non-small company till it does not cross both the limits. This question is being raised because of use of word 'or' between sub-clause (i) and (ii) which makes one to interpret that it will be small company till both the limits are not crossed.
If one read the provisions carefully, one would reach to the conclusion that it will be small company only if the company does not cross the limits given in both the sub-clauses. Both sub-clauses are in negative, and therefore, 'or' becomes 'and'.
Secondly, if we do purposive construction, we will find that it provides for two criteria one based on paid up capital and other based on turnover. So, if a company exceeds the limit for paid-up capital, though it may not have any turnover during the year, it will not be a small company. Similarly, a company may have small capital but may be having turnover exceeding the limit given; it will also not be a small company. A support may be taken from Companies (Accounting Standard) Rules which defines Small and Medium Sized Company. There also 5 conditions have been given and they all are mutually exclusive and have to be independently tested.
The courts have also held that 'the word 'or' is normally disjunctive and 'and' is normally conjunctive but at times they are read as vice versa to give effect to the manifest intention of the Legislature as disclosed from the context.It has now been made clear that in order to claim a private company as a small company both the criteria of paid-up share capital and turnover needs to be fulfilled in order to enjoy relaxation for small company.
Issue 2: Specific Exclusion from definition
A question arises whether a private limited company which is a holding company of another private limited company and its capital and turnover are within the prescribed limit, will it be a 'small company'?
The answer is in negative. A company will be out of definition of 'small company' if it is either a holding company or a subsidiary of another company, even if such other company is not a public company.
In accounting standard rules, only those holding and subsidiary companies are excluded which are holding or subsidiaries of non small and medium sized company. However, in the Companies Act, 2013, proviso excludes all holding and subsidiary companies from the definition of 'small company'. If a company becomes either holding company or subsidiary company, it cannot claim to be 'small company'.
Issue 3: Date for determination
Next question which arises is as to the date on which the status of company is to be determined.
Turnover criterion is to be tested based on last profit and loss account. The next question is which is 'last'. Whether it is of last year or any other profit and loss account prepared for any purpose. It may be concluded that it will be of last previous year because it is the profit and loss account which has got legal sanctity under the law. Hence, even if the turnover exceeds the limit, it will continue to be 'small' during the year but will cease to be so in the next year. Since now, annual return is to be as on the last day of the financial year, in my view, the turnover will be required to be seen of the immediately previous year.
The second criterion of paid-up capital is to be seen on each occasion when the exemption or privilege of being small is claimed. In case of increase in share capital, it will cease to be small, as soon as the shares are allotted. In case of buy-back or reduction of share capital, it will be entitled to claim the status of 'small' as soon as the process of buy-back is complete.
The reason behind its introduction
The concept of small companies in India is relatively new. It was introduced by the Companies Act 2013 to support better facilitation of small businesses. A small company is nothing but a new form of a private company registered under the Companies Act 2013. A private company is classified into a small company based on its size, i.e., paid-up share capital and turnover. In other words, such companies may be called small-sized private companies.
The intent of distinguishing small companies from the rest is to give them a special status and to grant them certain benefits under the law.
Upon the recommendations received from an expert committee of Dr. JJ Irani, a renowned Indian industrialist, the concept of small companies was incepted in the Companies Act, 2013.
It was felt that a simplified framework should be applied to small companies through the aid of giving exemptions under company law. There is no reason why small businesses should suffer the repercussions of legislation designed to ensure that big, widely owned corporations balance the interests of their stakeholders. By relieving such companies from selected statutory internal/administrative procedures, company law should allow streamlined decision-making procedures.
The need was felt for such businesses to be subject to reduced financial reporting and audit standards and to streamlined capital maintenance schemes. In essence, small companies should have a regime that enables them to achieve transparency at a low cost.
Need for this amendment
- The limits were not amended from many years and considering the overall growth in the economy it was imperative that the limits need to be increased. The benefit of this amendment would be available to a large number of companies.
- The number of accounting standards and disclosure requirements has increased over the years. These standards are being continuously revised to align with the international requirements. The implementation of these changes requires additional taskforce of accountants who understand the requirements.
- The time for preparation of the financial statements have increased substantially considering the various disclosure requirements. This has increased the compliance burden on the SMC companies also.
- As stated above, the definition for small and medium companies was amended in MSME Act. This change also helps in alignment of the definitions under both Acts to certain extent.
There are many benefits granted to small companies but there are three major intents behind classifying them separately.
- Firstly, considering the size in which they operate, small companies get to function under lighter regulatory oversight.
- Secondly, they could be offered lesser and cost-effective compliances when comparing with larger companies.
- Thirdly, small companies should not be caught in the stringent regulations for the maintenance of stakeholders interests meant for the wider ranging companies.
Special legal provisions
Small companies are also provided with a small set-up between two small companies that can function without the interference of a tribunal but rather with just the approval of Central Government (Regional Director) as mentioned in the Companies Act, 2013.
Features of a small company as per Companies Act 2013
A small company can only be a private company
It has limited Area of operation.
It has a fewer number of employees.
Companies Act 2013 provides certain benefits to Small Company.
It holds a limited amount of Investment.
It has Separate legal entity from its owners.
The status of a Small Company may change from year to year as capital and turnover changes every year.
It cannot be a public company, holding company, subsidiary company, a charitable company registered under Section 8, or a company governed by any Special Act.
Small companies are subject to lesser penalties for non-compliance with any of the provisions of the Companies Act
It is worth noting that the status of a small company may change from year to year depending upon the range of paid-up share capital and turnover. This means that if a company crosses any of the thresholds provided (either for paid-up capital or turnover), the benefits that are available during a given year may be removed in the following year and may be made available again in the subsequent year (or years).
Characteristics of a Small Company
Following are the characteristics of a small company:
Low Profitability and Revenue
A small company has less revenue compared to medium and large companies. The revenue depends on the type of business and the capability to generate revenue. However, lower revenue cannot be considered as lower profitability of the company.
Fewer Employees
Since small companies have less paid-up capital and turnover, they onboard a small team of employees than large companies. Sometimes, small companies may even be handled by a single person or one team. Close labor-owner relations;
Smaller Market Area
Small companies serve the smaller sections of the community or society, like convenience shops in a rural township. Thus, they have a small market area for operating business activities.
Fewer locations
Generally, small companies have a limited area instead of several branches. They are usually not established in other countries and several states. The sales of small companies are confined to a single area
Rapid decision-making;
Quick gestation period;
Mostly owner financed;
Little emphasis on long-term planning;
Low capital and limited investment;
Lack of modern technology;
Less legal formalities;
Easy control.
With gradual growth of business, if a company cross any of the thresholds provided, either for paid-up capital or turnover, the company must give up the status of the small company and the benefits granted for such companies.
Benefits of a small company as per Companies Act 2013
Some privileges and exemptions are offered by law to companies holding the status of a ‘small company’. They enjoy various relaxations or advantages over other companies, some of which are as follows:
| Section | Nature of privilege granted |
| Proviso to Section 2(40) | Cash flow statement: The financial statements of a small company need not include a cash flow statement. |
| Section 67(2) | Financial assistance for buy-back: Financial assistance (by way of loan, guarantee, etc.) can be given for the purchase of own shares in the company or in its holding company. |
| Section 92(1) | The signing of annual return: The annual return of a small company needs to be signed by the company secretary, or where there is no company secretary, by the company’s director. However, it need not be signed by a company secretary in practice. The annual return filing of a small company can be signed by either a Company Secretary (CS) or a company director. The annual return filing of a private limited company other than a small company must be signed by both a director and a CS. |
| Section 121(1) | Report on AGM: A small company is not required to prepare a report on Annual General Meeting. |
| Section 134(3)(p) | Statement showing performance of BOD: A small company is not needed to prepare a statement showing the manner in which formal annual evaluation of the performance of the Board, its Committees, and individual directors has been made. |
| Section 149(1) | The number of directors: A small company need not have more than 2 directors on its Board. |
| Section 149(4) | Independent directors: A small company is not required to appoint independent directors on its Board. |
| Section 152(6) | Rotation of directors: Unlike a public company, a specified proportion of directors are not needed to retire every year in a small company. |
| Section 164(3) | Disqualification of director: A small company, may by its Articles, provide for any additional grounds for disqualification for appointment as a director of the company. |
| Section 165(1) | The number of directorships: The restrictive provisions concerning the total number of directorships that an individual can hold in a public company (maximum 10) do not include directorships held in small companies that are neither a holding company nor a subsidiary company of a public company. |
| Section 167(4) | Vacation of office of director: A small company, may by its Articles, provide for any additional grounds for vacation of the office of a director of the company. |
| Section 173(5) | The number of board meetings: Unlike other companies that need to hold four Board Meetings in a calendar year, a small company is needed to hold at least one meeting of the Board of Directors in each half of a calendar year and the gap between the two Board meetings must not be less than ninety days. Small companies must have a maximum of two meetings in a financial year. Whereas a private limited company that is not considered a small company must conduct four board meetings in a financial year. |
| Section | Nature of privilege granted |
| Section 190(4) | Contract of employment: The provisions relating to the contract of employment with managing directors or whole-time directors are not applicable to a Small Company. |
| Section 197(1) | Managerial remuneration: Unlike a public company, the total managerial remuneration payable by a small company, to its directors, including managing director and whole-time director, and its manager in respect of any particular financial year may exceed eleven percent of the net profits. Also, where other companies require providing details of remuneration to directors and key managerial personnel, small companies are required to provide details of the only aggregate amount of remuneration drawn by directors in their Annual Return. |
| CARO, 2020 | CARO: The reporting requirements laid down under the Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order, 2020 for matters to be included in an auditor’s report do not apply to a small company. |
| Rule 8A of Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014 | Matters in Board’s report: For the purpose of compliance with Section 134(3), the Board’s report of a small company shall be prepared in an abridged form as prescribed by the Central Government. Small companies are exempted from the matters to be included in the Board’s report as per Rule 8 of Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014. MCA has introduced the abridged format of the Directors’ Report for a Small Company. Abridge report means, director report of Small Company shall required to give less disclosures then a non-small Company. Small companies must file their annual returns in Form MGT-7A. Form MGT-7A is the abridged version of Form MGT-7, which is filed by medium and large companies. |
| Section 143(3) | Auditor’s report: The auditor’s report in the case of a small company is not required to indicate whether there are adequate internal financial controls in place (with reference to financial statements) and the operating effectiveness of such controls. |
| Section 139(2) | Rotation of auditors: Every company needs to mandatorily change its auditor by rotation in pursuance of Section 139(2) of the Companies Act 2013. However, a small company need not comply with this section and hence is exempt from meeting the requirements of this section. Small company it is not required to mandatory change the auditor by rotation. An auditor firm or individual auditor can get appointment as auditor in small Company ever after 10 year or 5 years of appointment also. |
| Section 446B | Lesser penalties: If a penalty is payable by a small company for non-compliance with any of the provisions of the Companies Act, then such company and its officer in default shall be liable to a penalty not more than one-half of the penalty specified in such provisions. But this is subject to a maximum of 2 lakh in the case of a company and 1 lakh in the case of an officer who is in default. |
| Section 233 | Amalgamation: Special provisions has been made in the Act for merger of two or more small companies or between a holding company and its wholly owned subsidiary company or such other class or classes of companies as may be prescribed. This provides for liberal methodology for amalgamation without going to the Tribunal, if the Registrar and the Official Liquidator has no objection or suggestions to the scheme. In such a case, the Central Government shall register the scheme and issue a confirmation thereof. |
Other notable conditions
- Audit exemption takes effect from the beginning of the next financial year after the establishment of the company.
- A company that has corporate stakeholders but also fulfills the eligibility criteria to become a small company can be entitled to small company audit exemption.
- Foreign companies are mostly not entitled to the audit exemption except for Singapore-based companies.
- Even though a company qualifies as a small company but the group to which it belongs doesn’t satisfy the conditions, the company cannot be entitled to avail small company audit exemption.
- Fees for Small Companies-There are substantial rebate in fees for registration of small companies. It is also provided that such fees will be applicable only if it remains small for a minimum period of one year from the date of its incorporation.
Annual Corporate Compliances / Annual Compliance for Small Company
Below given are some of certain annual compliances which are required to be followed by companies which fall under the definition of small company.
Director’s Interest
- Every director shall at the first meeting of the Board in which he participates as a director and thereafter at the first meeting in every financial year or whenever there is any change in the disclosures already made, then at the first Board meeting held after such change, disclose his concern or interest in other entities and in the company which shall include the shareholding.
- The changes in the director’s interest, if any, shall be given in forms MBP-1 in the next board meeting.
Appointment of Directors
- At least one director must be ‘Resident in India’.
- A person who stays more than 180 days in a calendar year India is regarded as a ‘Resident’.
Appointment of Auditors
- Appointment of an auditor should be made in the BOD meeting within 30 days of Incorporation.
- Auditor shall be appointed in 1st Annual General Meeting (AGM) i.e. the ‘Shareholders Meeting’ for 5 years.
- The company shall inform the auditor concerned of his or its appointment, and also file a notice of such appointment with the Registrar by filing mandatory form ADT-1 within 15 days of the meeting in which the auditor is appointed.
Annual General Meeting
- The small Company should hold a general meeting (meeting of Shareholders) at the Registered Office each year as AGM.
- Notice of Annual General Meeting shall be sent to all the Directors, Members, Auditors, legal representative of any deceased member and the assignee of an insolvent member.
- Notice shall be sent by hand or by ordinary post or by speed post or by registered post or by courier or by facsimile or by email or by any other electronic means.
Board meetings
- The Board shall hold its first Meeting within 30 days of the date of incorporation of the company.
- Every Small Company shall hold at least two meetings of Board of Directors (BOD) in a financial year (April-March). That is to say 1 meeting of BOD in each half of calendar and the gap between two meetings shall not be less than 90 days.
- Directors can participate in BOD in person or through video conferencing or other audio visual mode which can be recorded.
Audit of Accounts
- The Company shall Coordinate with their auditors to prepare and file the Tax Audit Report on the prescribed due dates.
- It is a special & separate report required by Income Tax Act in case the Annual Turnover exceeds 1crore.
Filing of Financial Statements
- It would be mandatory to file the audited financial statements with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) together with Form AOC-4 and the consolidated financial statements, if any, with Form AOC-4 CFS.
- More over the Company shall send to all the members of the Company, all trustees for the debenture holders and to all persons being the persons so entitled, copy of the (approved) Financial Statements (including consolidated Financial Statements, if any, auditor’s report and every other document required by law to be annexed/ attached to the financial statements) at least 21 clear days before the Annual General Meeting. Except in case where AGM is called on shorter notice pursuant to section 101(1)
Annual Return
- Every Company shall file Its Annual Return within 60 days of holding of AGM or where no AGM is held in any year within 60 days from the date on which the AGM should have been held together with the statement specifying the reasons for not holding the AGM.
- With a view to facilitate ease of doing business and for reducing the burden of Small Company, the Central Government has prescribed abridged form of Annual Return to be annually filed by Small Companies.
- The Annual Return of every Small Company shall be signed by the company secretary or where there is no company secretary by the director of the company.
Apart from the above mentioned compliance the company shall also maintain some register which are mandatory namely register of members, register of debenture holders, register of any other security holders etc.
However, as you strive to grow your Small Company, there is one thing to keep in mind, and i.e. ensuring its compliance. If you fail to do so, you can you can lose your protections and accrue fees and penalties.
Summary of Annual Compliance Calendar for a Small Company
| S. No. | Month | Compliance |
| 1. | April |
|
| 2. | May |
|
| 3. | June |
|
| 4. | July | Filing of FLA with RBI, if having foreign liability or assets |
| 5. | August |
|
| 6. | September |
|
| 6. | September |
|
| 7. | October |
|
| 8. | November |
|
| 9. | December |
|
| 10. | January | |
| 11. | February | |
| 12. | March |
|
Note:
* Small companies must have a maximum of two meetings in a financial year- at least one meeting of the Board of Directors in each half of a calendar year and the gap between the two Board meetings must not be less than ninety days.
Conclusion
A small company is not specifically registered with a different name and is merely a private company having less turnover and investment. But owing to the entitlement of special status under the Companies Act 2013, small companies are given some benefits and exemptions considering their small size. This is done as a measure to relieve small companies from the compliance burden and stringent regulations of the larger ones.
Therefore, a private limited company may be called a small company immediately after its incorporation, subject to conditions provided above. The promoters and directors are generally unaware of the eligibility status of Small Company and the benefits being given to them. Hence, it is necessary for them to be aware of such provisions to claim the beneficial position.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is a small company?
-
The concept of small companies was introduced by the companies act, 2013 for the first time. According to the Act some companies are termed as small companies based on their capital and turnover for the purpose of providing certain relief/exemptions to these companies.
A small company is a private limited company that satisfies both the following conditions:- Paid-up share capital does not exceed 2 crores or such higher prescribed amount which shall not be more than 10 crores, and
- Turnover of the preceding financial year does not exceed 20 crores or such higher prescribed amount which shall not be more than 100 crores.
The above definition of a small company is not applicable to the following (i.e., a small company cannot be the below ones):
- A public company
- A holding company or a subsidiary company
- A company registered under Section 8
- A company or body corporate that is governed by any Special Act like Banking Companies, Electricity Companies, Insurance companies, NBFC etc. will not be 'small company'.
- 2. What companies can claim to be the Small Company?
-
According to the definition given above, the companies which fulfill the following provisions can be featured as the small company:
- Company should be Private Limited
- Paid Up capital should not be more than 2 crore
- Turnovers should not exceed more than 20 crore
- 3. What is the difference between a small company and private company?
-
A small company is a private company whose capital does not exceed 2 crores or such higher amount as prescribed which shall not be more than 10 crores and turnover does not exceed 20 crores or such higher amount as may be prescribed which shall not be more than 100 crores while a Private company includes a Small Company.
- 4. What will be the consequence if my threshold limit for capital and turnover exceeds the limit prescribed for Small Company under the Companies Act 2013?
-
If the capital of a Small Company or turnover exceeds the threshold limit, it is no more considered as a Small Company and it can no more enjoy the privileges granted to a Small Company under the Act.
- 5. When should I file the Annual returns of my small company?
-
Companies are required to file their Annual Accounts and Returns disclosing details of its shareholders, directors, etc to the Registrar of Companies. Such compliances are required to be made once a year.As a part of the Annual Filing, the following forms are to be filed with the ROC
- Form MGT-7A (Annual Return): Every Small Company is required to file its Annual Return within 60 days of holding of Annual General Meeting. Annual Return will be for the period 1st April to 31st March.
- Form AOC-4 (Financial Statements): Every Small Company is required to file its Balance Sheet along with a statement of Profit and Loss Account and Director Report in this form within 30 days of holding of Annual General Meeting.
The Annual Return of every Small Company shall be signed by the company secretary or where there is no company secretary by the director of the company.
- 6. How can I close my small company?
-
There are different kinds of methods that can be opted for closing down the Small Company. Here are some of the ways by which you can close down your Small Company legally.
- Selling the Company- This is the common method wherein the owner of the company can sell all the shares of the company to any third person. With this, all of the rights and responsibilities of the company are transferred to the other person.
- Strike off the Company- Any defunct company who desires to get its name struck off from the registers of ministry can apply to the registrar in the form Fast Track Exit form. Also, the registrar can itself strike off the name of the defunct company if has reasonable reasons to believe that it is required. In the second situation, the opportunity of being heard must be provided to the company.
- Voluntary Winding Up - Voluntary winding occurs when the members of the company of the creditors decide among themselves to close down the company. Under this closing down the court, supervision is not there. But after the completion of winding up the relevant documents must be submitted with the court for obtaining the order of dissolution.
- 7. What are the minimum requirements to register small company?
-
To register a small company following are the minimum requirements which are same as Private Limited Company:
- There need to be minimum 2 members to act as shareholders
- It needs to have a minimum of 2 directors
- It requires no minimum share capital to register a small company but paid up capital should not be more than 2 crore
- From the above 2 directors at least one should be an Indian Resident.
- The person should mandatory hold a PAN card
- The person should carry a valid Id and Address proof in his own name.
- He should have a registered office space in India.
- 8. Is registration necessary for small Companies in India?
-
Yes, Registration for a small Company is necessary as, without registration, there can be no existence of a company and no privileges and exemptions are offered by law to companies holding the status of a ‘small company’ can be availed.
- 9. What is the ROC compliance for a small Company?
-
Here is mandatory ROC compliance for a small Company:
- Form ADT 1: First Auditor of the company shall be appointed by the BOD within 30 days of Incorporation who shall hold the office till the conclusion of 1st AGM.
- Form MGT 7A: Form MGT-7 must be filed by all companies registered in India every year. It is an electronic form provided by the Ministry of Affairs to all the corporations in order to fill in their annual return details. The due date for filing MGT-7 is within 60 days from the date of the Annual General Meeting.
- Form AOC 4: Every Private Limited Company is required to file its Balance Sheet along with a statement of Profit and Loss Account and Director Report in this form within 30 days of holding of Annual General Meeting.
The above forms need to be certified by CA/CS/CWA. The annual return filing of a small company can be signed by either a Company Secretary (CS) or a company director. The annual return filing of a private limited company other than a small company must be signed by both a director and a CS.
- 10. Do small Companies have to release annual reports?
-
It is mandatory for all the companies which are registered under MCA to file their annual reports with the concerned ROC every year. However, for Private Limited Companies (including small Companies) , it is not mandatory to publish or release their annual report for Public access.
- 11. Are annual filings required for fast track exit closure of a Small Company, which failed to commence business?
-
No, Annual filings are not required for the Fast Track Exit (FTE) closure of a small Company which failed to commence business.
There are only two criteria which are as follows:
- The company applying under FTE should not have any assets and liability.
- The company should not have commenced any business activity or operation since incorporation or at least one year must have been passed since the last business activity or operation.
The Company desirous to get its name struck off from the Register shall file an application in the prescribed Form STK-2 online with the Registrar. The form shall be accompanied by an affidavit, an indemnity bond, a statement of account duly certified by a Chartered Accountant in practice or auditor of the company, and a copy of board resolution showing authorization for filing the form.
- 12. As per Indian law, how many maximum directors can a Small Company have?
-
As per Indian law, The Indian companies Act, 2013 states that a small Company in India can have a minimum of 2 directors and a maximum of 15 directors.
However, The Company may appoint more than 15 directors, only after passing a special resolution.
- 13. A Small company failed to hold AGM within the due date due to a natural disaster, what do I do?
-
If you have failed to hold an AGM (Annual General Meeting) within the due date due to a natural disaster, You may seek the remedy from the Registrar of Companies, as ROC may extend the timeline for holding of AGM for a maximum of three months if there is a genuine and special reason for not holding the AGM within the specified time.
As in your case you have a genuine reason for not holding AGM due to natural disaster, the ROC may extend the timeline.
For this, you need to file e-form: GNL-1 with concerned ROC with a certified true copy of board resolution citing reason & period of extension required along with prescribed fees.
- 14. What are the documents required to add a director in a Small company?
-
To add a director to a Small company, all you need is three things:
- A valid Digital Signature Certificate(DSC)
- Director Identification Number
- A Consent letter from the proposed director.
- 15. Is an audit mandatory for a startup Private Limited Company or a Small company?
-
Be it a Startup or an established Private Limited company or a Small company, It is mandatory compliance to have the company’s account audited.
Even the appointment of an auditor within 30 days of the incorporation is mandatory compliance for a Private limited company.
- 16. What are the minimum requirements to register a Small company?
-
To register a Small Company, the following are the minimum requirements:
- 2 Directors, one of which has to be an Indian resident and an Indian Citizen.
- 2 shareholders who can be a natural person or a legal entity.
- There is no requirement of minimum share capital to start a company. A company can be registered even with 10,000/- but paid up capital should not be more than 2 crore to be called a small company where the turnover should not exceed 20 crores.
- 17. Is it possible for a small firm to register as a private limited company?
-
Yes, a small firm can register with the Indian government as a private limited company. It gives them credibility and a positive image of their company in the eyes of suppliers, future customers, and financial institutions. It assists the organization in obtaining loans with minimal compliance from banks or potential clients when going into contracts.