Non-Banking Financial Company Registration in India
NBFC stands for Non-Banking Financial Company and is registered under the Companies Act, 2013 and managed by RBI with activities very similar to the bank except for some major differences. NBFC is known to provide financial support and services to businesses and individuals. One of the principal objectives of a Non-Banking Financial Company is to provide loans, personal loans, working capital loans, shared investments, other stocks and debenture issued by the Government or the other local authorities, leasing, chit business, hire purchase, insurance business as well as offers Market Place Lending Platform (P2P) for businesses.

The NBFC Registration comes under the Companies Act 2013 and the RBI Act 1934. In India, The Reserve Bank of India is the supreme regulator of the NBFC. An NBFC is different from the Traditional Banks in the following ways:
- A Bank is registered under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, whereas an NBFC is registered under the Companies Act 2013 or 1956 and RBI Act, 1934.
- NBFC Provides Banking services to People without holding a Bank license
- Unlike Banks, NBFCs cannot accept and lend deposits.An NBFC cannot accept Demand Deposits i.e. NBFCs are not allowed to accept deposits, which have to be refund on demand. The RBI gives no guarantee of the repayment of deposits by the NBFCs.
- Deposit insurance facility of the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation is not available for NBFC depositors, unlike banks.
- The RBI gives no guarantee of the repayment of deposits by the NBFCs. The deposits are not secured.
- An NBFC cannot indulge Primarily in Agricultural, Industrial Activity, Sale-Purchase, Construction of Immovable Property
- Foreign Investment in Banks is limited up to a specific fixed limit, whereas foreign investment in NBFC is allowed 100%.
- Banks can issue a self-demand draft on itself, whereas NBFCs are not allowed to issue a self-demand draft as they are not the part of the settlement system or the part of the payment system. NBFC can accept only term Deposits.
- Bank provides a variety of transaction services, whereas NBFCs do not facilitate transaction services.
- An NBFC does not guarantee insurance or the credit facility.An NBFC is not required to maintain Reserve Ratios (CRR, SLR etc.)
- All NBFCs are allowed to take the public deposits for the minimum period of 12 months which goes up to maximum period of 60 months.
- The NBFCs must have minimum investment-grade credit rating.
- companies cannot offer the interest rate higher than the ceiling rate fixed by RBI on time to time
- The companies are not allowed to offer any gifts, incentives, or any other benefit to the depositors
Some of the things that are not included under the ambit of NBFC are as under:
An NBFC does not necessarily include an institution with the following principal business. Such as:
- Agriculture Activity
- Industrial Activity
- Sales or Purchase of any goods excluding securities
- Providing services such as purchase/construction/sales of an immovable property.
NBFC are meant to meet the financial needs of the majority of the underserved section of the business which is not accepted by the Traditional Banks of India. Also, the entire process of loaning money from the Traditional Bank is much slower in comparison to the NBFC and involves a lot of paper work which is not a case in NBFC. Credit Decision in NBFC takes lesser time which is a pro when it comes to loaning money from the banks.
Classification of Non-Banking Financial Company according to the nature of business
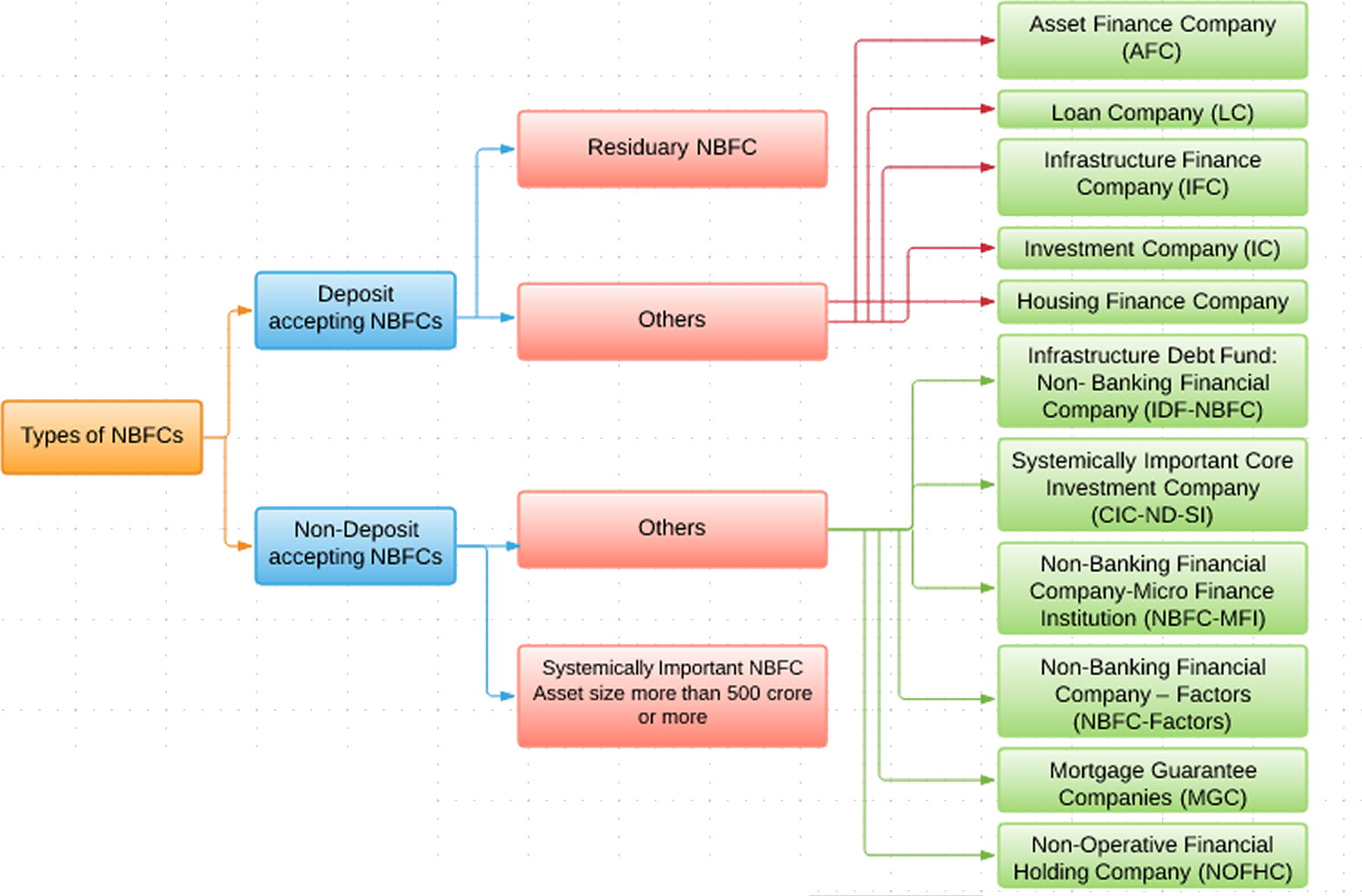
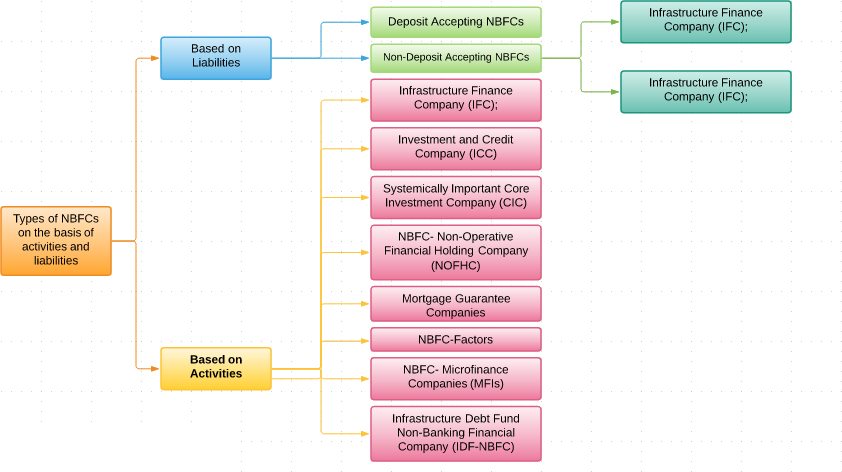
NBFC Registered with RBI
| S. No. | Types of NBFC | Principal Business Activities | Minimum Criteria to be Recognized |
| 1 | Assets Finance Company |
Financing Real and physical Assets supporting economic activity. An AFC is a company which is a financial institution carrying on as its principal business the financing of physical assets supporting productive/economic activity, such as automobiles, tractors, lathe machines, generator sets, earth moving and material handling equipments, moving on own power and general purpose industrial machines. Principal business for this purpose is defined as aggregate of financing real/physical assets supporting economic activity and income arising therefrom is not less than 60% of its total assets and total income respectively. |
|
| 2 | Investment Company | financial institution carrying on as its principal business as Acquisition of Shares and securities of other company | |
| 3 | Loan Company | Financial institution carrying on as its principal business to make Loan and advances for working capital of the Business (Not for Physical or real assets) | |
| 4 | Infrastructure Finance Company | To make available infrastructure loans |
|
| 5 | Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC)NBFC-CIC-ND | Investment in Shares, securities or Loans in a Group Companies. |
|
| 6 | Infrastructure Debt Finance Company(IDF) NBFC-ND | To Facilitate the flow of Long Terms Debt in Infrastructure Projects | To be Sponsored only by Infrastructure Finance Company NBFC raise resources through issue of Rupee or Dollar denominated bonds of minimum 5 year maturity. |
| 7 | Micro Finance Institutions NBFC-MFI-ND | To make finance in the form of Loan and advances to lower Income group people |
|
| 8 | Factor- NBFC-ND | Principal Business of Factoring-acquisition of Receivables by way of assignment of such receivables or financing |
|
| 9 | Mortgage Guarantee Company | Business of Mortgage Guarantee |
|
| 10 | Non- Operative Financial Holding Company | Financial Holding Company through which the promoters hold the NBFC and other finance company. |
Regulations of Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFC)
Depending on the type of NBFC’s registered under the Companies Act 2013, following regulators are followed, they are as under:
- National Housing Bank – Housing Finance Institutions
- NBFC registered with RBI where supervision, regulation, surveillance and enforcement are carried out under the Reserve Bank of India.
- Non- Financial and Non-Banking Companies with the supervision, regulation and surveillance under the Companies Act of 2013.
Registration and regulations of NBFC’s are done by the Reserve Bank of India. All Activities and transactions of NBFC’s are supervised and controlled by the Reserve Bank of India through its Acts, regulations, prudential norms and guidelines.
However certain categories of NBFC’s are exempted from Registration with RBI avoid implications of dual regulations :
| S. No. | Types of NBFC’s Exempted from Registration with RBI | Regulators of Those Companies |
| 1. | Merchant Banking Company/ Venture Capital Fund Companies/Stock Broking Companies | Securities and Exchange Board of India |
| 2. | Insurance Companies | Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India. |
| 3. | Housing Finance Companies | National Housing Bank |
| 4. | Mutual Benefit Companies and Nidhi Companies | Ministry of Corporate Affairs |
| 5. | Chit Fund Companies | State Governments |
Financial Companies which are not regulated by the Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India supervises and regulates the companies that are engaged in the financial activities as their principal business. Any Company with the financial asset of more than 50% of its total asset is termed as an NBFC and is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. Also, the income from financial assets must constitute 50% of the total income.
It is governed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs as well as the Reserve Bank of India. The License for operation is obtained from the RBI and it is incorporated as a company under applicable laws of the land.
The following NBFCs are not required to obtain any registration with the Reserve Bank of India under the idea that they are regulated by other regulators:
- Core Investment Companies – (assets are less than ₹100 crore or public funds not taken)
- Merchant Banking Companies
- Companies which are engaged in the business of stock-broking
- Housing Finance Companies
- Companies engaged in the business of Venture Capital
- Insurance companies holding a certificate of registration issued by IRDA.
- Chit Fund Companies as defined in the Sec 2 clause (b) of the Chit Fund Act, 1982
- Nidhi Companies as notified under Section 620(A) of the Companies Act 1956.
Pre-Requisites for Incorporation of NBFC
For incorporation of NBFC in India following conditions must be fulfilled :
- The Company must be registered under the Companies Act 1956 or Companies Act 2013.
- The Company is required to have a Net-Owned Capital Fund of ₹2 crore, which includes Share Capital, Premium on Shares, and Reserves, if any.
- At least one of the Directors of the Company must have a working experience with NBFC/Banking.
- The CIBIL records of the Company must be clear without exception.
- The applicant company is required to draft a detailed business plan for the next five years.
- The middle name of the Company must have either of the keywords out of Finance, Leasing, Capital Fintech, etc.
- In case of an FDI, the necessary FDI Compliances as per the FEMA Act must be complied with.
- Before incorporating an NBFC, it is important for the Company to have an experienced NBFC consultant.
Advantages of NBFC Incorporation

Low cost & Time
Registering a NBFC is considerably easy task as compared to register a small Bank. The cost & time both are excessive in terms of opening a Bank.

Easy Registration
NBFC Registration process is very easy if the consultant you have is experienced and having NBFC Registration experience.

Industry Growth Ratio
At present, the fintech industry is at boom as everyone needs an easy source of funding, it can be an advantage for aspiring Entrepreneurs to register a NBFC and earn good return in Fintech Industry

Easy Recovery of Loans
Since NBFCs are very systematic and they offer considerably less loan amount, therefore, borrowers return the amount easy which makes it convenient for lenders.

Foreign Direct Investment
The Government has allowed 100% FDI in Non- Banking Financial services through automatic route without any capitalization norms and limited ambit of activities. Now, the NBFC’s which are governed by financial regulators like, RBI, SEBI, IRDA, National Housing Bank or any other regulator as notified by the Government are eligible to receive 100% FDI under automatic route.
FDI in Non- Banking Financial activities which are not regulated by any financial sector regulatory body would be allowed with prior Government approval subject to condition of minimum capitalization as prescribed by the Government.
Requirements of Non-Banking Finance License for Finance Companies
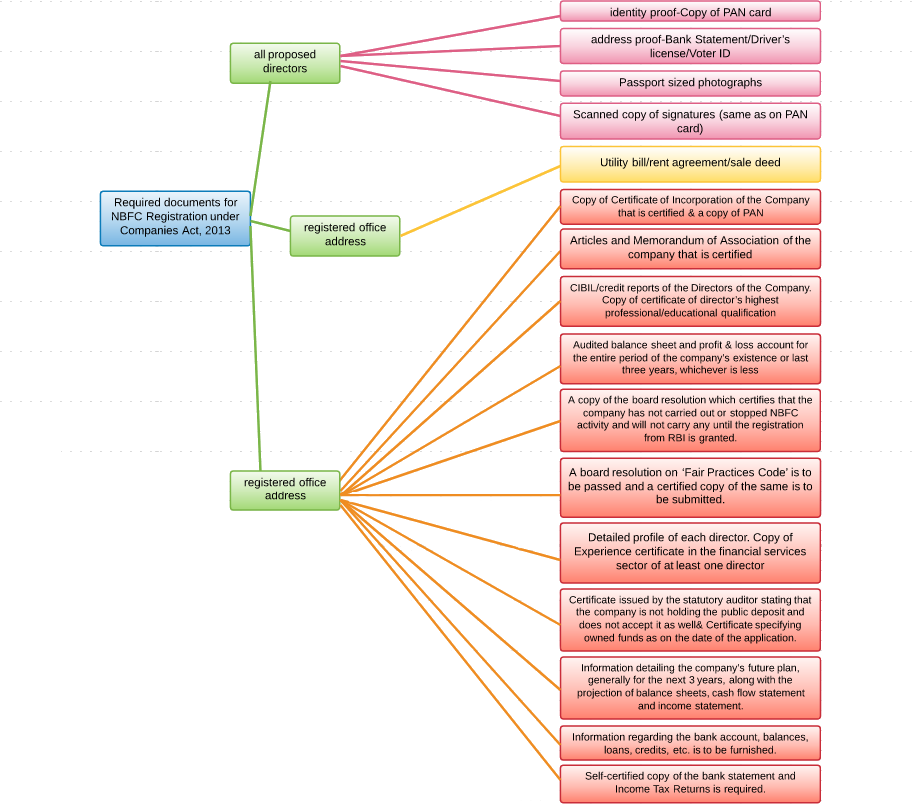
There are various documents that are required before filing the application for COR with RBI for the NBFC License. The requirements are mentioned below:
- It is mandatory for the middle name of the company to be keywords such as Finance, Investment, Leasing, Capital Fintech, etc.
- Documents showing the highest qualification of the directors associated with the company.
- Net worth certificate of the shareholders, company, and directors which needs to be CA Certified.
- Registration of the company as a Public Limited or a Private Limited Company.
- There should be an explicit clause in the MOA explaining the financial or Investment of the company
- It is important to have certified documents for the certification of Incorporation, MOA, as well as AOA, verified from the respective regional registrar of the companies.
- Document supporting the income proof of the shareholders, founders and directors of the company along with their KYC.
- Having a Banker Report regarding No Lien remark on the Initial Final deposit of ₹ 2 Cr.
- A company must have an experienced NBFC Consultant.
- Report analysis of the credit card owned by the shareholders and the directors of the company.
- In case of an FDI, all the necessary FDI Compliance as per the FEMA Act must be compiled.
- Submitting one of the directors’ profile who has a financial experience of 10+ years as a Senior Management in Bank or NBFC.
- It is important to have the credit report of the directors and the shareholders verified which keeps them from repaying the loan or financial facilities over life. In case there is a proper clarification of the delay, the RBI may accept the application for the same.
- The Initial capital of ₹ 2 Cr cannot be a borrowed capital.
- There needs to be a high-level business plan in order to get through the process of an NBFC License.
- A detailed action plan should be in place regarding the loan products and Credit & Risk Assessment Policy.
- An elaborate decision making as well as the organizational structure for the approval or the rejection of the application of a loan.
- Having a true copy of the Audited Balance Sheet with Profit & Loss account along with the auditor’s report of three years holding the company. This is mandatory if the applicant is a subsidiary of the Public Limited or Private Limited or Foreign Company.
NBFC Registration Fees
NBFC Registration Fees under various types
While registering the company, a fee based on the authorized capital of the company is to be paid to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
A company would also need to pay fees on the basis of the authorized capital and other few factors for the MOA (Memorandum of Association) and AOA (Articles of Association) of the company
Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company electronically (SPICe) filling might also require the company to pay certain fees
For a Reserve Unique Number (RUN) and Director Identification Numbers (DIN), a predetermined fee is to be paid to the MCA
A Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) is required for every director and thus its generation would require a payment of periodic fees
Additional fees is required to be paid while submitting the application to the registrar.
Pre-requisites for registering as a NBFC company
- The applicant company should be registered under the provisions, rules and regulations of the details as specified under the Companies act of 2013 or previously followed Companies Act of 1956.
- If any company is able to generate a solid financial flow of more than 50% from its initial capital investment, then the NBFC certification is mandatory.
- The paid-up capital of the company applying for NBFC registration should be at least be₹2 Crores. In case a foreign company is applying for the NBFC registration then the paid up equity share capital should be around ₹5 crore.
- It should be noted that at the time of applying for the NBFC registration, the net equity fund should be reserved as an evidence of eligibility of NBFC certificate in the bank account.
Incorporation of Non-Banking Financial Company
A company should first be registered under the Companies Act 2013 or should already be registered under Companies Act 1956 as either a Private Limited or a Public Limited Company. Open a Bank Account. Collect all the documents from the directors. Collect all the documents from the directors. Prepare a detailed application on COSMOS.
Deposit the amount of ₹ 2 crores in the bank account of the company.The minimum net owned funds of the Company should be Rs. 2 Crore (except for NBFC-MFIs, NBFC-Factors and CIC).
1/3rd of the Directors must possess finance experience.
The CIBIL records of the Company should be clean.
The company must have a detailed business plan for five years.
The company must comply with the requirements for capital compliances and FEMA.
After the submitted documents are approved, the regional office sends an application to the central office of the Reserve Bank of India which then goes through the intricate examination and background checking of the documents which then grants a certificate to the applicants’ company.After the application is properly scrutinized, the License will be given to the Company.
A Hard copy of the application also has to be sent to the regional branch of the Reserve Bank of India.
A CARN Number will be generated (Company Application Reference Number).
After all of the above conditions have been satisfied the online application on the website of RBI should be filled and submitted along with the requisite documents.
After all of the above conditions have been satisfied the online application on the website of RBI should be filled and submitted along with the requisite documents.
A CARN Number will be generated (Company Application Reference Number).
A Hard copy of the application also has to be sent to the regional branch of the Reserve Bank of India.
After the submitted documents are approved, the regional office sends an application to the central office of the Reserve Bank of India which then goes through the intricate examination and background checking of the documents which then grants a certificate to the applicants’ company.After the application is properly scrutinized, the License will be given to the Company.
Post-Incorporation guidelines of Non-Banking Financial Company
Once the Company gets a valid license it has to adhere to the following guidelines:
- They cannot receive deposits which are payable on demand.
- The public Deposits which the company can take should be for a minimum time period of 12 months and a maximum time period of 60 months.
- The interest charged by the Company cannot be more than the ceiling prescribed by the Reserve Bank of India from time to time.
- The repayment of any amount so taken by the Company will not be guaranteed by the Reserve Bank of India.
- All the information about the company as well as any change in the composition of the Company has to be furnished to the Reserve Bank of India.
- The deposits taken by the Public will be unsecured.
- The Company has to submit its audited balance sheet every year.
- A statutory return on the deposits taken by the company has to be furnished in the form NBS – 1 every year.
- A Quarterly Return on the liquid assets of the company has to be furnished.
- A certificate from the auditors had to be taken stating that the company is in a position to pay back all the deposits or money taken from the Public.
- The credit rating has to be taken every 6 months and submitted to the RBI.
- A half-yearly Asset Liability Management (ALM) return has to be given by the company which has a Public Deposit of ₹20 Crore and above or has assets worth ₹100 Crore and above.
- A minimum level of 15% of the Public Deposits has to be maintained by the Company in Liquid Assets.
If the NBFC defaults in the payment of any amount taken, the consumer can go to the National Company Law Tribunal or the Consumer Forum to file a suit against the Company.
Certain guidelines have been laid down by RBI that has to be complied withonce the firm is registered. Submission of Income Tax Returns, ROC Returns, Statutory Audit, Tax Audit, various NBS returns for Deposit accepting and non-deposit accepting companies are some of the most important statutory compliances.
RBI Compliance for NBFC’s-NBFCs are required to submit various returns to RBI w.r.t their deposit acceptance, prudential norms compliance, ALM etc. Detailed instructions regarding submission of returns by NBFCs have been issued through various company circulars. A list of such returns to be submitted by NBFCs-D, NBFCs-ND-SI and others.
Submission of Annual Statements and Returns
List of compliance on basis of type of NBFC
| Submittedby non-deposit taking NBFC’S having asset size between ₹ 50 crores to₹ 100 crores | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Time limit |
| Quarterly Return | Quarterly Return by Non-Deposit taking NBFC’s with asset size of ₹ 50 - 100 Cr. | RBI |
| Submitted by Non-Deposit taking NBFCs having assets of ₹ 100 To ₹ 500 Crores | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| NBS8 | Annual Return on Non-Deposit taking NBFC’s With Asset Size from ₹100 Cr. to 500 Cr | RBI |
| Submitted by NBFC-ND-SI having asset size below ₹ 100Cr | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| NBS9 | Annual Return on NBFC¬-ND¬-SI with Asset Size Below ₹100 Cr | RBI |
| Non-¬Deposit Taking NBFCS SI Department(RBI) | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Time Limit |
| Monthly Return | Monthly Return with asset size of ₹100 Cr. & above | RBI |
| NBS_ALM1 | Statement of Short term dynamic liquidity (Within 10 days of the end of every month) | RBI |
| NBS-7 | Quarterly Statement of Capital Funds, Risk-Weighted Assets and risk assets Ratio etc. Unaudited Monthly return/audited Unaudited Monthly return NBS-7 | Unaudited Monthly (On or before 30th June) Audited monthly return (Upon completion) |
| SA & CEO certificate for NBS¬7 | Certifying NBS¬7 (Statutory Auditors certificate on Income & Assets) | On or before 30th June |
| NBS_ALM3 | Interest rate sensitivity | statement shall be filed with the Bank |
| ALM Return | Asset liability mismatches and interest rate exposure | RBI |
| NBFC monthly compliances submitted by all non-deposit taking NBFCS SI | ||
| Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| Monthly Return | Monthly Return on NBFC-NDSI with asset size of ₹100 CR. & above | RBI |
| NBS_ALM1 | Statement of Short term dynamic liquidity to be filed within 10 days of the closer month | RBI |
| To be submitted by all deposit-taking NBFC’s having asset size above ₹ 100 crores or public deposits of ₹ 20 crores and above | ||
| NBS6 | Monthly Return stating Exposure to Capital Market | RBI |
| NBFC ND SI Quarterly Compliances | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| To be submitted by all deposit-taking NBFC’s except residuary NBFC | ||
| NBS 1 | Quarterly Return on Material Financial Parameters of Deposit Taking NBFCs | RBI |
| NBS 2 | Quarterly Statement of Capital Funds, Risk Assets/Exposures and risk assets Ratio. | RBI |
| NBS 2: CA & CEO Cert. | Certifying NBS 2 | RBI |
| NBS 3 | Quarterly Return on Statutory Liquid Assets | RBI |
| To be submitted by all residuary non¬-banking companies | ||
| NBS 3A | Quarterly Return on Statutory Liquid Assets | RBI |
| Quarterly Return I | Return of investments | RBI |
| Submitted By All Non-Deposit Taking NBFCs | ||
| NBS -7 | Quarterly Statement of Capital Funds, Risk-Weighted Assets and risk assets Ratio etc. | RBI |
| NBS-7: SA & CEO Cert. | Certifying NBS -7 | RBI |
| Submitted by NBFCS having an asset size between ₹50 to 100 cr. | ||
| Quarterly Return | Quarterly Return by NBFC-¬ND with asset size of ₹50 ¬ 100 Cr. | RBI |
| Submitted by all securitization and reconstruction company | ||
| SCRC | Quarterly statement of assets acquired/ securitized/ reconstructed | RBI |
| NBFC ND SI Half Yearly Compliances | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| To be submitted by all deposit-taking NBFC’s having asset size ₹ 100 crores or more or public deposits of ₹ 20 crores and above | ||
| NBS_ALM2 | Details of any mismatches in Assets, liabilities and interest rate exposure (Within 20 days of the closure of half year) | The regional office of the Department in whose jurisdiction NBFC is registered |
| Submitted by all non-deposit taking NBFCS | ||
| NBS_ALM3 | Interest rate sensitivity | Statement shall be filed with the Bank |
| NBFC Yearly Compliances | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| Submitted by all non-deposit taking NBFCS | ||
| ALM Return | Asset liability mismatches and interest rate exposure | RBI |
| Submitted by all residuary non¬banking companies | ||
| Form NBS 1A | Annual Return on Deposits (Filed annually after March 31 and latest by September 30) | Regional Office of Department of Non-Banking Supervision, RBI where registered office of the company is situated |
| Submitted by NBFCS having the asset of ₹ 100 to ₹ 500 Cr | ||
| NBS8 | Annual Return on Non-Deposit taking NBFC with asset size from ₹100 Cr. to 500 Cr | RBI |
| Submitted by NBFCS having asset size below ₹ 100 Cr | ||
| NBS9 | Annual Return on NBFCNDSI With Asset Size Below ₹100 Cr | RBI |
| Submitted by all non¬banking financial companies accepting/holding public deposits, and MNBCS except residuary non¬banking companies | ||
| NBS4 | Repayment of Deposits only in respect of rejected/canceled companies | Department of Non-Banking Supervision, RBI |
| CA certificate form NBS – 4 | Certifying NBS4 | RBI |
| NBFC under Companies Act, 2013 | ||
| Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| E-Form MGT-7 | Annual Return (Within 60 days of conclusion AGM) | ROC |
| E-Form AOC-4 | Filing of annual financials i.e. Balance Sheet & Profit & Loss statement (Within 30 days of conclusion of AGM) | ROC |
| E-Form DIR-12 | If there is any change in Directors (Within 30 days of the date of that change) | ROC |
Compliances for listed NBFC-ND with NSE
| NBFC ND SI Quarterly Compliances | ||
| S No. | Particulars | Time limit |
| 1 | Filing of Listing Agreement of Issued Series | Within 30 days of Issuance |
| 2 | Publishing of Unaudited Half-yearly Result in two newspaper | Within 30 days from the end of Half-year |
| 3 | File Half-yearly Audited Result with NSE via mail | Within 30 days from the end of Half-year |
| 4 | File Quarterly result (Balance Sheet and P&L) via mail | Within 90 days from the end of Quarter |
| 5 |
Filing Umbrella Information Memorandum/Shelf Offer Document+ below letters:
|
At the end of Financial Year |
| Compliance by deposit taking NBFC’s with asset size of more than ₹ 100 Crores or having Public Deposits of ₹20 Crores or more | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| NBS6 | Monthly Return on Exposure Towards Capital Market | RBI |
| NBS_ALM2 | Asset liability mismatches and interest rate exposure (Within 20 days of the closure of half year) | Regional office of the Department in whose jurisdiction NBFC is registered |
| Compliance by deposit taking NBFC’s except residuary NBFC’s: | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| NBS 1 | Quarterly Return on Important Financial Parameters of Deposit Taking NBFCs | RBI |
| NBS 2 | Quarterly Statement of Capital Funds, Risk Assets/Exposures and risk assets Ratio. | RBI |
| CA & CEO certificate for NBS2 | Certifying NBS2 | RBI |
| NBS 3 | Quarterly Return stating Statutory Liquid Assets | RBI |
| NBS4 | Repayment of Deposits | Department of Non-¬Banking Supervision, RBI |
| (To be filed only in respect of rejected/cancelled companies) | ||
| CA certificate form NBS 4 | Certifying NBS4 | RBI |
| Submitted By All Residuary NBFC | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| NBS 3A | Quarterly Return on Statutory Liquid Assets | RBI |
| Quarterly Return I | Return of investments | RBI |
| Form NBS 1A | Annual Return on Deposits (Filed annually after closure of financial year and latest by September 30) | Regional Office of Department of Non-¬ Banking Supervision, RBI where registered office of the company is situated |
| Form Schedule “A” | General Information of the Company (filed annually as early as possible latest by the 30th September) | Regional Office of the Department of Supervision, Financial Companies Wing |
| Submitted By All Securitisationand Reconstruction Company | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| SCRC | Quarterly statement of assets acquired/ securitized/ reconstructed | RBI |
| Submitted By All NBFCs Whether Holding Public Deposits Or Not | ||
| Form Name | Purpose Of The Form | Department |
| Special Return | General information and Net Owned Funds | RBI |
| Branch Info | Branch Details | RBI |
Following are the types of returns that are required by both the types of NBFCs
Returns by Deposit Taking NBFC
| S. No. | Form Name | Purpose Of The Form |
| 1. | NBS-1 | These are the Quarterly returns on deposit in the first schedule. Such return is required to be furnished for the purpose of capturing financial details such as Profit and Loss Account, Components of assets and Liability. |
| 2. | NBS-2 | The Quarterly Return on prudential norms. The requirement to file this return is to get the details related to several norms like asset Classification, Capital Adequacy, NOF, Provisioning, etc. |
| 3. | NBS-3 | The Quarterly Return on liquid assets. The intent behind filing such norms is to capture information about statutory investment in Liquid states. |
| 4. | NBS-4 | The annual return of critical parameters which are by rejected companies those are holding public deposits. The objective behind filing this return is to find the repayment status of the rejected NBFCs accepting public deposits. |
| 5. | NBS-6 | Needs to be filed as Monthly return on exposure to capital market by deposit-taking NBFC with the total assets of ₹ 100 crore or more. |
| 6. | ALM return |
|
Returns required Non-Deposit NBFC
| S. No. | Form Name | Purpose Of The Form |
| 1. | NBS-1 | It is a quarterly statement providing information related to, risk assets ratio, capital funds, risk-weighted asset. |
| 2. | NBS-2 | The Quarterly Return on prudential norms. The requirement to file this return is to get the details related to several norms like asset Classification, Capital Adequacy, NOF, Provisioning, etc. |
| 3. | ALM Returns NBS-ALM-1 NBS-ALM2 NBS-ALM-3 ALM-YRLY |
ALM (Asset-Liability Management) Returns refer to multiple returns that are supposed to be submitted by NBFCs-ND-SI at several intervals as described below:
|
| 4. | Branch info return | Quarterly return on important financial parameters of non-deposit taking NBFC having assets of more than ₹ 50 crores and above but less than ₹ 100 crores. The requirement like name of the company, address, Net Owned Fund, profit/loss during the last three years needs to be furnished quarterly by non-deposit taking NBFCs with asset size between ₹ 50 crores and ₹ 100 crores. Every NBFCs-ND-SI must submit the branch information return on a quarterly basis. |
Compliances for NBFC-ND with RBI
Annual Compliances
| S. No. | Article | Term |
| 1. | Unaudited March Monthly return/NBS7 | On or before 30th June |
| 2. | Audited March Monthly return/NBS7 | Upon completion |
| 3. | Statutory Auditors certificate on Income & Assets | On or before 30th June |
| 4. | Information about Cos having FDI/Foreign Funds | On or before 30th June |
| 5. | Board Resolution of Non-acceptance of Public Deposit | Much before starting of the new Financial year |
| 6. | Annual Balance Sheet with profit and loss account details | One month from the date of sign-off |
| 7. | Declaration by Auditors, who are acting as auditors of the company | Annual basis |
Monthly Compliances
| S. No. | Article | Term |
| 1. | Monthly Return | by 7th of every month |
| 2. | Upload monthly | by 7th of every month |
Periodical Compliances
| S. No. | Article | Term |
| 1. | Appointment of Director(Annexure-III) | within 30 days of appointment |
| 2. | Resignation of Director (DIR-12 + Challan report) | within 30 days of the resignation |
| 3. | Adoption of any notification in the ensuing Board Meeting and filing the certified copy with RBI |
Other related forms : Branch Information (Half-Yearly Return)
| S. No. | Form Name | Purpose Of The Form |
| 1. | Form – Schedule ‘A’ | Special Return, required to be submitted by all NBFCs whether deposit-taking or non-deposit-taking |
| 2. | NBS-8 | NBS-8 (Annual return to be furnished by NBFCs which are having asset size between ₹ 100 to ₹ 500cr) |
| 3. | NBS-9 | NBS-9 (Annual return be furnished by NBFCs which are having asset size below ₹100cr) |
| 4. | Information about Cos having FDI/Foreign Funds | On or before 30th June |
Additional Compliances
Besides the compliances mentioned above, there are some other compliances under the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013, that all the NBFCs PAN-India must follow, which are as follows:
ADT-1, Appointment of Auditor
Maintenance of Books and Accounts
Maintenance of Statutory Registers
Preparation of the Financial Statements
Convene Statutory Meetings
Income Tax Returns (ITR) Filings
AOC-4, Filing of Financial Statements
MGT-7, Filing ROC (Registrar of Companies) Annual Returns
RBI Intimations Applicable on NBFCs
Filing of Annual Reports to RBI : It is compulsory for every for every NBFC (Non Banking Financial Institution) to submit its Annual Report within a period of 15 Days, Starting from the date of AGM (Annual General Meeting). Each financial institution should provide its Audited Balance Sheet, together with Audited P&L (Profit & Loss) Statement passed by the company in its Board Meeting. The directors of the company also need to annex a copy of Board Report or Directors Report to the Apex Bank.
Annual Returns : Every miscellaneous NBFC that is accepting or holding deposits must submit an annual return containing information in the format prescribed by the Apex Bank of India.
Specimen Signature of the Principal Officer who is authorised to sign on behalf of the Company.
SAC or Statutory Auditors Certificate : All the NBFCs having Registration PAN-India needs to collect a certificate from Statutory Auditors. This certificate will act as a declaration that the said NBFC or Non-Banking Financial Company is carrying out the functions of NBFC and is incorporated under section 45-IA of the RBI, Act, 1934. Further, the due date to file this certificate is one month from the date of finalization of the Balance Sheet. However, the period shall not exceed the date of 31st December.
Change in Principal Officers and Directors : In case an NBFC decides to change its Principal officers or Directors, and then it is compulsary for every non-banking financial institution to submit a written statement, including the details as follows:
Name and the Official Designation of its Principal Officers;
Name and Residential Address of the Directors of the Company;
Further, any change or amendment made by the Apex Bank in the guidelines provided above shall be informed by the Reserve Bank of India with 1 month from the incidence of such change or amendment.
Prudential Regulations
Besides the above mentioned RBI compliance for NBFCs having registration PAN-India, there are some other regulations mentioned under Chapter IV of the Master Director issued by RBI. Such regulations are known as Prudential Regulations. It is again mandatory got every NBFC to abide by the regulations as follows:
Leverage Ratio
- All the NBFCs other than NBFC-IFC (Infrastructure Finance Company) and NBFC-MFI (Micro Finance Institution) must maintain ratio upto 7 at any course of action.
Accounting Investments
- It is mandatory for the BOD (Board of Directors) of the NBFCs to frame investment Policies for the company and implement them as well. For example, the criterion to categorise investments into long term and current investments.
Frame Policies for Call or Demand Loans
- The BOD (Board of Directors) of a pertinent NBFC that intends to call or demand loans must frame a policy that will be implemented by the company.
Provisioning of the Standard Asset
- Every pertinent NBFC is required to make provisions regarding the standard assets at 0.25% of the total outstanding.
Classification of Assets
All the NBFCs pertinent under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction must classify their assets in the classes as follows :
- Standard Assets;
- Sub-Standard Assets;
- Doubtful Assets;
- Loss Assets;
Multiple NBFCs
- All the NBFC relevant under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction will be jointly aggregated for the purpose of checking the threshold of ₹ 500 crores asset size.
Disclosures in the Company's Balance Sheet
- Every NBFC relevant under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction will have separate disclosures provisions for bad or doubtful debts and depreciation in investments.
A loan taken against the shares of the Company are Prohibited
- No NBFCs pertinent under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction can either take or lend credit against its own shares.
Conclusion
Large segment of people in India are undercapitalized even being capable to generate the throughput. They don’t have access to capital market or are being declined by the traditional banking system due to assessment of credibility. Low Income –households and informal MSME Enterprises are far away from to the access financial support and services as they require due to lack of data and financials history of the segment. Retail and MSME segments are striving for its capital requirement to increase their length of operation. With right strategy, robust business model and strong governance and risk management, NBFC’s can grab the opportunity of fairly large segment of economy.
Annuals compliances are strictly mandatory for those NBFCs which have obtained License from RBI. Furthermore, according to ‘Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, 1934, the applicant must have a net owned fund of ₹2 crores and it must obtain a certificate of registration from the bank.’ Therefore, for the smooth functioning and to secure your NBFC from any hefty penalties, it’s mandatory to comply with all the NBFC annual compliances.
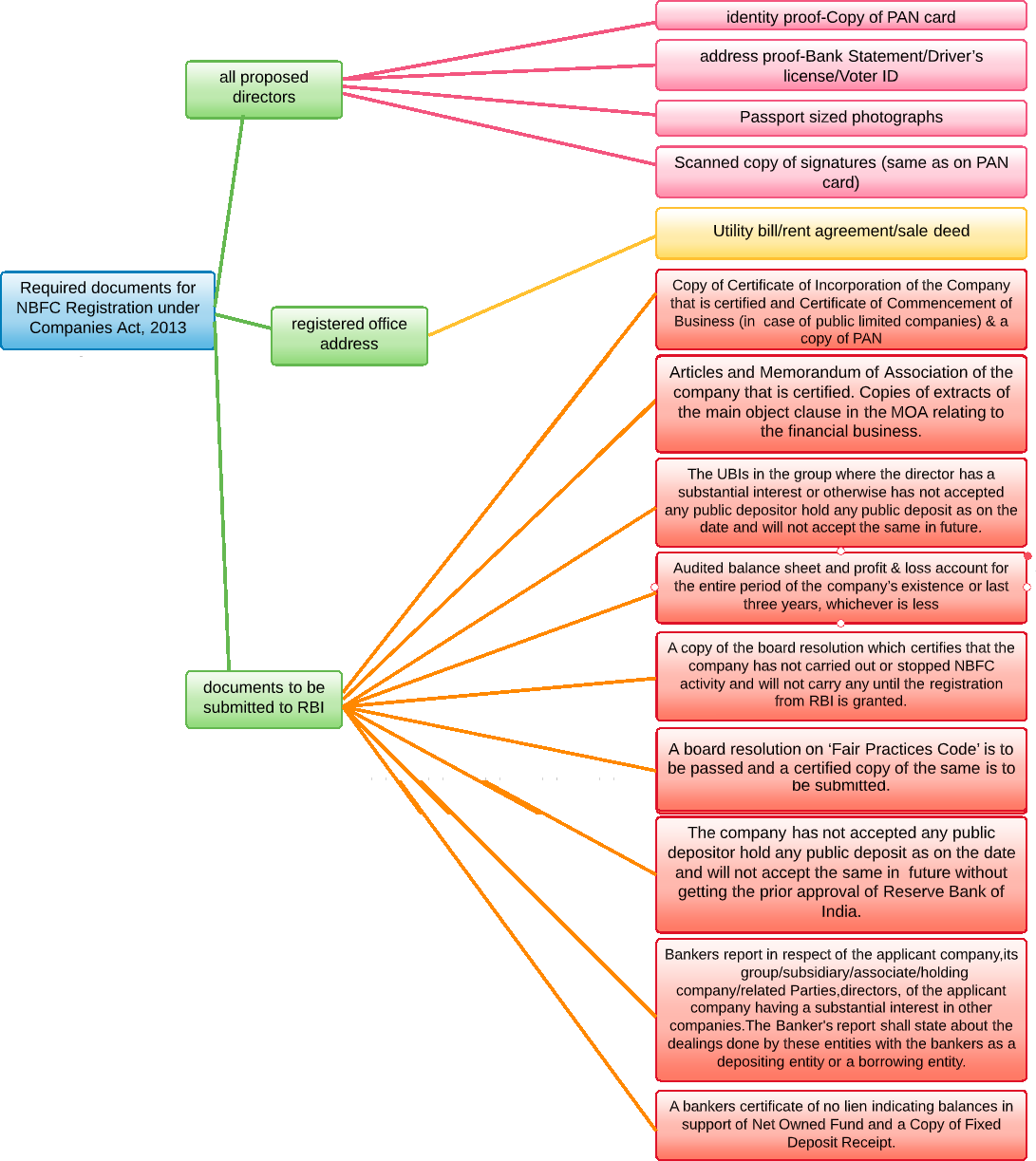
Checklist for Registration of NBFC in India
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are the minimum requirements to register a Company?
-
- Minimum 2 Directors in case of Private Limited and 3 Directors in case of Public Limited shall be appointed; out of which one must be a resident of India.
- Minimum 2 shareholders in case of Private Limited and 7 shareholders in case of public limited are required for this registration. Here, an individual may become shareholder and Director at the same time.
- A place of business in India must be provided as a registered office address.
- 2. What are the minimum requirements towards Capital?
-
- Authorised Capital (Limit up to which company can allot shares) is prescribed as Minimum Rupees One Lakh, however, since the Stamp duty and fee for Authorised Capital up to Ten Lakhs is same, we recommend it to be kept at Ten Lakhs only
- There is no minimum paid up capital requirement, however, atleast one share subscription each subscriber is a must, we recommend the paid up capital to be kept as One Lakh since initial expenditure and Bank account opening needs that kind of money.
- 3. What is the requirement of DSC (Digital Signature Certificate)?
-
- DSC is provided in the form of token issued by Certified Authorities and is a substitute of Physical Signature and enable the owner to sign documents digitally
- Company incorporation is a complete online process and all the forms required to be filed for incorporation of company are required to be signed digitally with the help of DSC of the Directors
- Company Sarthi helps its clients in the issuance of DSC
- 4. What is the requirement of Documents for DSC issuance?
-
- Self-attested Documents and Details required are :
- Duly filled and Signed Application Form
- Copy of PAN Card
- Copy of Aadhaar Card
- Passport size Photograph
- Valid and active Mobile Number and e-Mail id
- On submission of above documents with the DSC Authority partner, applicant will receive the OTP on the given Mobile and e-Mail ID and thereafter applicant has to complete Mobile and Video verification
- 5. What is the eligibility to become a Director in Company?
-
- Any natural person above the age of 18 years can become the director in the company after procuring Director Identification Number (DIN).
- There are no specific criteria provided in terms of citizenship or residency, a foreign national can also become a director.
- 6. What is Director Identification Number (DIN)?
-
- DIN is a unique number assigned by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs to Individuals on whose name the application is made, allowing that individual to become a Director in a Company or Designated Partner in an LLP
- DIN is allowed only once in lifetime and can be used to become a Director in any number of company as per eligibility criteria
- The application of DIN Allotment is now merged with the application for the formation of a company subject to a limit of maximum 3 DIN.
- 7. What is the requirement of Documents for DIN issuance?
-
- Self-attested Documents and Details required are :
- Copy of PAN Card
- Copy of Aadhaar Card
- Passport size Photograph
- Valid and active Mobile Number and e-Mail id
- Proof of Identity of Applicant (Any one)
- Valid Passport
- Driving License
- Voter ID Card
- Proof of Residence of Applicant (Any one not older than 2 months having same address as that in the Proof of Identity)
- Bank Statement
- Electricity bill
- Telephone bill
- Mobile bill
- 8. How to reserve the name of the Company?
-
- Applicant has to give few choices of the name which can be checked at the Company Sarthi for the availability
- On the availability of atleast one name, Company Sarthi inform you of the same and ask you to provide two options of that name and the priority preference
- Company Sarthi also seeks from you the main objects of the company and State in which Registered office will be situated
- Although Company Sarthi follows a rigorous process of checking availability of Name, the registrar may ask to re-submit application with a different name if names applied do not fall under the criteria of uniqueness, relevancy or do not fulfill other requirements
- 9. Does any subscriber have to be physically present for completing the process of Incorporation of the Company?
-
- No, none of the promoters are required to be physically present for completing the process of Incorporation of the Company
- All the forms are filed on the web portal and are digitally signed.
- Also, the required documents can be sent through e-mail or uploaded on our portal for filing.
- 10. What documents are required for registered office of Company?
-
- Business address Proof (Any one not older than 2 Months)
- Electricity Bill
- Pipe Lined Gas Bill
- Telephone Bill
- Mobile Bill
- No Objection Certificate to be obtained from the owner(s) of registered office.
- Rent Agreement of the registered office should be provided if property is on rent
- 11. What are the minimum requirements to obtain NBFC License?
-
- A Private or public limited is to be registered as per the Companies Act, 2013
- Minimum Net Owned Funds of the Company should be ₹2 crore or more
- There should be atleast 1 Director in the company from the same background
- Fixed Deposit should be created of ₹ 2 CR with any Nationalize Bank and obtain a certificate of no lien from the bank
- There should be atleast 1 director in the company from the same background
- Good CIBIL score is required to present in order to register as NBFC
- 12. What documents require for Non- Banking Finance Company Registration?
-
- Incorporation Certificate of the Company
- Documents related to the Management and administration of the Company.
- The documents stating the Article of Association and Memorandum of Association of the form or company.
- Documents verifying the location of the company.
- Company Account which has been well audited for last three years.
- Elaborate Information regarding the Director and the Partners associated with the Company.
- Resolution from the board favoring the formation of NBFC.
- A bank account with a minimum equity share of ₹ 2Cr.
- PAN Card of the Company
- Additional documents which can be asked at the time of verification
- 13. What is the procedure to obtain NBFC License?
-
- After meeting the above conditions an online application on the website of RBI should be filled and submitted along with the requisite documents
- After submitting all the documents a company application reference number (CARN) will be generated
- Once you have received CARN, you need to submit the physical application form along with the supporting documents to the regional office. The RBI will scrutinize the form and documents and will then send it to the head office
- After everything is found to be correct, the Head Office of RBI will, then, issue the NBFC license. The applicant can check the status of the application by keying in the acknowledgment number
- 14. What does conducting financial activity as “principal business” mean?
-
Financial activity as principal business is when a company’s financial assets constitute more than 50 per cent of the total assets and income from financial assets constitute more than 50 per cent of the gross income. A company which fulfils both these criteria will be registered as NBFC by RBI. The term 'principal business' is not defined by the Reserve Bank of India Act. The Reserve Bank has defined it so as to ensure that only companies predominantly engaged in financial activity get registered with it and are regulated and supervised by it. Hence if there are companies engaged in agricultural operations, industrial activity, purchase and sale of goods, providing services or purchase, sale or construction of immovable property as their principal business and are doing some financial business in a small way, they will not be regulated by the Reserve Bank. Interestingly, this test is popularly known as 50-50 test and is applied to determine whether or not a company is into financial business.
- 15. Is it necessary that every NBFC should be registered with RBI?
-
In terms of Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, 1934, no Non-banking Financial company can commence or carry on business of a non-banking financial institution without
(a) obtaining a certificate of registration from the Bank and without having a Net Owned Funds of ₹ 25 lakhs (₹ Two crore since April 1999). However, in terms of the powers given to the Bank, to obviate dual regulation, certain categories of NBFCs which are regulated by other regulators are exempted from the requirement of registration with RBI viz. Venture Capital Fund/Merchant Banking companies/Stock broking companies registered with SEBI, Insurance Company holding a valid Certificate of Registration issued by IRDA, Nidhi companies as notified under Section 620A of the Companies Act, 1956, Chit companies as defined in clause
(b) of Section 2 of the Chit Funds Act, 1982,Housing Finance Companies regulated by National Housing Bank, Stock Exchange or a Mutual Benefit company. - 16. What are systemically important NBFCs?
-
Those NBFCs whose asset size is of ₹ 500 crore or more as per last audited balance sheet are considered as systemically important NBFCs. The rationale for such classification is that the activities of such NBFCs will have a bearing on the financial stability of the overall economy.
- 17. What are the essential documents required to be submitted along with the application form to the Regional Office of the Reserve Bank?
-
- Non-Banking Financial Company Registration Form (For online registration, visit to our COSMOS website https://cosmos.rbi.org.in)
- Application for Certificate of Registration to commence the business of an Asset Reconstruction Company
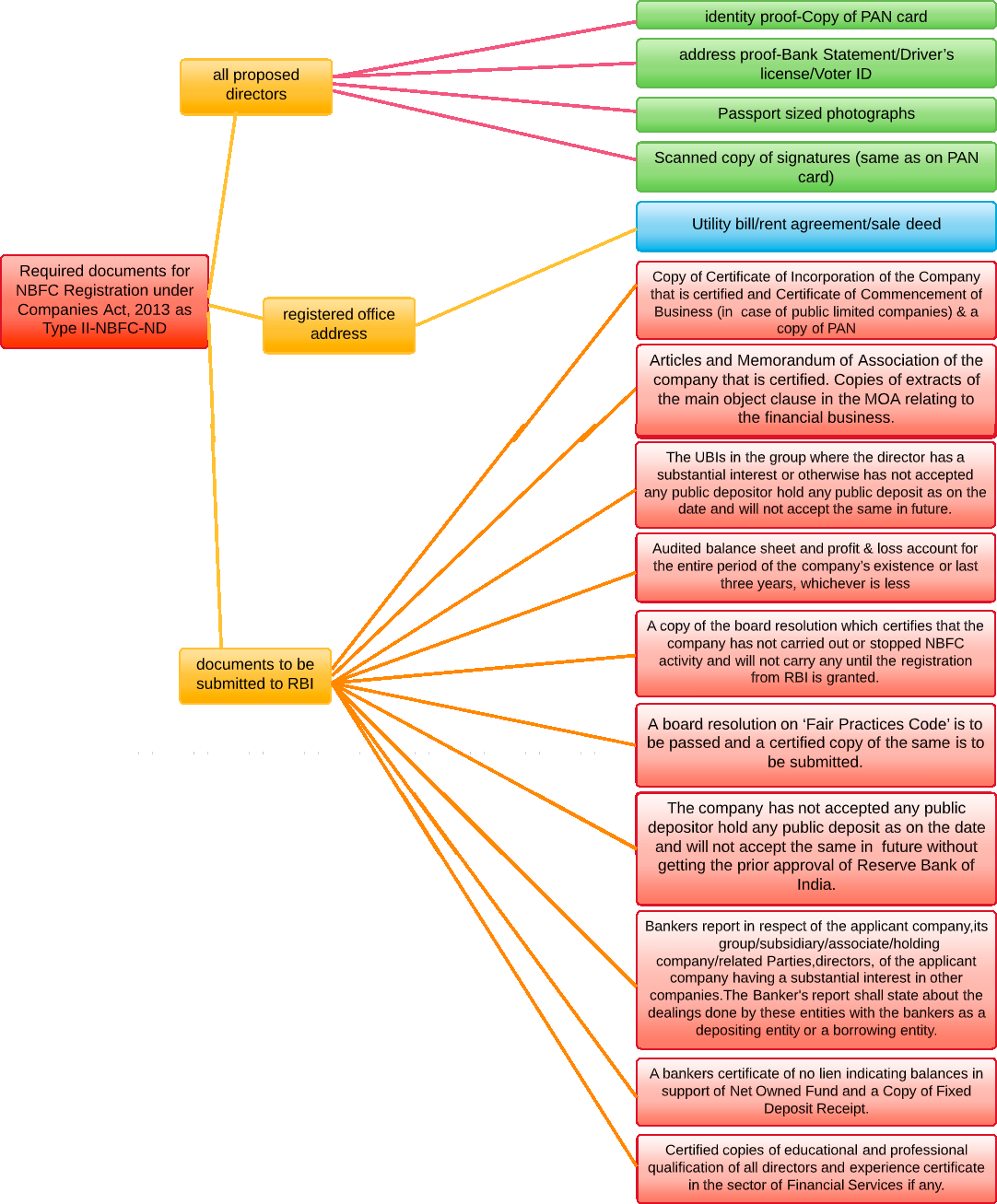
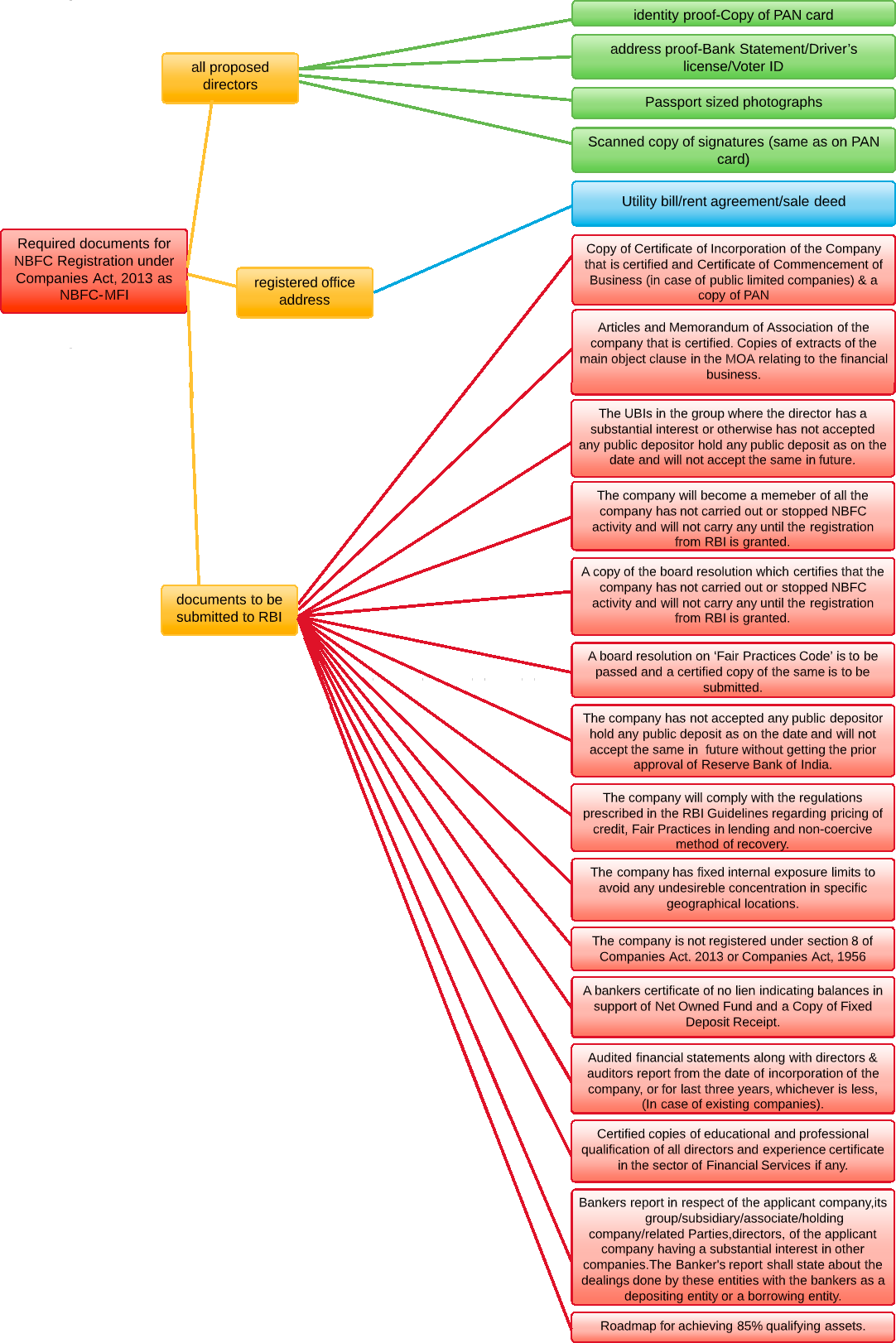
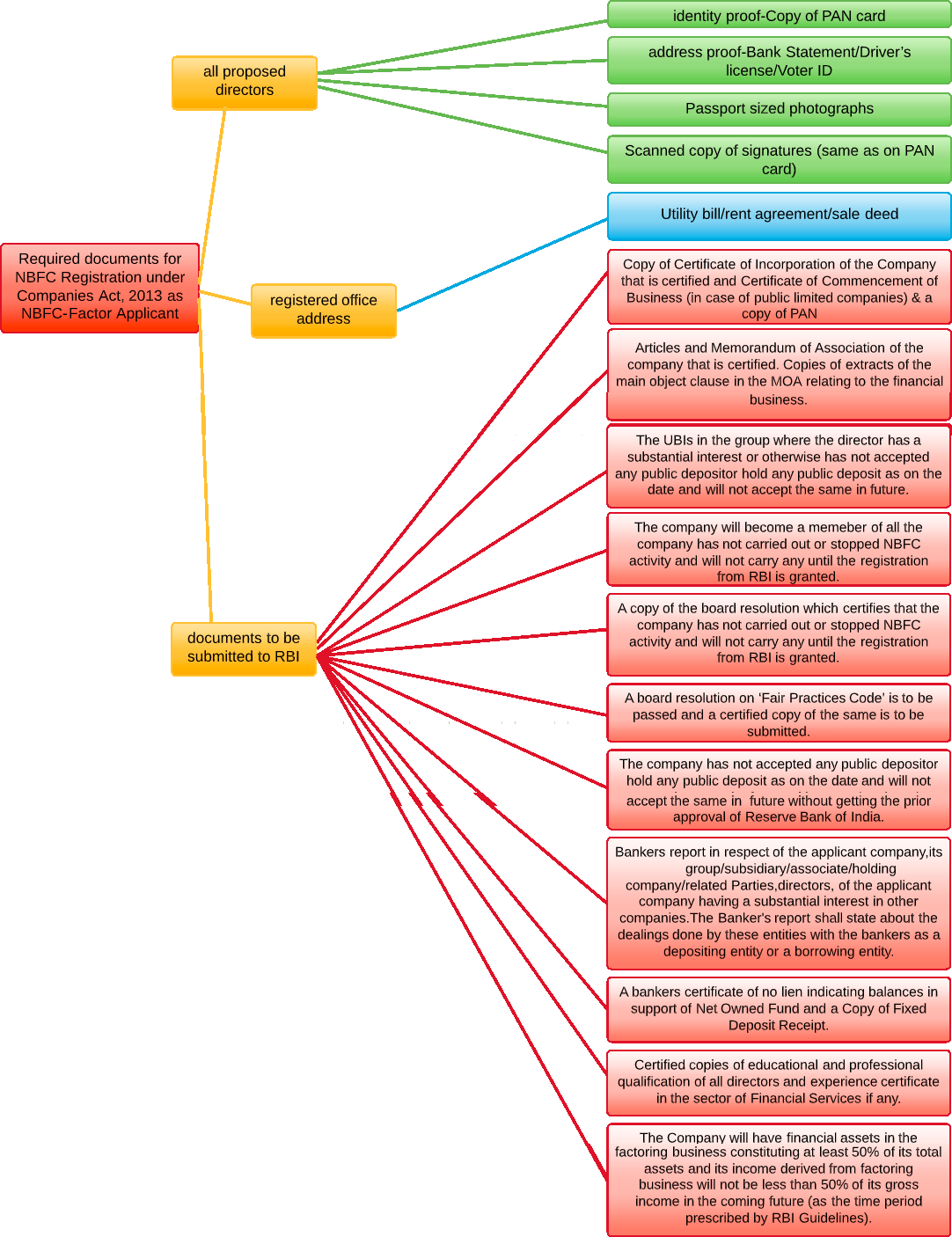
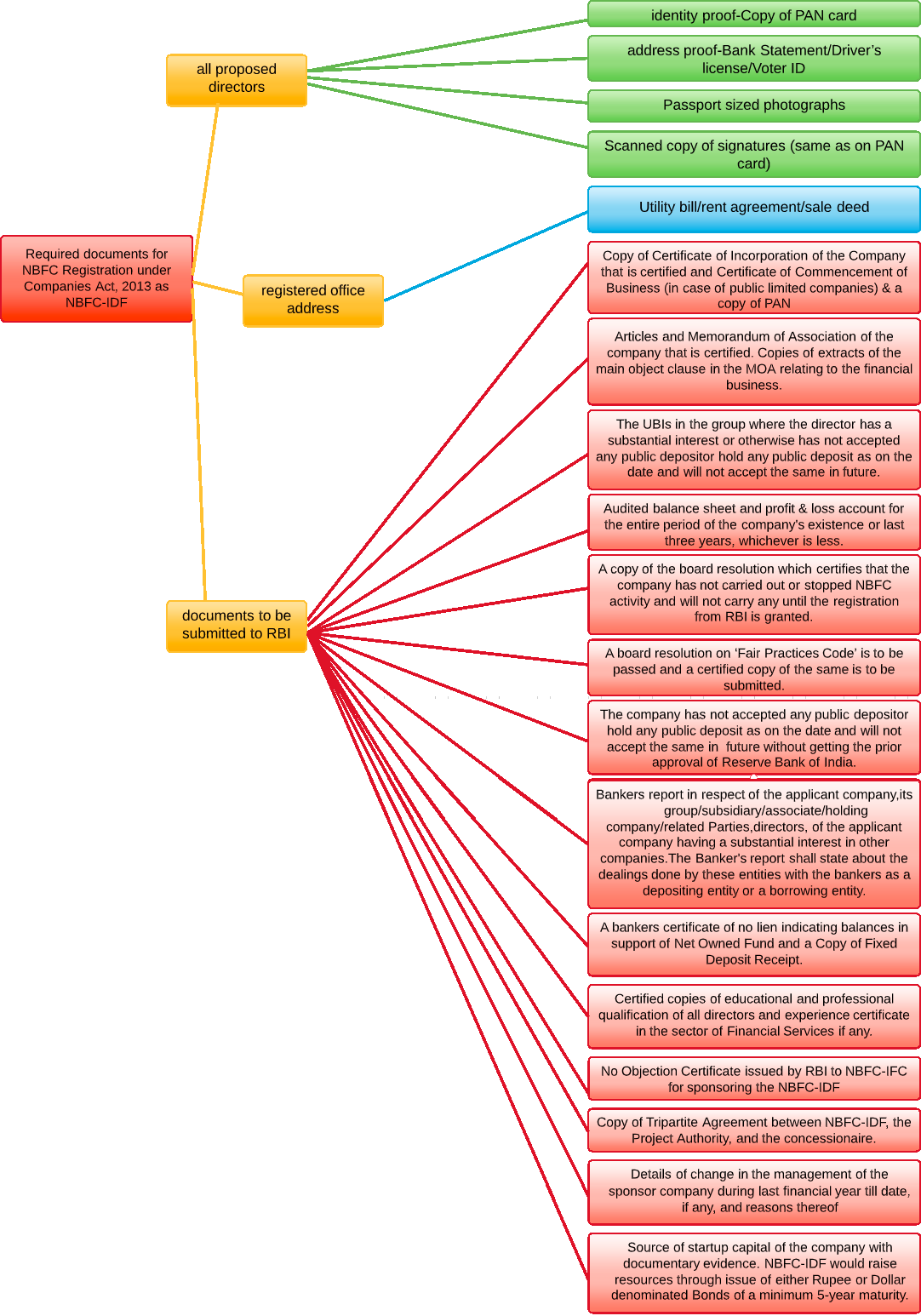
- Documents required for registration as NBFC-P2P
- Documents required for registration as NBFCs
- Documents required for registration of NBFC-MFI – New Companies
- Documents required for registration of NBFC – Factors
- Documents required for registration as an IDF-NBFC
- Documents required for registration as an Infrastructure Finance company
- Form - Schedule 'A'
- Special Return (To be submitted by all NBFCs whether holding public deposits or not)
- CEO and SA certificate for NBS 7
- Quarterly Return
- CA certificate for NBS 4
- CEO and CA certificate for NBS 2
- Core Investment Company
- Mortgage Guarantee Company
- Documents required for registration as CIC-ND-SI
- Documents required for registration of NBFC-MFI (Existing NBFCs)
- 18. What action can be taken against persons/financial companies making false claim of being regulated by the Reserve Bank?
-
It is illegal for any financial entity or unincorporated body to make a false claim of being regulated by the Reserve Bank to mislead the public to collect deposits and is liable for penal action under the Indian Penal Code. Information in this regard may be forwarded to the nearest office of the Reserve Bank and the Police.
- 19. What action is taken if financial companies which are lending or making investments as their principal business do not obtain a Certificate of Registration from the Reserve Bank?
-
If companies that are required to be registered with the Reserve Bank as NBFCs, are found to be conducting non-banking financial activity, such as, lending, investment or deposit acceptance as their principal business, without seeking registration, the Reserve Bank can impose penalty or fine on them or can even prosecute them in a court of law. If members of public come across any entity which does non-banking financial activity but does not figure in the list of authorized NBFC on RBI website, they should inform the nearest Regional Office of the Reserve Bank, for appropriate action to be taken for contravention of the provisions of the RBI Act, 1934.
- 20. What are the regulations applicable on non-deposit accepting NBFCs with asset size of less than ₹ 500 crore?
-
The regulation on non-deposit accepting NBFCs with asset size of less than ₹ 500 crore would be as under:
- They shall not be subjected to any regulation either prudential or conduct of business regulations viz., Fair Practices Code (FPC), KYC, etc., if they have not accessed any public funds and do not have a customer interface.
- Those having customer interface will be subjected only to conduct of business regulations including FPC, KYC etc., if they are not accessing public funds.
- Those accepting public funds will be subjected to limited prudential regulations but not conduct of business regulations if they have no customer interface.
- Where both public funds are accepted and customer interface exist, such companies will be subjected both to limited prudential regulations and conduct of business regulations.
- 21. What is a Residuary Non-Banking Company (RNBC)? In what way it is different from other NBFCs?
-
Residuary Non-Banking Company is a class of NBFC which is a company and has as its principal business the receiving of deposits, under any scheme or arrangement or in any other manner and not being Investment, Asset Financing, Loan Company. These companies are required to maintain investments as per directions of RBI, in addition to liquid assets. The functioning of these companies is different from those of NBFCs in terms of method of mobilization of deposits and requirement of deployment of depositors' funds as per Directions. Besides, Prudential Norms Directions are applicable to these companies also. Residuary Non-Banking Company cannot forfeit any amount deposited by the depositor, or any interest, premium, bonus or other advantage accrued thereon.
- 22. What is the rate of interest that an RNBC must pay on deposits and what should be maturity period of deposits taken by them?
-
The minimum interest an RNBC should pay on deposits should be 5% (to be compounded annually) on the amount deposited in lump sum or at monthly or longer intervals; and 3.5% (to be compounded annually) on the amount deposited under daily deposit scheme. Interest here includes premium, bonus or any other advantage, that an RNBC promises to the depositor by way of return. An RNBC can accept deposits for a minimum period of 12 months and maximum period of 84 months from the date of receipt of such deposit. They cannot accept deposits repayable on demand. However, at present, the only RNBCs in existence (Peerless) has been directed by the Reserve Bank to stop collecting deposits, repay the deposits to the depositor and wind up their RNBC business as their business model is inherently unviable.
- 23. What are the salient features of NBFC regulations which the depositor may note at the time of investment?
-
Some of the important regulations relating to acceptance of deposits by NBFCs are as under:
- The NBFCs are allowed to accept/renew public deposits for a minimum period of 12 months and maximum period of 60 months. They cannot accept deposits repayable on demand.
- NBFCs cannot offer interest rates higher than the ceiling rate prescribed by RBI from time to time. The present ceiling is 12.5 % per annum. The interest may be paid or compounded at rests not shorter than monthly rests.
- NBFCs cannot offer gifts/incentives or any other additional benefit to the depositors.
- NBFCs should have minimum investment grade credit rating.
- The deposits with NBFCs are not insured.
- The repayment of deposits by NBFCs is not guaranteed by RBI.
- Certain mandatory disclosures are to be made about the company in the Application Form issued by the company soliciting deposits.
- 24. What precautions should a depositor take before placing deposit with an NBFC?
-
A depositor wanting to place deposit with an NBFC must take the following precautions before placing deposits:
- That the NBFC is registered with RBI and specifically authorized by the RBI to accept deposits. A list of deposit taking NBFCs entitled to accept deposits is available at www.rbi.org.in → Sitemap → NBFC List. The depositor should check the list of NBFCs permitted to accept public deposits and also check that it is not appearing in the list of companies prohibited from accepting deposits, which is available at www.rbi.org.in → Sitemap → NBFC List → NBFCs who have been issued prohibitory orders, winding up petitions filed and legal cases under Chapter IIIB, IIIC and others.
- NBFCs have to prominently display the Certificate of Registration (CoR) issued by the Reserve Bank on its site. This certificate should also reflect that the NBFC has been specifically authorized by RBI to accept deposits. Depositors must scrutinize the certificate to ensure that the NBFC is authorized to accept deposits.
- The maximum interest rate that an NBFC can pay to a depositor should not exceed 12.5%. The Reserve Bank keeps altering the interest rates depending on the macro-economic environment. The Reserve Bank publishes the change in the interest rates on www.rbi.org.in → Sitemap → NBFC List → FAQs.
- The depositor must insist on a proper receipt for every amount of deposit placed with the company. The receipt should be duly signed by an officer authorized by the company and should state the date of the deposit, the name of the depositor, the amount in words and figures, rate of interest payable, maturity date and amount.
- In the case of brokers/agents etc. collecting public deposits on behalf of NBFCs, the depositors should satisfy themselves that the brokers/agents are duly authorized by the NBFC.
- The depositor must bear in mind that public deposits are unsecured and Deposit Insurance facility is not available to depositors of NBFCs.
- The Reserve Bank of India does not accept any responsibility or guarantee about the present position as to the financial soundness of the company or for the correctness of any of the statements or representations made or opinions expressed by the company and for repayment of deposits/discharge of the liabilities by the company.
- 25. We hear that in a number of cases Official Liquidators have been appointed on the defaulting NBFCs. What is the procedure adopted by the Official Liquidator?
-
An Official Liquidator is appointed by the court after giving the company reasonable opportunity of being heard in a winding up petition. The liquidator performs the duties of winding up of the company and such duties in reference thereto as the court may impose. Where the court has appointed an official liquidator or provisional liquidator, he becomes custodian of the property of the company and runs day-to-day affairs of the company. He has to draw up a statement of affairs of the company in prescribed form containing particulars of assets of the company, its debts and liabilities, names/residences/occupations of its creditors, the debts due to the company and such other information as may be prescribed. The scheme is drawn up by the liquidator and same is put up to the court for approval. The liquidator realizes the assets of the company and arranges to repay the creditors according to the scheme approved by the court. The liquidator generally inserts advertisement in the newspaper inviting claims from depositors/investors in compliance with court orders. Therefore, the investors/depositors should file the claims within due time as per such notices of the liquidator. The Reserve Bank also provides assistance to the depositors in furnishing addresses of the official liquidator.
- 26. What are the symbols of minimum investment grade rating of different companies? When a company’s rating is downgraded, does it have to bring down its level of public deposits immediately or over a period of time?
-
The symbols of minimum investment grade rating of the Credit rating agencies are:
Name of rating agencies Nomenclature of minimum investment grade credit rating (MIGR) CRISIL CRISIL FA- (FA MINUS) ICRA ICRA MA- (MA MINUS) CARE CARE CARE BBB (FD) FITCH Ratings India Pvt. Ltd. SMERA tA-(ind)(FD) SMERA A Brickwork Ratings India Pvt. Ltd. BWR FBBB It may be added that A- is not equivalent to A, AA- is not equivalent to AA and AAA- is not equivalent to AAA.
However, if rating of an NBFC is downgraded to below minimum investment grade rating, it has to stop accepting public deposits, report the position within fifteen working days to the RBI and bring within three years from the date of such downgrading of credit rating, the amount of public deposit to nil. With the introduction of revised regulatory framework in November 2014 deposit taking NBFCs have to mandatorily get investment grade credit rating for being eligible to accept public deposits.
- 27. What are Unincorporated Bodies (UIBs)? Has RBI any role to play in curbing illegal deposit acceptance activities of UIBs? Who has the power to take action against Unincorporated Bodies (UIBs) accepting deposits?
-
Unincorporated bodies (UIBs) include an individual, a firm or an unincorporated association of individuals. In terms of provision of section 45S of RBI act, these entities are prohibited from accepting any deposit. The Act makes acceptance of deposits by such UIBs punishable with imprisonment or fine or both. The State government has to play a proactive role in arresting the illegal activities of such entities to protect interests of depositors/investors.
UIBs do not come under the regulatory domain of RBI. Whenever RBI receives any complaints against UIBs, it immediately forwards the same to the state government police agencies (Economic Offences Wing (EOW)). The complainants are advised to lodge the complaints directly with the State government police authorities (EOW) so that appropriate action against the culprits is taken immediately and the process is hastened.
As per Section 45T of RBI Act, both the RBI and State Governments have been given concurrent powers. Nonetheless, in order to take immediate action against the offender, the information should immediately be passed on to the State Police or the Economic Offences Wing of the concerned State who can take prompt and appropriate action. Since the State Government machinery is widespread and the State Government is also empowered to take action under the provisions of RBI Act, 1934, any information on such entities accepting deposits may be provided immediately to the respective State Government’s Police Department/EOW.
Many of the State Governments have enacted the State Protection of Interests of Depositors in Financial Establishments Act, which empowers the State Government to take appropriate and timely action.
RBI on its part has taken various steps to curb activities of UIBs which includes spreading awareness through advertisements in leading newspapers to sensitise public, organize various investors awareness programmes in various districts of the country, keeps close liaison with the law enforcing agencies (Economic Offences Wing).