Public Private Partnerships (PPP) - Introduction
In a public-private partnership (PPP), companies and government bodies or civil society organizations work together. The partnership may be solely financial (donations and sponsorship), but may also involve a more concrete collaboration. PPP is based on two main principles:
- Both parties invest in the project. In a financial sense (manpower, materials budget) and in an expertise-related sense (knowledge, networks).
- The parties contribute to a societal and often also commercial purpose.
PPP involves a contract between a public sector and a private party, in which a government service or private business venture is funded by both the parties and executed through a partnership of public authority and private sector companies. A public- private partnership covers all types of collaborations between the public and private sectors, where public sector delivers policies, infrastructure etc. Hence, Public Private Partnership means an arrangement between a government/ statutory entity/ government owned entity on one side and a private sector entity on the other. It is often done for the provision of public assets or public services, through investments being made and/or management being undertaken by the private sector entity, for a specified period of time. There is well defined allocation of risk between the private sector and the public entity. The private entity who is chosen on the basis of open competitive bidding, receives performance linked payments that conform (or are benchmarked) to specified and pre-determined performance standards, measurable by the public entity or its representative.
- Public Ownership and operation
- Quasi public agency
- Operations assistance
- Contract operations and maintenance
- Contracts operations and financing
- Design/ Build/ Operate
- Lease and Operate
- Joint Ownership
- Private Ownership
India has systematically rolled out a PPP program for the delivery of high-priority public utilities and infrastructure and, over the last decade or so, developed what is perhaps one of the largest PPP Programs in the world. With close to 2000 PPP projects in various stages of implementation, according to the World Bank. India is one of the leading countries in terms of readiness for PPPs.
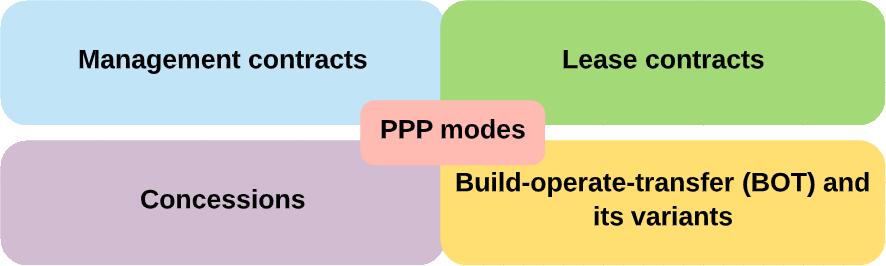
Types of PPP modesThe four major “families” of PPP modes are
PPPs have given rise to an array of acronyms for the names that describe the variations in each modal family. Different PPP modes can be compared on a spectrum ranging between low and high levels of private participation and involvement.
Brief history about public–private partnership Brief history about public–private partnership
A public–private partnership (PPP, 3P, or P3) is an arrangement between two or more public and private sectors of a long-term nature. Typically, it involves private capital financing government projects and services up-front, and then drawing profits from taxpayers and/or users over the course of the PPP contract. Public–private partnerships have been implemented in multiple countries and are primarily used for infrastructure projects. They have been used for building, equipping, operating and maintaining schools, hospitals, transport systems, and water and sewerage systems.
Cooperation between private actors, corporations and governments has existed since the inception of sovereign states, notably for the purpose of tax collection and colonization. However, contemporary "public-private partnerships" came into being around the end of the 20th century. They were associated with neoliberal policies to increase the private sector's involvement in public administration. Originally, they were seen by governments around the world as a method of financing new or refurbished public-sector assets outside their balance sheet. At the dawn of the millennium, this vision of PPPs came under heavy criticism as taxpayers or users still had to pay for those PPP projects, with high interest. PPPs initiated after 2010 are generally included in the public balance sheet.
PPPs continue to be highly controversial as funding tools, largely over concerns that public return on investment is lower than returns for the private funder. PPPs are closely related to concepts such as privatization and the contracting out of government services. The lack of a shared understanding of what a PPP is and the secrecy surrounding their financial details makes the process of evaluating whether PPPs have been successful, complex. P3 advocates highlight the sharing of risk and the development of innovation, while critics decry their higher costs and issues of accountability. Evidence of PPP performance in terms of value for money and efficiency, for example, is mixed and often unavailable.
Government of India is committed to improving the level and the quality of economic and social infrastructure services across the country. In pursuance of this goal, the Government envisages a substantive role for Public Private Partnership (PPPs) as a means for harnessing private sector investment and operational efficiencies in the provision of public assets and services. India has already witnessed considerable growth in PPPs in the last one and half decade. It has emerged as one of the leading PPP markets in the world, due to several policy and institutional initiatives taken by the central as well as many state governments. Government of India has set up Public Private Partnership Appraisal Committee to streamline appraisal and approval of projects. Transparent and competitive bidding processes have been established. To provide a broader cross-sectoral fillip to PPPs, extensive support has been extended through project development funds, viability gap funding, user charge reforms, provision of long tenor financing and refinancing as well as institutional and individual capacity building. PPPs are now seen as the preferred execution mode in many sectors such as highways, ports and airports. Increasingly, PPPs are being adopted in the urban sector and in social sectors. Over the years an elaborate eco-system for PPPs has developed, including institutions, developers, financiers, equity providers, policies and procedures. The growing PPP trends, especially in the last decade, justify the need for a broad policy framework that sets out the principles for implementing a larger number of projects across diverse sectors to complement the inclusive growth aspirations of the nation. The National PPP Policy seeks to facilitate this expansion in the use of PPP approach, where appropriate, in a consistent and effective manner, through:
- Setting out the broad principles for pursuing a project on PPP basis;
- Providing a framework for identifying, structuring, awarding and managing PPP projects;
- Delineating the cross-sectoral institutional architecture and mechanisms for facilitating and implementing PPPs.
Public–private partnerships in India
The Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) defines PPPs as-PPP means an arrangement between a government or statutory entity or government owned entity on one side and a private sector entity on the other, for the provision of public assets and/ or related services for public benefit, through investments being made by and/or management undertaken by the private sector entity for a specified time period, where there is a substantial risk sharing with the private sector and the private sector receives performance linked payments that conform (or are benchmarked) to specified, pre-determined and measurable performance standards. The level of private sector participation in infrastructure can cover a spectrum from short-term service contracts at one end all the way through to full privatization (disinvestment) at the other. Service contracts and disinvestments are generally not considered as PPPs in India. An infrastructure PPP in India is therefore more than just a short-term contract for services with the private sector but does not go so far as to include complete private sector ownership and control. A PPP is an arrangement between a public (government) entity & a private (non-government) entity by which services that have traditionally been delivered by the public entity are provided by the private entity under a set of terms and conditions that are defined at the outset.Public Private Partnership (PPP) is a contract between a public sector institution/municipality and a private party, in which the private party assumes substantial financial, technical and operational risk in the design, financing, building and operation of a project.
Traditionally, private sector participation has been limited to separate planning, design or construction contracts on a fee for service basis – based on the public agency’s specifications. Expanding the private sector role allows the public agencies to tap private sector technical, management and financial resources in new ways to achieve certain public agency objectives such as greater cost and schedule certainty, supplementing in-house staff, innovative technology applications, specialized expertise or access to private capital. The private partner can expand its business opportunities in return for assuming the new or expanded responsibilities and risks. PPPs provide benefits by allocating the responsibilities to the party – either public or private – that is best positioned to control the activity that will produce the desired result. With PPPs, this is accomplished by specifying the roles, risks and rewards contractually, so as to provide incentives for maximum performance and the flexibility necessary to achieve the desired results. The Planning Commission of India has defined the PPP in a generic term as “the PPP is a mode of implementing government programmes / schemes in partnership with the private sector. It provides an opportunity for private sector participation in financing, designing, construction, operation and maintenance of public sector programme and projects”. In addition, greenfield investment1 in the infrastructure development has also been given more encouragement in India. Greenfield investment is defined as an investment in a start-up project, usually for a major capital investment and the investment starts with a bare site in a greenfield.
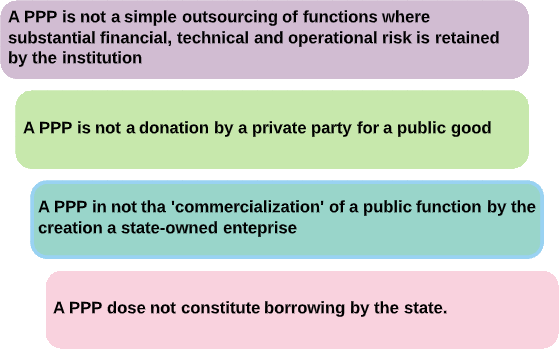
What is not a PPP?
The way a PPP is defined in the regulations makes it clear that:
PPPs can follow a variety of structures and contractual formats. However, all PPPs incorporate
three key characteristics:
- nA contractual agreement defining the roles and responsibilities of the parties,
- Sensible risk-sharing among the public and the private sector partners, and
- Financial rewards to the private party commensurate with the achievement of pre-specified Outputs.
(1).Arrangement with Private Sector Entity: The asset and/or service under an arrangement will be provided by the Private Sector Entity to the public.
(2).Public asset or service for public benefit: Has the element of facilities/ services being provided by the Government as a sovereign to its people. To better reflect this intent, two key concepts are elaborated below:
- ‘Public Services’ are those services that the State is obligated to provide to its citizens (towards meeting the socio-economic objectives) or where the State has traditionally provided the services to its citizens. For example, provision of security, law and order, electricity, water, etc. to the citizens.
- Public Asset’ is that asset the use of which is inextricably linked to the delivery of a Public Service. For example, public road which is linked to public transportation or, those assets that utilize or integrate sovereign assets to deliver Public Services, like right of way on highways or use of river / water bodies, etc.
Features of public–private partnership
PPPs in India have ensures the speedy and cost effective of key projects in sectors such as power, technology and infrastructure. This has great value for taxpayers who are benefiting from the impact of such ventures.
All risks pertaining to design, building, financing and operation transferred to the private entity Transfer of demand risk depends on the extent to which the private sector can influence usage
Public-private partnerships in India have integrated public infrastructure with the superior financing and maintenance provided by private enterprises. The synergistic collaborations between the public sector and private firms and companies have led to the generation of resources and knowledge transfer.
- Contracts specify the service outputs required rather than asset configuration/mode of service delivery Emphasis on type of service & performance standards Private entity incentivized to deliver outputs using innovation in design, construction, operation and financing
PPPs have overcome the capacity constraints of the economy by generating huge productivity through optimal utilization of labor and capital resources.
Whole life asset performance- Private entity takes responsibility & assumes risk for the performance of the asset and delivery of service over a long term
Joint ventures and partnerships between the leading companies and the government have been very successful in generating jobs as well as growth in key economic sectors.
Payment for Performance- Revenue/ Payment to private entity is subject to performance in relation to specific & quantified criteria enshrined in the contract
The public sector has regulated the projects to ensure accountability and delivery of quality products and services.
Innovation and excellence characterize the public-private partnerships that have emerged across the years in India. These PPPs are ensuring the effective utilization of state assets in a manner that is productive as well as profitable.
Infrastructure created using these partnerships is of a superior quality. This has led to the development of many good airports and buildings across India. India needs more basic infrastructure and PPPs are the best way to accomplish this.
PPPs also help the public sector to develop a more commercial approach. This is essential as most parties in India are very oriented towards social welfare and they often do not consider factors such as profit. Any partnership is only successful if it is able to meet the needs of the masses and also generate a profit.
PPPs have also ensured that the Indian public gets value for its money. India is a nation that has to meet the challenges of generating enough resources to meet the needs of the people.
India has one of the fastest growing populations in the world. Using the finances of the private firms to complete the PPP ventures has led to conservation of national and governmental resources.
Significance of Public-Private Partnership
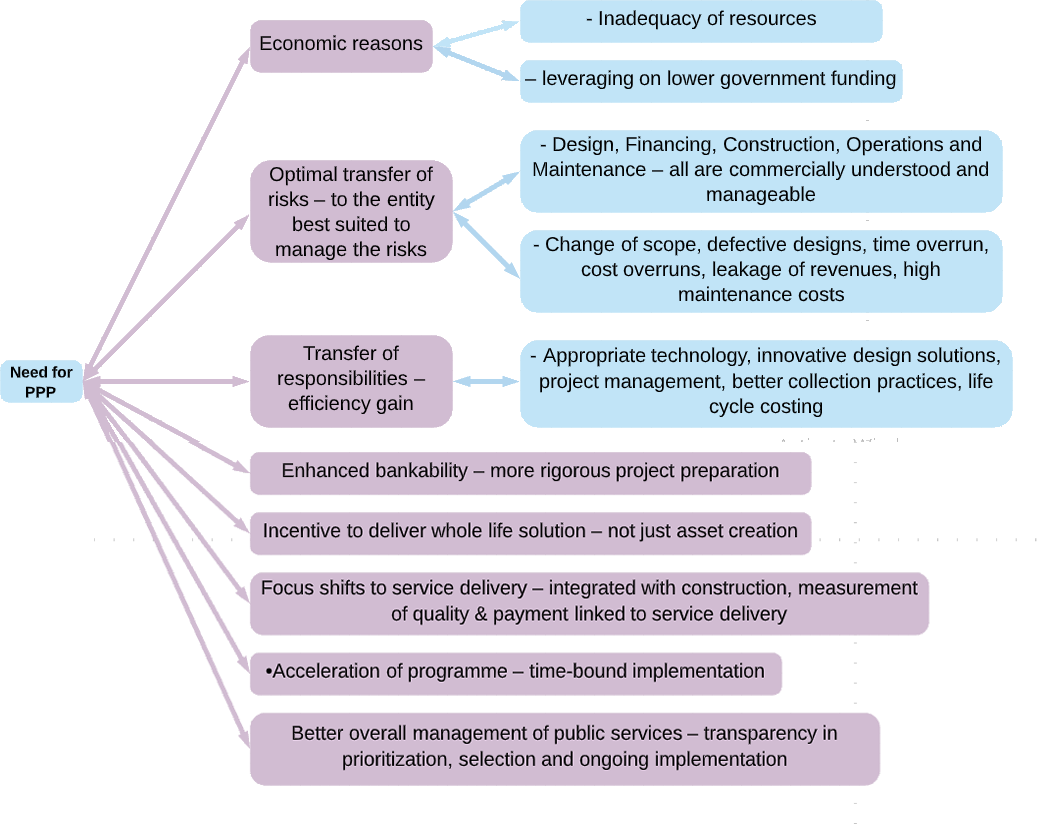
Financial and managerial resources are critically required for successful implementation and more so, the sustainability of e-Governance initiatives. While the normal preference for any reform initiative is through the exclusive use of in-house resources, the merits of inducting the private sector resources into the e-Governance sector have now been appreciated and accepted by policy-makers in Government. Public-Private Partnership has thus become one of the cornerstones of NeGP. PPP, as applied to the e-Governance sector is still in a stage of evolution. While early PPP projects like eSeva had attempted a simple version of PPP, more complex projects like MCA 21 required considerable innovation and experimentation in designing and adoption of an appropriate PPP model. The following is an attempt to examine PPP in light of the significance of the e-Governance sector. New technologies demand new types of implementation models. In the conventional approach, the project ownership lies with the public sector itself along with the responsibility for funding it and bearing the entire risk. The concept of PPP has been in operation for more than a decade, primarily in relation to the construction and operation of public infrastructure projects like bridges, airports, highways, hospitals etc. PPP is a mechanism that attempts to capture the strengths of both – a government organization as well as a private enterprise.
There are many compelling reasons why governments should look at PPP in relation to their e-Governance plans. Some reasons are enumerated below:
The PPP model can combine the accountability mechanisms and domain expertise of the public sector with the efficiency, cost-effectiveness and customer-centric approach of the private sector. As compared to the public sector, the private sector is more efficient and innovative in adopting and applying new technologies. This is also true in the specific case of Information and Communications Technology. Therefore, the PPP approach in the field of e-Governance is well suited in combining the core strengths of the public and private sectors for the delivery of efficient online services.
2.The pace of implementation:New innovations in the field of Information Communication Technology are happening at a fast rate. This applies to all its segments – hardware, software and networks. Newer versions and releases of operating systems, database servers, application servers, and security software are continuously being released at regular intervals. The typical life cycle of a large e-Governance initiative is 18 to 24 months from initiation to completion. It has been observed that the private sector is generally faster than the government in adopting and making use of the latest technology. This is a compelling reason to join hands with the private sector.
3.Resources:The combined effect of the huge size of e-Governance effort and the speed of implementation is that investments required in the e-Governance sector are very large over a continuous period of 5 years. It is estimated that India needs over 45,000 crore of investment in the e-Governance sector over a period of 3-5 years – excluding the cost of communication and access infrastructure. This is sixteen times higher than the current annual IT expenditure of about 3000 crore in the government sector. In addition to this, high quality managerial and human resources are required. It is difficult to mobilize such large amounts of financial and human resources within the government. Tapping the financial, managerial and manpower resources of the private sector is a viable alternative in this regard.
Characteristics of PPP
The private sector is responsible for carrying out or operating the project and takes on a substantial portion of the associated project risks
During the operational life of the project the public sector’s role is to monitor the performance of the private partner and enforce the terms of the contract
The private sector’s costs may be recovered in whole or in part from charges related to the use of the services provided by the project, and may be recovered through payments from the public sector
Public sector payments are based on performance standards set out in the contract
Often the private sector will contribute the majority of the project’s capital costs, although this is not always the case
It will often be necessary to build or add to existing assets in order to meet the infrastructure needs of the economy and users. However, an important part of the infrastructure PPP concept is that:
• A PPP is focused on outputs, and the outputs of the PPP are infrastructure services, not infrastructure assets.
The reason for the focus on outputs and services rather than assets is to encourage efficient use of public resources and improved infrastructure quality.
A PPP brings the public and private sectors together as partners in a contractual agreement, for a pre-defined period (e.g. 30 years) matched to the life of the infrastructure assets used to provide the services. The private partners (investors, contractors and operators) provide specified infrastructure services and, in return, the public sector either pays for those services or grants the private partner the right to generate revenue from the project. For example, the private partner may be allowed to charge user fees or receive revenue from other aspects of the project.
The best PPPs will have the public and private partners working together to build and sustain a long-term relationship that is of benefit to all.
Reasons for direct government involvement
Other than its strategic, financial and economic interest, the government may also like to directly participate in a PPP project. The main reasons for such direct involvement include:
- To address political sensitivity and fulfill social obligations
- To ensure commercial viability
- To provide greater confidence to lenders
- To have better insight to protect public interest.
Government involvement in PPPs
The government has an important stake in infrastructure development. Considering its public good in nature, strategic importance, profound effects on other sectors, and related issues in public safety and security, and utilization of natural resources, governments always take interest in infrastructure development, whether implemented by the public sector or the private sector. There are also other reasons of government's interest which include:
- The network nature of most infrastructures implies that they cannot be considered as isolated projects (road, energy transmission line, telephone line, etc.)
- Can be used as a policy tool for development
- Infrastructure is important and needed but individual projects are not always commercially viable (water supply, rural/local roads, for example)
- Bulky nature and large size of investment requirements
- Long to very long existence with perpetual liability through generations
There are legal, social, economic, political and administrative issues involving PPPs. The government has responsibility in addressing a wide range of issues in PPPs if a country has to run a successful PPP programme. Private participation in infrastructure development requires the government to continue to play a key role in planning, policy formulation and regulatory matters. Further, in order to promote private participation, the government needs to implement a series of economic, financial and legal reforms which only it can initiate. In these respects, the major responsibilities of government are in:
- Formulation of a PPP policy framework
- Creation of an enabling environment
- Establishment of an administrative mechanism
- Promotion of good governance
- Addressing the social and political concern of PPP projects
- Capacity-building of the public sector
These responsibilities are discussed in the following.
Why a policy framework?Formulation of a policy framework is an important step towards building an enabling environment for PPPs. The existence of a clear framework can remove ambiguities and uncertainties about government's intention to PPP development.
Contents: Such a framework may have two parts:
- the first part on common matters to all PPPs such as objectives, principles and general policy issues; and
- the second part on issues specific to each sector
Social objectives can be incorporated in the policy framework as well as in legal and regulatory regimes.
Defining the roles of public and private sectors
The roles of public and private sector should be clearly defined in the framework. Private sector friendly policies can be formulated and their implementation needs to be coordinated across all sectors and at all spatial levels. It is also important to include in the framework (and follow) certain core principles of good governance namely transparency, accountability and participatory approach in decision making to promote PPPs. Formulation of a policy framework is also important in view of the fact that many aspects of it can be turned into legal and regulatory instruments.
The creation of PPP-enabling environment is one of the main responsibilities of the government. Main reasons why the existing environment may not be conducive to PPPs? Deficiencies of the regulatory and legislative framework: laws and regulations will control whether, or how, PPPs can be implemented. At minimum, the legal and regulatory framework should allow the Government to enter in PPP type of contracts with the private sector. In many cases, the existing regulatory environment may also be conservative and too restrictive and may not be favorable for undertaking PPPs. In order to address these issues, governments may consider enacting new legislations or suitably amend the existing ones to address these issues;
- Prevailing unfavorable general perception and understanding of PPP and the absence of clear policies on the role of private and public sectors which should be addressed through the development of a clear policy framework and
- Imperfections in market and sector structure.
More often than not, the existing market and sector structure is not conducive to PPPs. Lack of relevant market regulation leads to monopoly and sector inefficiencies. In fact, sector inefficiencies can be major deterrents to private participation in infrastructure. For example, the existence of barriers such as public monopoly and distortion in the pricing of competing transport modes is a serious problem for the motivation of the private sector to invest in the transport sector in many countries.
It is necessary to formulate rules and clear guidelines defining the administrative process involved in project implementation, in order to overcome the administrative difficulties faced by the bureaucracy. Establishment of procedures for various tasks and administrative approval from competent authorities at different stages of project implementation process are also necessary in running a successful PPP programme. Streamlined administrative procedures reduce uncertainties at different stages of project development and approval and enhance investors' confidence in a PPP programme.
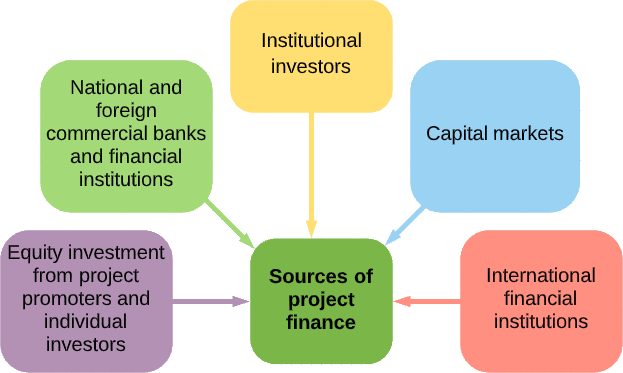
Project financing
PPPs in infrastructure are normally financed on project basis (as opposed to corporate financing). This refers to financing in which lenders look to the cash flows of an investment for repayment, without recourse to either equity sponsors or the public sector to make up any shortfall.
This arrangement has several advantages:
- tors;
- more careful project scrutiny, risk analysis leading to change in project structure, reduction in level of risk and more appropriate allocation of risks between parties
However, project financing also has manydisadvantages which include:
more complex transactions than corporate or public financing;
- higher transaction costs (the due diligence process conducted by parties results in higher development costs, which could be up to 5-10 per cent of project value);
- protracted negotiation between parties;
- Requirement of close monitoring and regulatory oversight (particularly for the potential expostulate guarantees).
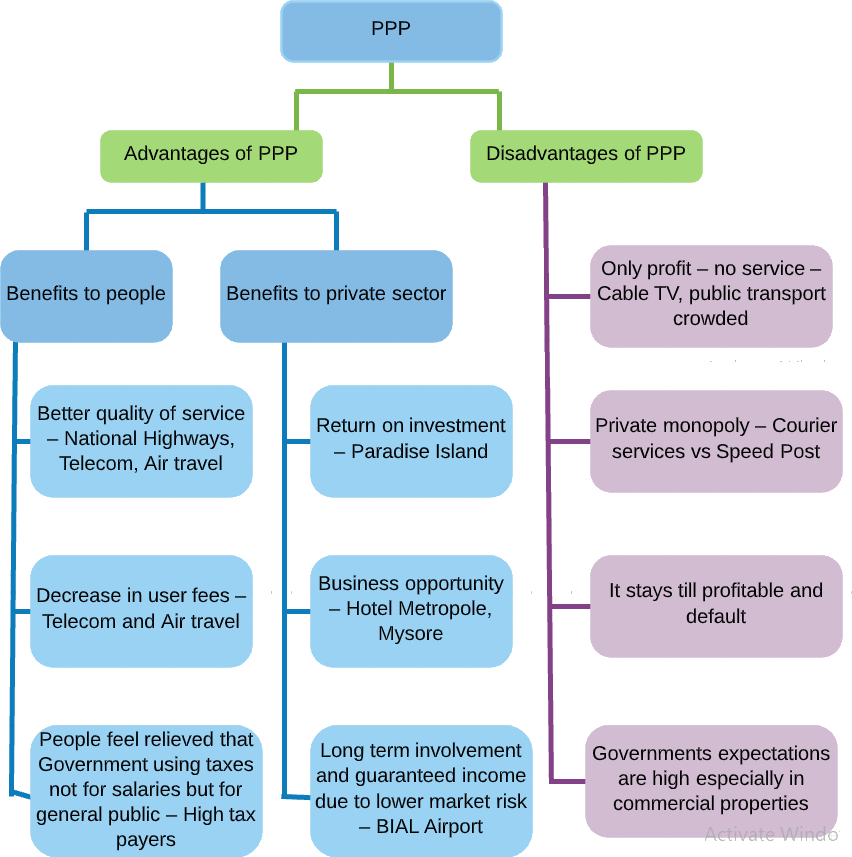
Advantages of PPP
Access to private sector finance
- India has a very large infrastructure need and an associated funding gap. PPPs can help both to meet the need and to fill the funding gap. PPP projects often involve the private sector arranging and providing finance. This frees the public sector from the need to meet financing requirements from its own revenues (taxes) or through borrowing.
Better infrastructure
- They provide better infrastructure solutions than an initiative that is wholly public or wholly private. By shifting the responsibility for finance away from the public sector PPPs can enable more investment in infrastructure and increased access to infrastructure services.
Optimum utilization of skills
- Efficiency advantages from using private sector skills and from transferring risk to the private sector
- Enlargement of focus from only creating an asset to delivery of a service, including maintenance of the infrastructure asset during its operating lifetime
- This broadened focus creates incentives to reduce the full life-cycle costs (ie, construction costs and operating costs)
Increased transparency in the use of funds
- A well-designed PPP process can bring procurement out from behind closed doors. The PPP tender and award process based on open competitive bidding following international best practice procedures lead to transparency.
Less delays
- They result in faster project completion and reduced delays on infrastructure projects by including time-to-completion as a measure of performance and therefore of profit.
Risk distribution
- Transfer of risks is the most important advantage of PPP projects. In PPP projects, there is a possibility to transfer most or all of the risks to the private entity. The private entities explore opportunities, even though they involve risks.
Constant cash flow
- The state budget is formed of fixed budgets for each ministry. Major investments are temporary modifications of the budget of a ministry, and this problem can be difficult to deal with within the budgetary process. Avoiding major investments by having a constant cash flow is an important driver when the state looks at the advantages of PPP.
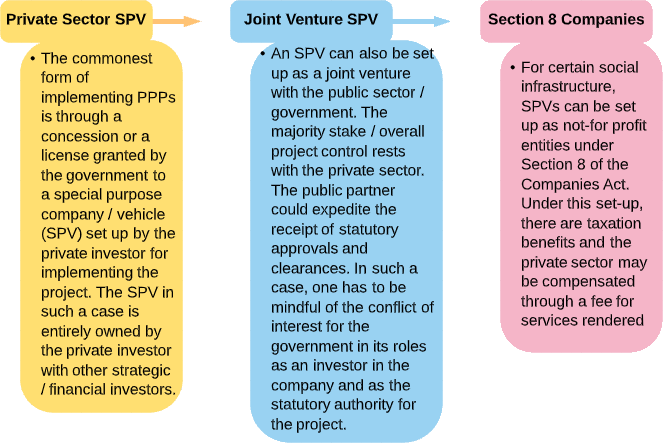
Implementation Structures
Different organizational structures may be used to implement PPP projects. These include:
PPPs often cover a long-term period of service provision (e.g. 15-30 years, or life of the asset). Any agreement covering such a long period into the future is naturally subject to uncertainty. If the requirements of the public sponsor or the conditions facing the private sector change during the lifetime of the PPP the contract may need to be modified to reflect the changes. This can entail large costs to the public sector and the benefit of competitive tendering to determine these costs is usually not available. This issue can be mitigated by selecting relatively stable projects as PPPs and by specifying in the original contract terms how future contract variations will be handled and priced.
Difficulty in Demonstrating Value for Money in AdvanceIdeally, a project should be procured as a PPP on the basis of a clear demonstration that it provides value for money (VFM) compared with public sector procurement. However, it is difficult to demonstrate VFM in advance due to uncertainties in predicting what will happen over the life of the project and due to a lack of information about comparable previous projects. However, the standard for VFM is different in India to more economically developed countries such as Australia or the UK. In those countries there is a much smaller funding need. In India, many projects procured in the public sector, experience time and cost over runs, and hence it is likely that well-managed private procurements will deliver savings. Furthermore, the funding gap is far greater than the Public Sponsor can meet by itself. In this case, it may sometimes not be a question of public vs. private procurement, but rather the choice between private procurement or none at all. If this is the case then the focus should be on making a careful assessment of alternative project options to be sure that the projects that are selected are the best ones economically and financially.
- The public sector environment is suited to supporting PPPs
- The project is suitable to being carried out as a PPP –
- The potential barriers to successful project implementation have been identified and can be overcome
Given that these conditions are satisfied, the project must be commercially viable for the private sector and offer value for money (VFM) for the public sector.
Commercial viability
Commercial viability is crucial if the project is to attract a private partner. For a project to be commercially viable does not mean it cannot receive some financial and other support from the public sector. In some cases such support may be necessary, and initiatives such as Viability Gap Funds (VGF) have been established for this purpose.
Careful and appropriate risk allocation between the public and private partners is a critical focus of PPP design to achieve value for money.If private partners do not bear the risks that are under their control, their incentives for efficiency will be weakened and PPP benefits may be reduced. The requirements for effective risk transfer and the ability to harness private sector efficiencies means PPPs are best suited to projects for which:
- It is possible to clearly specify the requirements in terms of service outputs – the idea is to capture as much of the private sector efficiencies as possible by allowing scope for bidders to introduce efficiencies through innovations proposed in their bids
- The requirements can be specified so as to enable monitoring of performance against measurable standards and enforcement of penalties where standards are not met
- The requirements of the public sector sponsor are likely to be stable throughout the life of the PPP – the aim is to avoid the need to renegotiate the contract at a later date due to changes to project scope or requirements
Pre-requisites for Implementing PPP projects
Certain pre-requisite conditions must be fulfilled in order to use PPPs or derive benefits from their use as a tool for project implementation.
Enabling authority: The public entity should unambiguously have the enabling authority (that is, legal power) to transfer (to the private party) its responsibility of providing the service in question. This authority may stem from the enabling legislative and policy framework or from an administrative order. The instrument of transfer is through a legally enforceable contract between the authorized public entity and the private party. For example, the Department of Telecom (DoT) could issue Cellular and Basic Services Licenses only after appropriate amendments to the Indian Telegraph Act, 1884. The National and State Highways legislation needed appropriate amendments to enable private parties to develop and maintain highways and levy and collect tolls / user fees.
To derive benefits from PPPs projects would need to incorporate the following features:
Financial obligations: The transfer of responsibility to the private party should be of significant proportions, usually involving large financial investment obligations on part of the private party. This would bring in efficiencies in the way projects are financed and could bring down costs for users.
Performance-based payment: Payment to the private entity for service provided whether paid maximum benefits. Thus, the tenure of the contract would be for periods always in excess of 5 years and may go to 50-60 years as well, depending on the economic life / life cycle of the underlying assets.
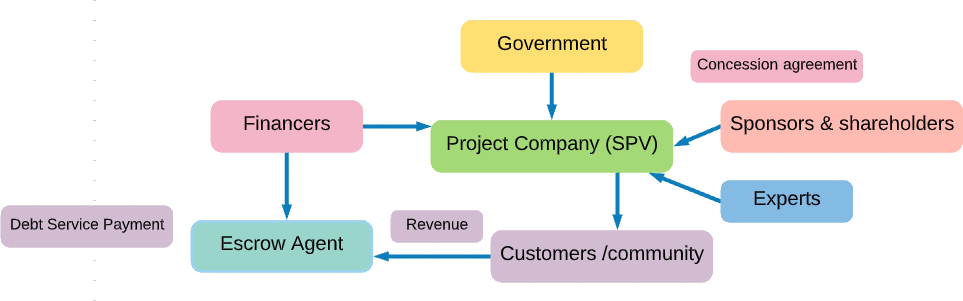
Special Purpose Vehicle
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), a new company, is set up to implement each project. Usually the sponsoring entity (majority-owing private partner) offers no additional balance sheet support except for the initial equity commitment. The majority of the project obligations are usually addressed through separate contractual arrangements for construction. O&M, supply agreements (for instance, waste supply in a MSW project or fuel supply agreement for a power generation project), off take (purchase of compost for a MSW treatment project or purchase of water / power) and financing – which would mirror the obligations passed on to the SPV under the concession agreement.
The benefit of using a SPV structure is that it is a bankruptcy-remove structure. The project and the sponsor are both insulated from each other. The main advantage for the government is that the project is protected from failure of the sponsoring entity.
Implementation of the PPP Model
The PPP model of implementation is more suitable for particular areas of e-Governance and not to all. The criteria for PPP include long-term nature of the demand for a service, profitability and amenability to structuring a commercial framework and business model for PPP. The following is an illustrative list of areas suited for PPP.
Public-Private Partnership projects also pose several challenges which need to be understood and addressed carefully. There is often a lack of congruence in the objectives of the two partners – government and the private sector. The success of PPP depends on the degree to which the public and private sector partners align their efforts in achieving these objectives. Clarity on objectives has to be achieved by both the parties at the outset.
Also, the organizational cultures in the private and public sector differ widely. This may result in conflicting situations since e-Governance involves substantial process reform needing interaction between the partner company and the government agency or agencies in charge of the ‘domain’. It is necessary to create an appropriate coordination and review mechanism that develops mutual trust and confidence. Also, the agreements defining the mutual role and responsibilities should be precisely drafted, following a transparent process of selection of the private partner.
Typical risks in Infrastructure PPP
| S.No. | Risk type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pre-operative task risks | |
| Delays in land acquisition | Refers to the risk that the project site (or sites) will be unavailable or unable to be used within the required time, or in the manner or the cost anticipated or the site will generate unanticipated liabilities due to existing encumbrances and native claims being made on the site. This risk is most relevant to greenfield projects involving treatment and storage facilities | |
| External linkages | Refers to the risk that adequate and timely connectivity to the project site is not available, which may impact the commencement of construction and overall pace of development of the project. | |
| Financing risks | Refers to the risk that sufficient finance will not be available for the project at reasonable cost (e.g., because of changes in market conditions or credit availability) resulting in delays in the financial closure for a project. | |
| Planning risks | Refers to the risk that the pre-development studies (technical, legal, financial and others) conducted are inadequate or not robust enough resulting in possible deviations from the outcomes that were planned or expected in the PPP project development. | |
| 2 | Construction phase risks | |
| Design risk | Refers to the risk that the proposed design will be unable to meet the performance and service requirements in the output specification. It can result in additional costs for modification and redesign. | |
| Construction risk | Refers to the risk that the construction of the assets required for the project will not be completed on time, on budget or to specification. It may lead to additional raw materials and labor costs, additional financing costs, increase in the cost of maintaining existing infrastructure or providing a temporary alternative solution due to a delay in the provision of the service. | |
| Approvals risk | Refers to the risk that delays in approvals to be obtained during the construction phase will result in a delay in the construction of the assets as per the construction schedule. Such delays in obtaining approvals may lead to cost overruns. | |
| 3 | Operation phase risks | |
| Operations and maintenance risk | Refers to the risks associated with the need for increased maintenance of assets or machinery over the term of the project in order to meet performance requirements. In a brownfield PPP, where the private partner takes over operation of existing assets, O&M risk is very sensitive to the starting condition of the assets. In this case the private operator's O&M risk is related to the risk of poor or incomplete information about the quality of the assets that it will take over. | |
| Volume risk | Refers to the risk that demand for water or sanitation services will vary from the initial forecast, such that the total revenue derived from the project over the project life will vary from initial expectations. | |
| Payment risk | Refers to the risk that charges for services are not collected in full or are not set at a level that allows recovery of costs. Who bears the payment risk depends on whether the charges for services are paid directly by users, or are paid by the municipality. If charges are paid by the municipality (via taxes) the public sector bears this risk. | |
| Financial risk | Refers to the risk that the concessionaire introduces too much financial stress on a project by using an inappropriate financial structure for the privately financed components of the project. It can result in additional funding costs for increased margins or unexpected refinancing costs. Currency risk can also impact on financial risk if the project includes funding denominated in foreign currency. | |
| Performance risk | This is a risk that the quality of services delivered will not meet the performance standards agreed in the Concession Agreement. The Concession Agreement should stipulate penalties or compensation terms in this case. | |
| Environmental risk | Refers to the risk of environmental damage in excess of what is planned for in the environmental impact mitigation plan. For example, ground water pollution from sewerage release. |
| S.No. | Risk type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Handover risks | |
| Handover risk / Terminal value risk | Refers to the risk that the concessionaire will default in the handover of the asset at the end of the project life, or that it will fail to meet the minimum quality standard or value of the asset that needs to be handed back to the public entity. This risk (and terminal value risk) generally relates to concession and BOT type PPPs. However, it may also be relevant to performance based management contracts in which the private partner is responsible for investing in meters. | |
| 5 | Other risks | |
| Change in law | Refers to the risk that the current legal / regulatory regime will change, having a material adverse impact on the project. | |
| Force Majeure | Refers to the risk that events beyond the control of either entity may occur, resulting in a material adverse impact on either party's ability to perform its obligations under the PPP contract. These events are sometimes also called "Acts of God", to indicate that they are beyond the control of either contracted party. | |
| Concessionaire risk | Refers to the risk that the concessionaire will prove to be inappropriate or unsuitable for delivery of the project, for example due to failure of their company. | |
| Sponsor risk | Refers to the risk that the Sponsor will prove to be an unsuitable partner for the project, for example due to poor project management or a failure to fully recognize the agreed terms of the Concession Agreement. | |
| Concessionaire event of default | Refers to the risk that the concessionaire will not fulfill its contractual obligations and that the public Sponsor will be unable to either enforce those obligations against the concessionaire, or recover some form of compensation or remedy from the concessionaire for any loss sustained by it as a result of the breach. | |
| Government event ofdefault | Refers to the risk that the public Sponsor will not fulfill its contractual obligations and that the concessionaire will be unable to either enforce those obligations against the Sponsor, or recover some form of compensation or remedy from the Sponsor for any loss sustained by it as a result of the breach. |
Problems with PPP Projects
Uncertainties: PPPs often cover a long-term period of service provision (e.g. 15-30 years). Any agreement covering such a long period into the future is naturally subject to uncertainty. If the requirements of the public sponsor or the conditions facing the private sector change during the lifetime of the PPP, the contract may need to be modified to reflect the changes. This can entail large costs to the public sector.
Policy and regulatory gaps: Inadequate regulatory framework and inefficiency in the approval process have been considered as serious disincentives for developers and contractors. Indian government has a poor record in regulating PPPs in practice. For example, more than two years were needed for the Gujarat Pipavav port project to receive the necessary clearances after achieving financial closure. Moreover, most of the large projects involve dealings with various ministries where coordination remains inefficient.
Crony capitalism: In many sectors, PPP projects have turned into conduits of crony capitalism. It is worth noting that a large chunk of politically connected firms in India are in the infrastructure sector, which has used political connections to win contracts in the past. Metro projects become sites of crony capitalism and a means for accumulating land by private companies.
Renegotiation: While private firms accept stringent terms of PPP contracts initially, they lose no opportunity for renegotiating contracts, in effect garnering a larger share of public resources than originally planned. Rather than being an exceptional clause, renegotiation has become the norm in PPP projects in India. PPP firms use every opportunity for renegotiating contracts by citing reasons like lower revenue or rise in costs which becomes a norm in India. Frequent renegotiations also resulted into drain of larger share of public resources. These firms create a moral hazard by their opportunistic behavior.
- PPP projects have been stuck in issues such as disputes in existing contracts, non-availability of capital and regulatory hurdles related to the acquisition of land.
- Across the world PPPs are facing problems, performance of PPPs has been very mixed according to study conducted by various research bodies.
- It is also argued that PPP is mere a ‘’language game” by governments who find it difficult to push privatization, or when politically it is difficult to contracting out.
- Loans for infrastructure projects are believed to comprise a large share of the non-performing asset portfolio of public sector banks in India.
- Checking Viability: PPPs should not be used to evade responsibility for service delivery to citizens. This model should be adopted only after checking its viability for a project, in terms of costs and risks. Further, PPP structures should not be adopted for very small projects, since the benefits are not commensurate with the costs.
- Risk allocation and management: Public-Private Partnership PPP contracts should ensure optimal risk allocation across all stakeholders by ensuring that it is allocated to the entity that is best suited to manage the risk. A generic risk monitoring and evaluation framework should be developed covering all aspects of a project’s life cycle.
- Strengthening governance: The Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 should be amended to distinguish between genuine errors in decision making and acts of corruption by public servants.
- Strengthening institutional capacity: A national-level institution should be set up to support institutional capacity building activities and encouraging private investments with regard to PPPs. Independent regulators must be set up in sectors that are going for PPPs. An Infrastructure PPP Adjudication Tribunal should also be constituted. A quick, efficient, and enforceable dispute resolution mechanism must be developed for PPP projects.
- Strengthening contracts: The private sector must be protected against such loss of bargaining power. This could be ensured by amending the terms of the Public-Private Partnership PPP contracts to allow for renegotiations.
The success of Public-Private Partnership to a large extent depends on optimal risk allocation among stakeholders, the environment of trust and robust institutional capacity to timely implementation of PPP projects. To foster the successful implementation of a PPP project, a robust PPP enabling ecosystem and sound regulatory framework is essential.
Types of PPP

PPP Options
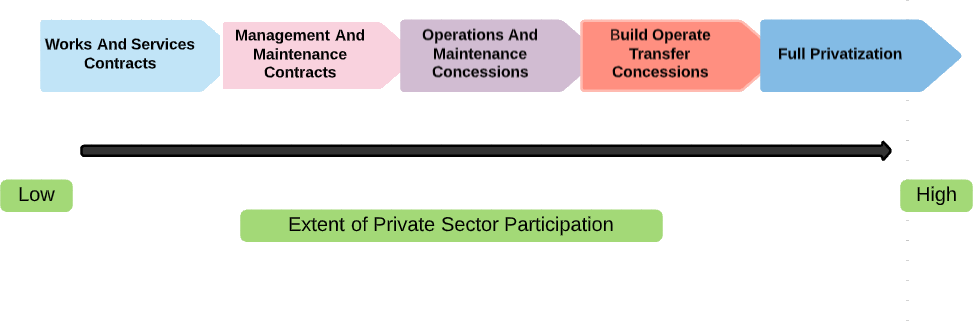
Types of Investment Models
Public Investment Model: In this model Government requires revenue for investment that mainly comes through taxes.
As the world is facing the prospect of an extended period of weak economic growth, by enhancing public-sector investment large pools of savings can be channelized into productivity.
Properly targeted public investment can do much to boost economic performance, generating aggregate demand quickly, fueling productivity growth by improving human capital, encouraging technological innovation, and spurring private-sector investment by increasing returns.
Though public investment cannot fix a large demand shortfall overnight, it can accelerate the recovery and establish more sustainable growth patterns.
Private Investment Model: For a country to grow and increase its production investment is required. Presently tax revenue of India is not adequate to meet this demand so government requires private investment.
Private investment can be source from domestic or international market.
From abroad private investment comes in the form of FDI or FPI.
Private investment can generate more efficiency by creating more competition, realization of economies of scale and greater flexibility than is available to the public sector.
Public-Private Partnership Model: PPP is an arrangement between government and private sector for the provision of public assets and/or public services. Public-private partnerships allow large-scale government projects, such as roads, bridges, or hospitals, to be completed with private funding.
In this type of partnership, investments are undertaken by the private sector entity, for a specified period of time.
These partnerships work well when private sector technology and innovation combine with public sector incentives to complete work on time and within budget.
As PPP involves full retention of responsibility by the government for providing the services, it doesn’t amount to privatization.
There is a well defined allocation of risk between the private sector and the public entity.
Private entity is chosen on the basis of open competitive bidding and receives performance linked payments.
PPP route can be alternative in developing countries where governments face various constraints on borrowing money for important projects.
It can also give required expertise in planning or executing large projects.
Models of Public Private Partnership
These models are different on level of investment, ownership control, risk sharing, technical collaboration, duration, financing etc. Commonly adopted model of PPPs include
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
- It is conventional PPP model in which private partner is responsible to design, build, operate (during the contracted period) and transfer back the facility to the public sector.
- Private sector partner has to bring the finance for the project and take the responsibility to construct and maintain it.
- Public sector will allow private sector partner to collect revenue from the users. The national highway projects contracted out by NHAI under PPP mode is a major example for the BOT model.
Build-Own-Operate (BOO)
- In this model ownership of the newly built facility will rest with the private party.
- On mutually agreed terms and conditions public sector partner agrees to ‘purchase’ the goods and services produced by the project.
- A BOO transaction may qualify for tax exempt status and is often used for water treatment or power plants.
Build – Own – Operate – Transfer (BOOT)
- In this variant of BOT, after the negotiated period of time, project is transferred to the government or to the private operator.
- BOOT model is used for the development of highways and ports.
- The private sector builds and owns the facility for the duration of the contract, with the primary goal of recouping construction costs (and more) during the operational phase. At the end of the contract the facility is handed back to the government. This structure is suitable when the government has a large infrastructure financing gap as the equity and commercial risk stays with the private sector for the length of the contract. This model is often used for school and hospital contracts.
Build-Operate-Lease-Transfer (BOLT)
- In this approach, the government gives a concession to a private entity to build a facility (and possibly design it as well), own the facility, lease the facility to the public sector and then at the end of the lease period transfer the ownership of the facility to the government.
Design-Build-Operate-Transfer (DBFOT)
- In this model, entire responsibility for the design, construction, finance, and operation of the project for the period of concession lies with the private party.
- The private sector designs, builds, finances, operates an asset, then leases it back to the government, typically over a 25 – 30 year period. Public sector long-term risk is reduced and the regular payments make it an attractive option to the private sector.
Lease-Develop-Operate (LDO)
- In this type of investment model either the government or the public sector entity retains ownership of the newly created infrastructure facility and receives payments in terms of a lease agreement with the private promoter.
- It is mostly followed in the development of airport facilities.
Design–build–operate–transfer (DBOT)
- This funding option is common when the client has no knowledge of what the project entails. Hence they contracts the project to a company to design, build, operate, and then transfer it. Examples of such projects are refinery constructions.
Design – Construct – Maintain – Finance (DCMF)
- Design, Construct, Maintain and Finance is very similar to DBFM. The private entity creates the facility based on specifications from the government body and leases it back to them. This is generally the convention for PPP prison projects.
- A private entity is entrusted to design, construct, manage, and finance a facility, based on the specifications of the government. Project cash flows result from the government's payment for the rent of the facility. Some examples of the DCMF model are prisons or public hospitals.
O & M (Operation & Maintenance)
- In an O&M contract, a private operator operates and maintains the asset for the public partner, usually to an agreed level with specified obligations. The work is often sub-contracted to specialist maintenance companies. The payment for this contract is either via a fixed fee, where a lump sum is given to the private partner, or more commonly a performance-based fee. In this situation, performance is incentivized using a pain share / gain share mechanism, which rewards the private partner for over-performance (according to the agreed SLAs) or induces a penalty payment for work which has fallen short.
Design–build–finance–maintain (DBFM)
- The private sector designs, builds and finances an asset and provides hard facility management or maintenance services under a long-term agreement." The owner (usually the public sector) operates the facility. This model is in the middle of the spectrum for private sector risk and involvement.
Design–build–finance–maintain–operate (DBFMO)
- Design–build–finance–operate is a project delivery method very similar to BOOT except that there is no actual ownership transfer. Moreover, the contractor assumes the risk of financing until the end of the contract period. The owner then assumes the responsibility for maintenance and operation. This model is extensively used in specific infrastructure projects such as toll roads. The private construction company is responsible for the design and construction of a piece of infrastructure for the government, which is the true owner. Moreover, the private entity has the responsibility to raise finance during the construction and the exploitation period. Usually, the public sector begins payments to the private sector for use of the asset post-construction.
Different Levels of Private sector engagement in PPP contracts
| Model | Identify Infrastructure Need | Propose solution | Project design | Project financing | Construction | Operation | Maintenance | Ownership | Whether Concession? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bid–build | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||||
| Design–bid–build | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||
| Design–build | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||
| Design–build–finance | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||||
| Design–build–finance–maintain | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||
| Design–build–finance–operate | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||||
| Design–build–finance–maintain–operate | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||||
| Build–finance | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | No | |||||
| Operation & maintenance contract | Private sector | Public sector | No | ||||||
| Build-operate-transfer | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | Temporary | |||||
| Build–lease–transfer | Public sector | Private sector | Public sector | Private sector | Temporary | ||||
| Build–own–operate–transfer | Public sector | Private sector | Temporary | ||||||
| Build–own–operate | Public sector | Private sector | Yes | ||||||
| Market-led proposals | Private sector | Public sector | no |
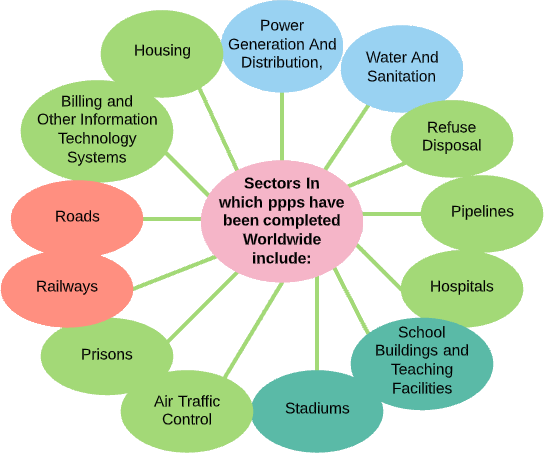
Typical modes and characteristics
| Model | Asset ownership | Duration | Capital investment focus & responsibility | Private partner risks | Private partner roles | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management Contract | Public | Short – medium (e.g. 3-5yrs) | Not the focus Public | Low (Pre-determined fee, possibly with performance incentive | Management of all aspects of operation and maintenance. | This involves contracting to the private sector most or all of the operations and maintenance of a public facility or service. Although the ultimate obligation of service provision remains with the public authority, the day-to-day management control is vested with the private sector. Usually the private sector is not required to make capital investments. These are prevalent in India across sectors. e.g., Karnataka Urban Water Supply and Improvement Project, performance based maintenance contracts in highways. |
| Management Contract | Public | Medium – long | Limited Focus Brownfield (Rehabilitation / expansion) Private | Medium (Tariff / Revenue share) | Minimum Capex, Management, Maintenance | This is similar to management contracts but include limited investments for rehabilitation or expansion of the facility. This mode has been adopted in the power distribution and water supply sectors e.g. Bhiwandi Distribution Franchise, Latur Water Supply Project. |
| Lease Contracts - Asset is leased, either by the public entity to the private partner or vice-versa. | ||||||
| Lease Contracts | Public | Medium (e.g., 10-15yrs) | Not the focus Public | High Revenue from Operations | Management and maintenance | e.g. Leasing of retail outlets at railway stations by Indian Railways |
| Build Lease Transfer (BLT) or Build-Own-Lease-Transfer (BOLT) | Private (Leased to the government) | Medium (e.g. 10-15yrs) | Greenfield Private | Low-medium Pre-set lease from the government. | Capex | Involves building a facility, leasing it to the Govt. and transferring the facility after recovery of investment. Primarily taken up for railway projects such as gauge conversion in India in the past, with limited success. |
| Build-Transfer-Lease (BTL) | Public | Medium (e.g., 10-15yrs) | Greenfield Private | High Revenue from User Charges | Capex and Operations | Involves building an asset, transferring it to the Govt, and leasing it back. Here the private sector delivers the service and collects user charges. |
| Concessions - Responsibility for construction (typically brownfield / expansions) and operations with the private partner while ownership is retained by the public sector. | ||||||
| Area Concessions | Public | Long (e.g. 20-30 yrs) | Brownfield/ Expansions Private | High Tariff revenue | Design, finance, construct, manage, maintain | Private sector is responsible for the full delivery of services in a specified area, including operation, maintenance, collection, management, and |
| Model | Asset ownership | Duration | Capital investment focus & responsibility | Private partner risks | Private partner roles | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| construction and rehabilitation of the system. Operator is now responsible for all capital investment while the assets are publicly owned even during the concession period. The public sector’s role shifts from being the service provider to regulating the price and quality of service. e.g water distribution concession for a city or area within the city. | ||||||
| Build-Operate-Transfer Contracts - Responsibility for construction (typically Greenfield) and operations with the private partner while ownership is retained by the public sector. | ||||||
| Design-build-operate (DBO) | Public | Short-medium (e.g. 3-5 yrs) | Greenfield Public | Medium-High Tariff revenue | Design, construct, manage, maintain | Not very common in India. Typically financing obligation is not retained by the public sector. |
| Build-operate-transfer (BOT)/ Design-Build-Finance-Operate-Transfer (DBFOT) | Public | Long (e.g. 20-30 yrs) | Greenfield Private | High Tariff revenue | Design, finance, construct, manage, maintain | Most common form of BOT concession in India. e.g. Nhava Sheva International Container Terminal, Amritsar Interstate Bus Terminal, Delhi Gurgaon Expressway, Hyderabad Metro, Salt Lake Water Supply and Sewage Disposal System. |
| Build-operate-transfer (BOT) Annuity | Public | Long (e.g. 20-30 yrs) | Greenfield Private | Low Annuity revenue / unitary charge | Design, finance, construct, manage, maintain | This has been adopted for NHAI highway projects in the past. More recently, it is the preferred approach for socially relevant projects where revenue potential is limited. e.g. Tuni Anakapalli Project, Alandur Underground Sewerage Project |
| Build-own-operate Transfer (BOOT) Contracts - Private partner has the responsibility for construction and operations. Ownership is with the private partner for the duration of the concession. | ||||||
| Build-own-operate-transfer (BOOT) or DBOOT | Private | Long (e.g. 20-30 yrs) | Greenfield Private | High Tariff revenue | Design, construct, own, manage, maintain, transfer | Most common form of BOOT concession in India. For example, Greenfield minor port concessions in Gujarat are on a BOOT basis. |
| BBuild-own-operate (BOO) | Private | Perpetual | Greenfield Private | High Tariff revenue | Design, finance, construct, own, manage, maintain | Under this structure the asset ownership is with the private sector and the service / facility provision responsibility is also with the private sector. Not common in India. |
Contractual Framework
A PPP project operates under a contractual framework, where the intended outcomes are explicitly set out. This contract is called the Concession Agreement. The concession agreement lays out the rights and obligations of both the private party and the public entity, and the consequences in case of non-fulfillment of any obligation.
The importance of the contract lies in the fact that it is usually the only tangible security available to both parties in case of non-performance.
The contracting parties are usually the government agency (concessioning authority) which is procuring the service, and the private party (concessionaire) that is providing the service. The other parties may include the state government, lenders, and supplies of services. It is important to remember that a concession is a license, wherein certain rights are enjoyed by the private party in return for performing certain obligations.
- All intentions need to be set out in a contract
- Concession Agreement - bundle of rights & obligations and consequences in case of non fulfillment
- Usually the only tangible security available
- Contracting parties: Government Agency – Concessioning Authority and Private Party – Concessionaire
- Other parties – state government, Lenders, Suppliers of services
- A concession is a license – rights enjoyed for obligations performed.
- Striking a balance between differing concerns & objectives of parties
- Legislative Back up
- Rights and obligations of parties
- Identification and allocation of risks
- Penalties and rewards which would ensure performance
The different modes and variants of them will be appropriate to different projects. This will depend in particular on the nature of the service or output required, which in turn depends on the sector and subsector, and the political and economic climate in which the PPP will be carried out.
New (“Greenfield”) or existing assets – Greenfield developments, which include major capital expenditure to build new infrastructure, have different requirements to the rehabilitation or management of existing assets in Brownfield developments. The scope of potential private sector roles is broader in greenfield projects. The chosen PPP mode will reflect whether the private sector will be responsible for the design, finance and construction of the project (e.g.: DBO agreement or a variation) or only some of these roles.
Ownership flexibility – There may be legal restrictions on public ownership (as is the case in India for highways or port frontages). Other practical issues need to be taken into account in deciding ownership, such as political acceptability (e.g. due to resistance to public ownership of certain facilities that are seen as providing strategic or ‘vital’ services, such as may be the case in electricity).
Restrictions on ownership rule out PPP modes that specifically contain ownership aspects, such as Build-own-operate (BOO) and its variants (e.g. BOOT). In this case other options such as lease management contracts, BOT, BTL, could be considered.
Lifetime of the asset and scale of capital costs – infrastructure assets that involve large upfront capital costs, such as roads, require long timeframes for cost recovery. Such assets may be suited to long-term contracts (e.g. BOT, BLT etc). However, long timeframes also bring greater risk of future unknowns. The public sector may be required to take on some of these risks by providing some guarantee to cost recovery in order to attract private sector project finance. For example, for a road project where future traffic volumes are uncertain the PPP might be structured with annuity payments rather than being toll-based, to reduce the revenue risk to the private operator. Alternatively, if long-tenor finance from the private sector is not available public sector financing may need to step into the gap (e.g., IIFCL). The willingness or ability of the public sector partner to meet these risks is a further factor to be considered in determining the length of contract. For example, if facilities to support long-tenor debt are not available shorter term contracts with renewal clauses may be appropriate.
The nature of the service to be provided and the supporting infrastructure assets – More broadly, the nature of the end-user service itself will tend to favor a type of contracting structure. This is related to the capital cost structure (scale and timing) and the nature of the assets (physically fixed to their location or transportable). Large capital-intensive network infrastructure assets tend to be natural monopolies and require some form of institutional price and quality regulation, either within the terms of contract or by a dedicated regulatory agency. By contrast, some services such as those that are provided on the network (e.g. municipal buses, electric energy) or solid waste collection can be subject to market competition. A different contracting structure is possible in this case, including greater opportunity for shorter contracts and periodic competitive re-bidding to maintain pressure on costs.
Cost recovery options – Whether the revenue from the PPP will be from a user-charge or a management fee or annuity paid by the public sector has important implications for the nature of the risk sharing.
Stability of demand for the services required – long-term PPP contracts are best suited to the provision of infrastructure services which are not expected to change much through time. These projects have lower risk of unforeseeable outcomes compared with projects whose services are subject to change, for example in sectors that are subject to rapid technological change.
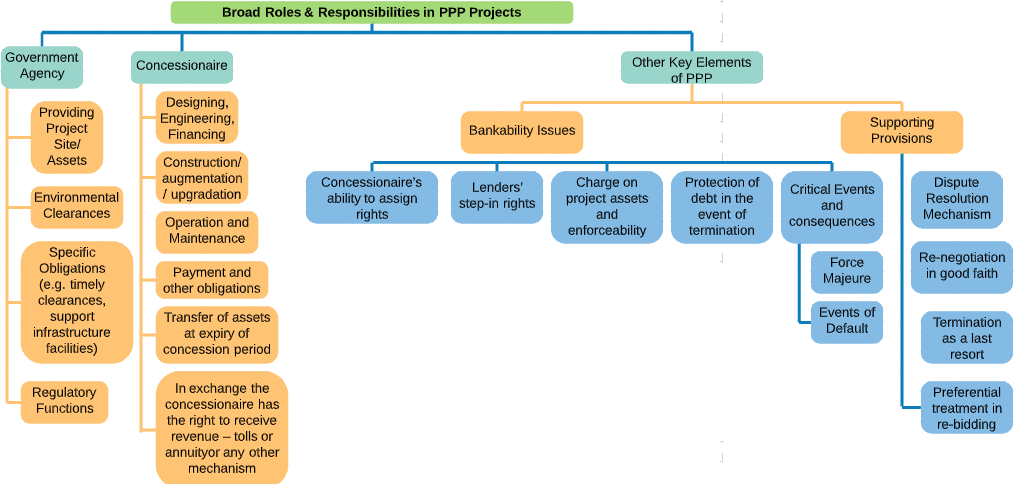
Role of Different Stakeholders in the PPP Process
| Stakeholder | Role |
|---|---|
| Political decision makers | Establish and prioritize goals and objectives of PPP and communicate these to the public Approve decision criteria for selecting preferred PPP option Approve recommended PPP option Approve regulatory and legal frameworks |
| Company management and staff | Identify company-specific needs and goals of PPP Provide company-specific data Assist in marketing and due diligence process Implement change |
| Consumers | Communicate ability and willingness to pay for service Express priorities for quality and level of service Identify existing strengths and weaknesses in service |
| Investors | Provide feedback on attractiveness of various PPP options Follow rules and procedures of competitive bidding process Perform thorough due diligence resulting in competitive and realistic bidding |
| Strategic consultants | Provide unbiased evaluation of options for PPP Review existing framework and propose reforms Act as facilitator for cooperation among stakeholders |
Why does India need a new public-private partnership policy?
Public-Private Partnership has a mixed track record of failures and successes but the government is confident about it, given its success in airports, railways and many highways, and wants a new policy that will facilitate private investment. The central government announced on June 28 that it would formulate a new public-private partnership (PPP) policy to improve the ease of doing business by cutting red tape and reduce the number of clearances.
In the 2021-22 Budget speech, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman had announced that monetizing operating public infrastructure assets is a very important financing option for new construction.
The PPP model has delivered mixed results in India on account of overextended balance sheets, contract disputes, land acquisition problems, and lack of a dispute-resolution mechanism.
However, the government is extremely confident about the PPP model because of its success in the airports, roads, and railway sectors.
change.
But what are the issues the government will need to address in its new PPP policy?
India is a federal state where land is a common subject for the central and state governments.
While most PPP projects in India are awarded by the central government or by a regulatory body under the central government, projects are implemented in the jurisdiction of state governments.
The key execution challenges during construction project developers’ face include acquisition of land and right of way, securing necessary clearances, and financial closure. The two biggest issues the government currently faces are land acquisition-related challenges because of the procedural delays involved and the compensation involved in buying the land. In many road PPP projects, the delay between the project being awarded and the actual date for construction to start ranges 9 to 15 months.
As per most PPP concession agreements in India, it is the responsibility of the government authority to hand over the required land and right of way to the concessionaire, failure of which resulted in the time and cost overrun of the projects. But there have been cases where state authorities did not act proactively to make available land or resolved land-related issues. As observed in the case of Mumbai metro rail and national highway projects, the concessionaire received delayed Right of Way to complete the construction work. Further, most PPP projects in India are still awarded after two layers of approvals from a Standing Finance Committee and the Public-Private Partnership Appraisal Committee.
Projects that are bigger than 1,000 crore also require the approval of the Union Cabinet, which delays them further. PPP projects that involve government funding in the form of viability gap funding are further delayed due to regulatory approvals.
If viability-gap funding is needed, then the projects go through an additional layer of scrutiny, as the government needs to invest in the project, these causes a delay in awarding projects.
Environment and social considerations are also important but more critical in these projects. In certain cases, these issues can become very complicated and politically challenging.
For instance, in the development of the Mumbai Metro, about 800 acres of land in Mumbai's Aarey was declared a reserve forest, and the project developer, Reliance Infra, was forced to shift their plans to construct a car shed elsewhere.
Given the long-term nature of these projects, it is difficult to identify all possible contingencies and issues that may come up during project development but were not anticipated by the parties when the contract was signed. It is also possible that some of the projects may fail or may be terminated prior to the projected term of the project, for reasons including changes in government policy, failure by the private operator or the government to perform their obligations, or due to external circumstances. A number of road operators in India have found actual traffic lower than the government’s projection. The major risk observed in the case of most of the failed road projects is lower-than-expected traffic growth and in turn, subdued toll/fee collections during the operation phase. The unrealistic traffic projections during the pre-bid stage phase of the project were the cause of this debacle. The GMR Ambala Chandigarh Expressways Pvt Ltd and L&T Halol Shamlaji Tollway Ltd are examples of such projects where actual traffic has been much lower than the government's projected traffic.
PPP projects have usually been a success in economic infrastructure projects in India, such as airports and toll roads. However, they have faced problems in social infrastructure such as water supply, solid waste management, health, and education; these projects have taken a hit. Private firms will also want to know that the rules of the game are to be respected by the government as regards undertakings to increase tariffs/fair regulation, etc. The private sector will also expect a significant level of control over operations if it is to accept significant risks. The electricity tariffs in Delhi and Mumbai are examples of such cases where private partners are subject to tariffs set by the respective state governments. In most PPP projects citizens will continue to hold the government accountable for the quality of utility services and the government will also need to retain sufficient expertise, to be able to understand the PPP arrangements, to carry out its own obligations under the PPP agreement and to monitor the performance of the private sector and enforce its obligations. Private sector will do what it is paid to do and no more than that – therefore incentives and performance requirements need to be clearly set out in the contract.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) – Recent Developments
Public-Private Partnership in India – As of November 2020, around 1100 PPP projects were launched in the country, representing a total of $274,959,000,000 of committed investments
Health Sector
- NITI (National Institution for Transforming India) Aayog has come out with Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Model to bring changes in the Health Sector. As per this PPP model developed by NITI (National Institution for Transforming India) Aayog, the gap in medical education will be addressed and the shortage of qualified doctors will be addressed. As per this model, existing or new private medical colleges will be linked with functional district hospitals.
Power Sector
- Government of India is planning to launch the Atal Distribution Transformation Yojana (ADITYA) Scheme. As per this scheme, if states will involve private sectors to improve the efficiency of state distribution companies (discoms), then the Central Government will provide incentives to the States. Such a scheme did not exist earlier. If Indian needs to become a $ 5 trillion economy then it requires a healthy power sector. The 3 important segments of the power sector are distribution, transmission and power generation. If progress needs to be done in desired pace and direction, then the distribution segment needs to be established as the strongest link hence the Central Government is focussing on increasing efficiency of the Distribution segment through ADITYA Scheme. Most of the developed countries have privatised their power distribution segment. The Public-Private Partnership model in Delhi was introduced in 2002, has proven to be a success. Delhi Vidyut Board was privatised by selling its majority stake (51%).
Railways
- Tejas Express is the 1st private train in India. Under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model, the services in the Tejas Express will be provided by private players. Services will include housekeeping, catering, ticketing, refunds, parcels. The Physical infrastructure for the Tejas Express will be Indian Railways. It includes coaches, locomotives, guards, loco pilots, guards.
Urban Housing
- Through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP), Government-funded housing in cities or urban areas will be converted into Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHC). This will be done so that migrants can avail housing at concessional rates in cities or urban areas.
Potential Benefits of Public Private Partnerships
The financial crisis of 2008 onwards brought about renewed interest in PPP in both developed and developing countries. Facing constraints on public resources and fiscal space, while recognizing the importance of investment in infrastructure to help their economies grow, governments are increasingly turning to the private sector as an alternative additional source of funding to meet the funding gap. While recent attention has been focused on fiscal risk, governments look to the private sector for other reasons:
Exploring PPPs as a way of introducing private sector technology and innovation in providing better public services through improved operational efficiency
Incentivizing the private sector to deliver projects on time and within budget
Imposing budgetary certainty by setting present and the future costs of infrastructure projects over time
Utilizing PPPs as a way of developing local private sector capabilities through joint ventures with large international firms, as well as sub-contracting opportunities for local firms in areas such as civil works, electrical works, facilities management, security services, cleaning services, maintenance services
Using PPPs as a way of gradually exposing state owned enterprises and government to increasing levels of private sector participation (especially foreign) and structuring PPPs in a way so as to ensure transfer of skills leading to national champions that can run their own operations professionally and eventually export their competencies by bidding for projects/ joint ventures
Creating personification in the economy by making the country more competitive in terms of its facilitating infrastructure base as well as giving a boost to its business and industry associated with infrastructure development (such as construction, equipment, support services)
Supplementing limited public sector capacities to meet the growing demand for infrastructure development
Extracting long-term value-for-money through appropriate risk transfer to the private sector over the life of the project – from design/ construction to operations/ maintenance
Potential Risks of Public Private Partnerships
There are a number of potential risks associated with Public Private Partnerships:
- Development, bidding and ongoing costs in PPP projects are likely to be greater than for traditional government procurement processes - the government should therefore determine whether the greater costs involved are justified. A number of the PPP and implementation units around the world have developed methods for analyzing these costs and looking at Value for Money.
- There is a cost attached to debt – While private sector can make it easier to get finance, finance will only be available where the operating cash flows of the project company are expected to provide a return on investment (i.e., the cost has to be borne either by the customers or the government through subsidies, etc.)
- Some projects may be easier to finance than others (if there is proven technology involved and/ or the extent of the private sectors obligations and liability is clearly identifiable), some projects will generate revenue in local currency only (e.g. water projects) while others (e.g. ports and airports) will provide currency in dollar or other international currency and so constraints of local finance markets may have less impact
- Some projects may be more politically or socially challenging to introduce and implement than others - particularly if there is an existing public sector workforce that fears being transferred to the private sector, if significant tariff increases are required to make the project viable, if there are significant land or resettlement issues, etc.
- There is no unlimited risk bearing – private firms (and their lenders) will be cautious about accepting major risks beyond their control, such as exchange rate risks/risk of existing assets. If they bear these risks then their price for the service will reflect this. Private firms will also want to know that the rules of the game are to be respected by government as regards undertakings to increase tariffs/fair regulation, etc. Private sector will also expect a significant level of control over operations if it is to accept significant risks
- Private sector will do what it is paid to do and no more than that – therefore incentives and performance requirements need to be clearly set out in the contract. Focus should be on performance requirements that are out-put based and relatively easy to monitor
- Government responsibility continues – citizens will continue to hold government accountable for quality of utility services. Government will also need to retain sufficient expertise, whether the implementing agency and/ or via a regulatory body, to be able to understand the PPP arrangements, to carry out its own obligations under the PPP agreement and to monitor performance of the private sector and enforce its obligations
- The private sector is likely to have more expertise and after a short time have an advantage in the data relating to the project. It is important to ensure that there are clear and detailed reporting requirements imposed on the private operator to reduce this potential imbalance
- A clear legal and regulatory framework is crucial to achieving a sustainable solution (for more, go to legislation and Regulation)
- Given the long-term nature of these projects and the complexity associated, it is difficult to identify all possible contingencies during project development and events and issues may arise that were not anticipated in the documents or by the parties at the time of the contract. It is more likely than not that the parties will need to renegotiate the contract to accommodate these contingencies. It is also possible that some of the projects may fail or may be terminated prior to the projected term of the project, for a number of reasons including changes in government policy, failure by the private operator or the government to perform their obligations or indeed due to external circumstances such as force majeure. While some of these issues will be able to be addressed in the PPP agreement, it is likely that some of them will need to be managed during the course of the project
According to World Bank, public-private partnership (PPP) is a long-term contract between a private party and a government entity, for providing a public asset or service, in which the private party bears significant risk and management responsibility, and remuneration is linked to performance. Public-private partnerships typically are long-term and involve large corporations on the private side. Some of the commonly adopted forms of PPPs include build-operate-transfer (BOT), build-lease-transfer (BLT), design-build-operate-transfer (DBFO), operate-maintain-transfer (OMT), etc. A key element of these contracts is that the private party takes on a significant portion of the risk.
The various Government incentives for PPPs
Viability Gap Funding (VGF) subsidy
- Viability Gap Funding of upto 40% of the cost of the project can be accessed in the form of a capital grant.
- The scheme aims at supporting infrastructure projects that are economically justified but fall marginally short of financial viability.
- Support under this scheme is available only for infrastructure projects where private sector sponsors are selected through a process of competitive bidding.
- The total Viability Gap Funding under this scheme will not exceed twenty percent of the Total Project Cost; provided that the Government or statutory entity that owns the project may, if it so decides, provide additional grants out of its budget, upto a limit of a further twenty percent of the Total Project Cost.
- VGF under this Scheme is normally in the form of a capital grant at the stage of project construction.
India Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF)
- Scheme supports the Central and the State Governments and local bodies through financial support for project development activities, feasibility reports, project structuring etc) for PPP projects
- The IIPDF would assist ordinarily up to 75% of the project development expenses.
- The IIPDF will be available to the Sponsoring Authorities for PPP projects for the purpose of meeting the project development costs which may include the expenses incurred by the Sponsoring Authority for achieving Technical Close of such projects.
- On successful completion of the bidding process, the project development expenditure would be recovered from the successful bidder.
- The procurement costs of PPPs, particularly costs of engaging transaction advisory services, are significant and often burden the budget of the Sponsoring Authority.
- Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) has identified the IIPDF as a mechanism through which Sponsoring Authority can source funding to cover a portion of the PPP transaction costs, thereby reducing the impact of costs related to such procurement on their budgets.
- From the Government of India's perspective, the IIPDF must increase the quality and quantity of bankable projects that are processed through the Central or States' project pipeline.
(IIFCL) India Infrastructure Finance Company
- long-term debt for financing infrastructure projects that typically involve long gestation periods since debt finance for such projects should be of a sufficient.
- There is urgent need for providing long-term debt for financing infrastructure projects that typically involve long gestation periods.
- Debt finance for such projects should be of a sufficient tenure which enables cost recovery across the project life, as the Indian capital markets were found deficient in long-term debt instruments;
- IIFC was set-up to bridge this gap.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- upto 100% FDI in equity of SPVs in the PPP sector is allowed on the automatic route for most sectors.
- PPP projects are permitted have 74% to 100% of its equity in the form of FDI – depending on the specific sectors.
Fiscal benefits
- PPP projects for sectors that are classified as infrastructure under theIncome Tax Act, 1961, can avail a tax holiday of 100% for 10 years in a block of 20 years.
Duty free imports
- High capacity and modern construction equipment may be imported duty for use in a PPP project.
Long concession periods
- PPP projects usually have concession periods of a longer duration. The period can be up to 30 years.
Eligibility criteria for getting support under the VGF scheme
In order to be eligible for funding under VGF Scheme, a PPP project should meet the following criteria: The project should be implemented (i.e. developed, financed, constructed, maintained and operated) for the Project Term by a Private Sector Company to be selected by the Government or a statutory entity through a process of open competitive bidding; provided that in case of railway projects that are not amenable to operation by a Private Sector Company, the Empowered Committee may relax this eligibility criterion. The PPP Project should be from one of the following sectors-
- Roads and bridges, railways, seaports, airports, inland waterways;
- Power;
- Urban transport, water supply, sewerage, solid waste management and other physical infrastructure in urban areas;
- Infrastructure projects in Special Economic Zones and internal infrastructure in National Investment and Manufacturing Zones;
- International convention centres and other tourism infrastructure projects;
- Capital investment in the creation of modern storage capacity including cold chains and post-harvest storage;
- Education, health and skill development, without annuity provision;*
- Oil/Gas/Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) storage facility (includes city gas distribution network);
- Oil and Gas pipelines (includes city gas distribution network);
- Irrigation (dams, channels, embankments, etc.);
- Telecommunication (Fixed Network) (includes optic fibre/wire/cable networks which provide broadband/internet);
- Telecommunication towers;
- Terminal markets;
- Common infrastructure in agriculture markets; and
- Soil testing laboratories.
(As per the Notification No. 3C/1/2012-PPP dated November 4, 2013 issued by Department of Economic Affairs, as regards medical college, VGF would be admissible only if the proposed medical college is located in one of the backward districts identified under various schemes of GoI, provided there is no medical college in that district as on the date of in-principle approval of VGF by the competent authority.)
- The project should provide a service against payment of a pre-determined tariff or user charge.
- The Government/statutory entity concerned should certify, with reasons:
- That the tariff/user charge cannot be increased to eliminate or reduce the viability gap of the PPP;
- That the Project Term cannot be increased for reducing the viability gap; and
- That the capital costs are reasonable and based on the standards and specifications normally applicable to such projects and that the capital costs cannot be further restricted for reducing the viability gap.
Recommendations of Kelkar Committee
The PPP Cell which was set up in 2006 in the DEA, acts as the Secretariat for Public Private Partnership Appraisal Committee (PPPAC), Empowered Committee (EC), and Empowered Institution (EI) for the projects proposed for financial support through Viability Gap Fund (VGF). The PPP Cell is responsible for policy level matters concerning PPPs, including Policies, Schemes, programmes, Model Concession Agreements and Capacity Building. The PPP Cell is also responsible for matters and proposals relating to clearance by PPPAC, Scheme for Financial Support to PPPs in Infrastructure (VGF Scheme) and India Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF). Finance Minister in the Union Budget 2015-16 announced that the PPP mode of infrastructure development has to be revisited and revitalized. In pursuance of this announcement, a Committee on Revisiting & Revitalizing the PPP model of Infrastructure Development was set-up which was chaired by Dr. Vijay Kelkar.
Key recommendations of the committee:- Periodic reviews - Such reviews should ideally therefore be done frequently, perhaps once every three years.
- Change in attitude and in the mind-set - The Committee urges all parties concerned to foster trust between private and public sector partners when they implement PPPs.
- The Government may take early action to amend the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 which does not distinguish between genuine errors in decision-making and acts of corruption.
- Structured capacity building programmes for different stakeholders including implementing agencies and customized programmes for banks and financial institutions and private sector need to be evolved. The need for a national level institution to support institutional capacity building activities must be explored.
- Optimal allocation of risks across PPP stakeholders - Project specific risks are rarely addressed by project implementation authorities in this “One-size-fits-all” approach.
- A rational allocation of risks can only be undertaken in sector and project-specific contexts. Committee also emphasizes that a generic risk monitoring and evaluation framework should be developed encompassing all aspects across project development and implementation lifecycle.
- The Committee recognizes the need for a quick, equitable, efficient and enforceable dispute resolution mechanism for PPP projects.
- The authorities may be advised against adopting PPP structures for very small projects, since the benefits of delivering small PPP projects may not be commensurate with the resulting costs and the complexity of managing such partnerships over a long period.
- Unsolicited Proposals (“Swiss Challenge”) may be actively discouraged as they bring information asymmetries into the procurement process and result in lack of transparency and fair and equal treatment of potential bidders in the procurement process.
- The Committee is of the view that since State Owned Entities (SoEs)/PSUs are essentially government entities and work within the government framework, they should not be allowed to bid for PPP projects.
- PPP should not be used as the first delivery mechanism without checking its suitability for a particular project.
- Monetization of viable projects that have stable revenue flows after EPC delivery may be considered.
- Equity in completed, successful infrastructure projects may be divested by offering to long-term investors, including overseas institutional investors as domestic and foreign institutional investors with long-term liabilities are best suited for providing such long-term financing, but have a limited appetite for risk.
- Improving a PPP project’s risk profile so that it is more suitable for overseas and domestic long-term investors can be accomplished through partial recourse to credible third-party institutions. This could be implemented through a partial credit guarantee or cash flow support mechanisms.
- It is necessary to explore options for sourcing long term capital at low cost. Towards this, the Committee recommends, encouraging the banks and financial institution to issue Deep Discount Bonds or Zero Coupon Bonds (ZCB). These will not only lower debt servicing costs in an initial phase of project but also enable the authorities to charge lower user charges in initial years.
Main steps of a national PPP program
The launch of a national PPP program is a major policy initiative, whether it is for a single stand-alone project or a pipeline of potential PPP projects. Three key steps are identified:
Establish a PPP taskforce
Develop and articulate a PPP policy framework
Identify initial projects
PPPs represent a policy at the heart of government, requiring the need for a Taskforce. Module 3 →PPP Policy Framework → Institutional Framework and Reform → PPP Units and the Role of the Highways Agency describes the role and establishment of PPP units. For an administration to embark successfully on a program of highway PPPs, this program must be regarded as a very significant policy initiative requiring the clear support of politicians and the most senior officials at the heart of government. This implies the serious involvement of the Prime Minister’s Office, the Finance Ministry and the Ministry responsible for Transport and/or Public Works and Local Government matters and any other Ministry which may be considering PPP projects. To identify and co-ordinate the steps required to articulate the new policy and to put that policy into effect, it is necessary to create an expert Taskforce. Such taskforces are normally attached to the Finance Ministry, report to ministerial level and have high level access throughout the Administration. To exercise the credibility and expertise required, the Taskforce needs to include experts across a range of disciplines (finance, law, civil engineering, planning and public policy) and for such experts to represent a mixture of Public and Private Sector experience. Critically, members of the Taskforce must be committed intellectually to the policy and have the presence and maturity to convince others. Support from an IFI can be invaluable at this stage to help guide the process and avoid mistakes made in other countries. The work of the Taskforce will fall broadly into two activities, a division that is sometimes reflected in the organization of the Taskforce itself: Development and articulation of PPP policy such that it is consistent with other policies within the Administration’s overall policy framework. The policy will include descriptions of the legal, regulatory, risk, financial, PPP process and other component parts of an enabling environment. A PPP policy may need to be targeted at different audiences e.g. the general public, investors and as an internal government document and this should be kept in mind- Helping to identify suitable initial (pilot) projects for subsequent project preparation, developing guidelines for partnerships including project cycle, draft model contracts and procurement methodology as well as the dissemination of PPP expertise.
The development and articulation of a PPP policy framework should be consistent with other policies within the Administration’s policy framework. The Toolkit provides detailed guidance on legal and regulatory framework assessment (Module 4 → Legislation → Framework Assessment) and on establishment of a PPP policy framework (Module 3 → PPP Policy Framework). The policy framework will provide statements describing the government’s approach and commitment under a number of headings. The policy document need not be lengthy and government may not have already worked out in detail all solutions. It must however, cover and explain clearly all the key points of their PPP program and provide/instill sufficient confidence in investors that they will continue to develop their initial interest further. The introduction of a PPP program may invoke examination of an array of policy considerations ranging from the constitutional to the legal, economic and social. One such key question, which in ways is also a political issue, is whether constitutionally an Administration can enter a long-term agreement which can survive its term in office. It will be of paramount importance to any prospective partner that the obligations of the Public Sector under the contract will be respected by subsequent governments and that the Courts will uphold the contractual rights reserved to Private Sector Partner throughout the life of the contract.
Other constitutional questions that are likely to be raised will focus on the powers of an Administration to delegate the responsibility to carry out certain public service functions and/or the powers to allow formal or economic ownership of infrastructure and public service to pass into private hands. The introduction of a PPP may require the clarification if not change in the constitutional and legal position. To clear the pathway for PPPs, other specific changes in the Law may be desirable or indeed imperative. Such changes may involve the introduction of a general concession law, amendments to procurement and tax laws. In relation to the first, experience has proven that it is better for a new law to express principles and introduce a general framework. At the early stages of a PPP initiative, it is normally counterproductive to attempt to enshrine in law a model contract. PPP’s may also require certain structural reforms in government which will require legislation. This can be the case where a public service is to be conducted by a Private Sector company where previously the service has been provided by a self-regulating State Body. It will then be necessary to create or appoint a Public Sector Agency to be responsible for policing the contract and protecting the consumer, public health, and environmental interests.
Beyond the need for formal legal clarification, the new PPP policy must be articulated in such a way that it is consistent with other economic and social objectives. Such objectives may include for instance regional development, the protection of employment and conditions of employment and the encouragement of small and medium-sized enterprises. A program of PPP’s is most likely to involve the following two consequences:
- the redeployment of public sector workers into the private sector and
- a significant if not leading role for foreign operating and financing companies in the delivery of public services.
The Prime Minister’s office and other Ministries must be prepared to cope with the political fall-out from these changes both within the body of the public employees and the wider electorate. Moreover, the PPP policy framework may recommend the establishment of a PPP unit (Module 3 → PPP Policy Framework → Institutional Framework and Reform →PPP Units and the Role of the Highways Agency). Specialized PPP Units are generally created in response to weaknesses in the existing government’s ability to manage a PPP program effectively. Governments in different countries will suffer from different institutional failures in PPP procurement. PPP Units therefore need different designs in different countries, so they can address the specific government weaknesses concerned. In other words, the medicine must fit the disease. A question that must be addressed under the financial framework is whether the PPP projects that are to be promoted will depend entirely on the users for the payment stream or whether the Administration or one of its dependent agencies will be partly or totally responsible for the payments. Payments to concessionaires can only come from users, from government or from a combination of these two sources. Policy will therefore normally reflect a desire by government to either have self-sustaining projects and/or minimize government contributions.
From these considerations flow two crucial issues:
- If projects are not financially sustainable or they concern services which conventionally have not been paid or fully paid for by the user, is the Administration prepared to introduce legislation to permit government support?
- If so, is their commitment to enforce the collection of such user charges and, where some categories of citizen are to be exempt from charges, is the Administration prepared to introduce for instance a voucher or viability gap scheme, with the cost of the resulting subsidies being paid for by the Administration?
If it is determined that projects will be promoted which will be partly or fully funded by the Public Sector, the implications for Public Finance budgeting and accounting must be fully weighed and a methodology developed by which annual amounts are allocated from the national budget to the relevant Ministries. From the Finance Ministry’s perspective, a decision must be taken on how to handle future PPP financial obligations and also how they should be reflected in the National Accounts, either on or off budget (Module 2 → Public Accounting).
As important as the Taskforce’s role in establishing a PPP policy within the overall constitutional and political context is the selection and delivery of the initial projects. There are examples of PPP policy being called into question not because it was flawed as a policy but in practice because inappropriate projects were chosen for PPP procurement. Module 5 shows a development path for the development of PPP programs including the identification, prioritization and selection of PPP projects. However, experience has demonstrated certain rules of thumb for initially selecting a few appropriate PPP projects. These are particularly important for the initial PPP projects where public and political sensitivity may be greatest and where a failure, or at least a perceived failure, may compromise the continuation of the program. The following are some of the more significant criteria:
- The project must be one for which there is plainly a social and economic need and the delivery of which is recognized as important to most political opinions. However, it is best to avoid grandiose politically sponsored schemes as they rarely meet other criteria.
- The project(s) should have only moderate risks, be reasonably well-developed (e.g. have an economic or preliminary study) and be ready in the sense of not having too many constraints to be overcome such as obvious and severe socio-environmental issues.
- The project should be one that involves known and tested technologies and for which there is a market place of potential suppliers with whom to enter partnership (i.e. not too complex and risky and technologically wise).
- The project should be one that is on the main priority list (e.g. the 5 year development program) of the sponsoring Ministry or Agency (there has been a tendency for skeptical Ministries to offer up their lower priority schemes for PPP procurement).
- Financially, the best projects are those that need little or no government financial support. However if support is needed, the project payment stream must be clearly affordable by the sponsoring Ministry or Agency (and/or supported by Ministry of Finance issued guarantees);
- The project should be of a sufficient size to interest international financiers and concession companies.
Ideally, the initial pilot schemes should represent a range across the key public service sectors and be representative of likely future schemes. From the Public Sector’s point of view, it is very important from the outset to be aiming to develop methods and methodologies, which will be replicable.
Once one or more pilot project(s) is/are selected, the Central Taskforce should be closely involved in the process by which a Private Sector Partner is chosen. However, the lead responsibility for the Partner selection process should always be with the projects sponsoring Ministry or Agency.
The selection/procurement process should demonstrate certain characteristics if it is to be effective. It must be fair and transparent, it must conform to best international practice in competitive public procurement and it must arrive at a result whereby the Public Sector opts for the partner offering the best long-term value by way of quality, security of provision and cost. However, as well as the process being one that leads to the selection of the best value bid, it must deliver a result which is demonstrably good value to the public sector.
Developing an effective method and methodology for procurement and applying such during the procurement projects must go hand in hand with a well focused program whereby both Public Sector officials and the national construction and service supply companies are led to understand and appreciate the detail and merits of the process. Effective implies to transparent and competitive procurement thus encouraging many and strong companies to prequalify and bid so that the government gets a good deal from a reliable partner.
The PPP Taskforce should provide guidance and expertise for the PPP program through the establishment of PPP policy framework and initial project preparation and tendering.
In doing so, they become not a pure center of expertise but that they take a very active role in teaching and promoting the PPP message and become adept at countering the intellectual and emotional objections that the initiative inevitably engenders. The Task Force, as mentioned above, can pave the way for a PPP unit (or units) within different government agencies e.g. Public Works/Highway Agency and Finance.
Steps in PPP Project Development Process
Project Identification- institutional due diligence and planning
Technical Feasibility Evaluation & financing plan
Financial Viability Analysis
Evaluation of Project Structuring Options
Resolution of Project Implementation Issues
Bid Documentation- Terms of Reference, Draft Contract & Bidding Requirements
Bidding Process- Bid Evaluation, Negotiation and Contract Signing
Project Approval & procurement
Final approval by Government /Competent Authority of contract agreement and issuance of lisence or permits
Contract management & Project operation
Public- Private Partnerships in Municipal Services
Today our urban local bodies /state authorities are finding that their existing water, sanitation, energy and other urban infrastructures are unable to service their rapidly expanding urban population. In addition, governments realize that their limited financial resources are not sufficient to cover the needed expansion of these services. Even where government does find the resources to subsidize public utilities, service is often poor and sectors of the population largely not served. It is becoming increasingly clear that government cannot meet the continually growing demand for water, waste, waste, energy and other urban services acting alone. Local governments are finding that their tax revenues are not providing sufficient resources to meet these needs, and official development assistance has not been able to fill the gap. It is in this backdrop that we are forced to think of alternate sources of finance, technical excellence and support one of the most viable options is to involve the private sector in the state monopolies.
This is done through associations with private sector on a project-to project basis and generally termed as PSP-private sector participation, PPP-Public private partnerships, PFI-Private finance initiatives etc. these usages though done interchangeably have slight differences in their specific definitions and operational frameworks but for the genera understanding itconveys the meaning of involvement of private sector in public services.
The term “private partnership” (PPP) describes a spectrum of possible relationships between public and private actors for the cooperative provision of infrastructure services. The only essential ingredient is some degree of private participation in the delivery of traditionally public – domain services. Private actors may include private businesses, as well as non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and community- based organization (CBOs).
Through PPPs, the advantages of the private sector- innovation, access to finance, knowledge of technologies, managerial efficiency, and entrepreneurial spirit- are combined with the social responsibility, environmental awareness, and local knowledge of the public sector in an effort to solve problems. In cities throughout the world, private firms have demonstrated their ability to improve the operation of infrastructure services. However, it is important to bear in mind that private involvement does not provide an automatic solution to urban infrastructure problems.
The need for private sector involvement in urban infrastructure development is indisputable in the above context and it has been proven beyond doubt that depending on the option of private participation used it could deliver the required benefits in urban infrastructure projects.
Private sector participation could help to bring technical and managerial expertise, improve operating efficiency, large scale injection of capital, greater efficiency in using the capital, rationalization/ cost base tariffs for services, better responsiveness to consumer needs and satisfaction.
Though we are clear that private sector participation is necessary and it could bring definite advantages into the system, it would be worthwhile to look into those critical factors which do or undo the partnership or the successful running of it.
The key factors that could be highlighted are clear, government commitment, legal and regulatory capacity, stakeholder involvement, intelligent transaction design, cost-recovery tariffs, the right option and a systematic approach.
It is not enough that the support of private sector be sought for the development but it should be well thought out and should be ventured into with adequate preparation and homework. There is a definite process to be followed for Private sector participation in infrastructure development this involves many systematic steps, but to put in general it is four phases. They are project preparation, selecting an appropriate PPP option, soliciting private sector participation, establishing a durable partnership.
In general these steps would include detailed steps as given.
Step 1 : Project Preparation
- The process from conceiving the idea to identifying the potentiality of the project and finding out the financial and economical feasibility of the same would come under this phase. They are conceiving the idea or problem definition, demand assessment, financial feasibility, economic feasibility and project feasibility (Generally a project feasibility report)
Step 2 : Selecting an appropriate PPP option
- This phase would depend on the project/problem in hand which is to be addressed ie, importance of the project, economics of the project, social and environmental back-drop, political and public interest, private sectors interest in terns of investment attractiveness.
- The steps involved would be structuring the project for private participation, setting the necessary changes/framework for the project, defining the terms of bidding (Bid design) and preparation of documents.
Step 3 : Soliciting private sector participation
- This involves the process of inviting private sector to participate in the project/venture and the subsequent steps of identifying the most appropriate partner in terms of technical and financial parameters. The steps would include pre-qualification, bid process, evaluation and negotiations.
Step 4 : Establishing a durable partnership
- The post bid scenario where the relationship of 10-20 years is maintained in good manner keeping in lines with the spirit of the contract- award of the contact, up keeping of the contractual obligations and considerate views on unforeseen events (Mutually)
Conclusion
The concept of PPP is new and emerging requiring different skills and Governance. This chapter has discussed the basic aspects of PPP in the Indian context. The definition, advantages and disadvantages, features, need, roles and responsibilities, risk sharing, characteristics, types of PPP, General steps in PPP and a list of PPP projects initiated in Karnataka State have been described. Broadly speaking, a typical PPP allows a private consortium to assume the financing risk and two or more phases of the project’s life-cycle. This may include the design and construction phases of the project and the subsequent maintenance and operation of the government facility under a carefully contrived long-term lease. This is in contrast to the private sector’s traditional role in infrastructure development where its involvement is limited to providing skilled labor under short-term contracts, with the delivery of the services being solely provided by the public authority. It is also important not to confuse PPPs with privatization- a situation where responsibility over the delivery of the public service is fully transferred to the private partner with little or no government oversight. Public Private Partnerships combine two or more of the project’s phases in a single bundle for the private consortium to deliver over the long-ter. This created economics of scale by motivating the private sector to organize its activities in a way that drives efficiencies and maximizes returns on investments.
Public private partnerships are designed so that risk is transferred between the public and private sectors, allocating particular project risk to the partner best able to manage that risk cost effectively. With financing risk routinely transferred to the private consortium, any delays in meeting the agreed upon timelines can lead to additional costs for the private partner as it alone carries the debt for a longer period of time. Therefore, the private sector has a direct financial interest in ensuring that projects and services are delivered on-time, if not sooner. By bringing the strengths from both the public and private sectors together, PPPs have the unique ability to share a diverse range of resources, technologies, ideas and skills in a cooperative manner that can work to improve how urban infrastructure assets and services are delivered to the people.
Public private partnerships represent good opportunities to lower overall project costs.
However, when compared with traditional procurement, the complete PPP process invites additional costs that, if not managed properly, can erode some of the potential economic benefits of this model. A key concern with the long-term committal nature of PPP procurement is that it limits the public sector’s ability to make changes to the contract if unexpected economic or situational challenges arise. In the event that a change is required to either the use of an infrastructure asset, or to the type of urban service offered, PPPs have proven to be inflexible both in terms of the time and administrative burden associated with altering the contract.
The Government of India (GoI), in FY 2019-20, undertook a first-of-its-kind and a whole-of-government exercise to lay the infrastructure vision for the country. Pursuant to which, the National Infrastructure Pipeline (‘NIP’), detailing the infrastructure vision for the country, was released in December 2019. NIP envisages investment of 111 lakh crores over five-year period (2020-25). With annual average investment of 22 lakh crore this is a significant step-up of 2.5 times vis-à-vis historical levels. Public Private Partnerships (PPP) in infrastructure represent a valuable instrument to speed up infrastructure development in India and bridge the gap envisaged under NIP. Currently, there are 7600 projects under NIP.
The success of the project would depend finally on getting the different stakeholder rallying for it which requires a high level of awareness and a genuine effort for a consensus. The emphasis on this point is because the relationship is for 20 year where in it is possible that governments change, ideologies change and market dynamics may change but the long-term policies should remain and the commitment given to private sector and public should be honored.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1.What is PPP?
-
Public Private Partnership (PPP) means an arrangement between a Government / statutory entity / Government owned entity on one side and a private sector entity on the other, for the provision of public assets and/or public services, through investments being made and/or management being undertaken by the private sector entity, for a specified period of time, where there is well defined allocation of risk between the private sector and the public entity and the private entity who is chosen on the basis of open competitive bidding, receives performance linked payments that conform (or are benchmarked) to specified and pre-determined performance standards, measurable by the public entity or its representative.
- 2.What are the main principles of PPP?
-
Both parties invest in the project. In a financial sense (manpower, materials budget) and in an expertise-related sense (knowledge, networks). The parties contribute to a societal and often also commercial purpose.
- 3.How does the PPP model work in India?
-
The public-private partnership (PPP or 3P) is a commercial legal relationship defined by the Government of India in 2011. The Government of India recognizes several types of PPPs, including User-fee based BOT model, Performance-based management/maintenance contracts, and modified design-build (turnkey) contracts. Today, there are hundreds of PPP projects in various stages of implementation throughout the country. The government of India is actively promoting PPPs in many sectors of the economy.
- 4. What are the different types of PPP?
-
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can take a wide range of forms varying in the degree of purpose, involvement of the private entity, legal structure and risk sharing. A PPP is generally memorialized in a contract or agreement to outline the responsibilities of each party and clearly allocate risk. The broad contractual forms, as covered by extant policy include:
- DBFOT/BOT: The most common form of PPP used where the private sector operator designs, builds, finances, owns and constructs the facility and operates it commercially for the concession period, after which the facility is transferred to the authority. In this case legal ownership of the asset vests with the public sector the concession period ends. The most common form of a BOT project is a Toll Road project.
- Operations & Maintenance (Service contract): the Government bids out the right to deliver a specific service or gives part of the undertaking to the private sector for operations and maintenance of the assets. Such contracts are normally of a shorter duration than concession contracts.
- Lease, Develop, Operate and Maintain (a variation of BOT): Assets are leased out to the private sector under specific terms, to operate and maintain the asset for the term of the concession period.
Ministry of Finance, GoI requires the Project sponsors to award PPP projects through a transparent open competitive bidding process, for greater transparency and consistency to the bid process and terms of contract, throughout the project life cycle and market discovery of rates. Unsolicited proposals and subsequent award of such proposals through the Bonus and Swiss challenge route is not supported as this introduces various asymmetries into the procurement process. These asymmetries, inter alia, includes informational asymmetry and bidding asymmetry between an Original Proponent (OP) and its competitors as the OP essentially gets an opportunity to make the BAFO (Best and Final Offer) after one or more rounds of negotiation- an opportunity that is denied to its competitors who are not authorized to submit an equal number of negotiated response. This would also lead to lack of robust bid submission by other potential bidders.
- 5.What are the various Government incentives for PPPs?
-
The Government has facilitated the PPP sector by offering:
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF): Viability Gap Funding of upto 40% of the cost of the project can be accessed in the form of a capital grant.
- India Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF): Scheme supports the Central and the State Governments and local bodies through financial support for project development activities (feasibility reports, project structuring etc.) for PPP projects
- IIFCL: long-term debt for financing infrastructure projects that typically involve long gestation periods since debt finance for such projects should be of a sufficient.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): upto 100% FDI in equity of SPVs in the PPP sector is allowed on the automatic route for most sectors.
- 6. Does the government extend financial support for PPP projects?
-
The Viability Gap Funding Scheme of the Government of India for Financial Support to Public Private Partnerships in Infrastructure, provides financial support of up to 40% of the Total Project Cost in the form of grant (one time or deferred) to infrastructure projects undertaken through public private partnerships with a view to making them commercially viable. Administered by the Ministry of Finance, budgetary provisions are made in the Annual Plans on a year-to-year basis for the Scheme. The detailed VGF guidelines may be accessed at: https://www.pppinindia.gov.in/documents/20181/21751/VGF_GuideLines_2013.pdf/
- 7. What is the Viability Gap Funding scheme?
-
The scheme aims at supporting infrastructure projects that are economically justified but fall marginally short of financial viability. Support under this scheme is available only for infrastructure projects where private sector sponsors are selected through a process of competitive bidding. The total Viability Gap Funding under this scheme will not exceed twenty percent of the Total Project Cost; provided that the Government or statutory entity that owns the project may, if it so decides, provides additional grants out of its budget, upto a limit of a further twenty percent of the Total Project Cost. VGF under this Scheme is normally in the form of a capital grant at the stage of project construction. The detailed VGF guidelines may be accessed at: https://www.pppinindia.gov.in/documents/20181/21751/VGF_GuideLines_2013.pdf/
- 8. What are the eligibility criteria for getting support under the VGF scheme?
-
In order to be eligible for funding under VGF Scheme, a PPP project should meet the following criteria: The project should be implemented (i.e. developed, financed, constructed, maintained and operated) for the Project Term by a Private Sector Company to be selected by the Government or a statutory entity through a process of open competitive bidding; provided that in case of railway projects that are not amenable to operation by a Private Sector Company, the Empowered Committee may relax this eligibility criterion. The PPP Project should be from one of the following sectors
- Roads and bridges, railways, seaports, airports, inland waterways;
- Power;
- Urban transport, water supply, sewerage, solid waste management and other physical infrastructure in urban areas;
- Infrastructure projects in Special Economic Zones and internal infrastructure in National Investment and Manufacturing Zones;
- International convention centres and other tourism infrastructure projects;
- Capital investment in the creation of modern storage capacity including cold chains and post-harvest storage;
- Education, health and skill development, without annuity provision;*
- Oil/Gas/Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) storage facility (includes city gas distribution network);
- Oil and Gas pipelines (includes city gas distribution network);
- Irrigation (dams, channels, embankments, etc.);
- Telecommunication (Fixed Network) (includes optic fibre/wire/cable networks which provide broadband/internet);
- Telecommunication towers;
- Terminal markets;
- Common infrastructure in agriculture markets; and
- Soil testing laboratories.
(As per the Notification No. 3C/1/2012-PPP dated November 4, 2013 issued by Department of Economic Affairs, as regards medical college, VGF would be admissible only if the proposed medical college is located in one of the backward districts identified under various schemes of GoI, provided there is no medical college in that district as on the date of in-principle approval of VGF by the competent authority.) The project should provide a service against payment of a pre-determined tariff or user charge. The Government/statutory entity concerned should certify, with reasons:
- That the tariff/user charge cannot be increased to eliminate or reduce the viability gap of the PPP;
- That the Project Term cannot be increased for reducing the viability gap; and
- That the capital costs are reasonable and based on the standards and specifications normally applicable to such projects and that the capital costs cannot be further restricted for reducing the viability gap.
- 9. What is the procedure for getting Viability Gap Funding?
-
Project proposals may be posed by a Government or statutory entity which owns the underlying assets. The proposals shall include the requisite information necessary for satisfying the eligibility criteria specified above and be submitted in formats with annexure as specified in the guidelines. Please see link https://www.pppinindia.gov.in/documents/20181/21751/VGF_GuideLines_2013.pdf
- 10. What is India Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF)?
-
For providing financial support for quality project development activities for PPP projects to the Central and the State Governments and local bodies, Scheme and Guidelines of India Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF), have been notified The IIPDF would assist ordinarily up to 75% of the project development expenses. On successful completion of the bidding process, the project development expenditure would be recovered from the successful bidder. The detailed IIPDF guidelines may be accessed at: https://www.pppinindia.gov.in/documents/20181/21751/IIPDF_GuideLines_2013.pdf
- 11. What is the purpose of the IIPDF fund?
-
The procurement costs of PPPs, particularly costs of engaging transaction advisory services, are significant and often burden the budget of the Sponsoring Authority. Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) has identified the IIPDF as a mechanism through which Sponsoring Authority can source funding to cover a portion of the PPP transaction costs, thereby reducing the impact of costs related to such procurement on their budgets. From the Government of India's perspective, the IIPDF must increase the quality and quantity of bankable projects that are processed through the Central or States' project pipeline.
- 12. What can the IIPDF funding be used for?
-
The IIPDF will be available to the Sponsoring Authorities for PPP projects for the purpose of meeting the project development costs which may include the expenses incurred by the Sponsoring Authority in respect of feasibility studies, environment impact studies, financial structuring, legal reviews and development of project documentation, including concession agreement, commercial assessment studies (including traffic studies, demand assessment, capacity to pay assessment), grading of projects etc. required for achieving Technical Close of such projects, on individual or turnkey basis, but would not include expenses incurred by the Sponsoring Authority on its own staff.
- 13. What is the India Infrastructure Finance Company (IIFC)?
-
There is urgent need for providing long-term debt for financing infrastructure projects that typically involve long gestation periods. Debt finance for such projects should be of a sufficient tenure which enables cost recovery across the project life, as the Indian capital markets were found deficient in long-term debt instruments; IIFC was set-up to bridge this gap.
- 14. Has the approval process been streamlined for PPP projects?
-
Yes, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) in its meeting of 27th October, 2005 approved the procedure for approval of public private partnership (PPP) projects sponsored by Central Government Ministries/ Central Public Sector Undertakings (CPUs)/ statutory authorities or other entities under their administrative control. Pursuant to this decision, a Public Private Partnership Appraisal Committee (PPPAC) was set up comprising of the following:
- Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs (in the Chair)
- Secretary, Planning Commission
- Secretary, Department of Expenditure;
- Secretary, Department of Legal Affairs; and
- Secretary of the Department sponsoring a project.
The Committee would be serviced by the Department of Economic Affairs, who has set-up a special cell for servicing such proposals. Proposals for the PPPAC are submitted to the DEA, PPP cell. The detailed PPPAC guidelines can be accessed at: https://www.pppinindia.gov.in/documents/20181/21751/PPPAC_GuideLines_2013.pdf
- 15. Has any guidance material (manuals, toolkits, etc.) been prepared for PPP?
-
The Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) has developed online PPP Toolkits covering five infrastructure sectors namely, State highways, Water and sanitation (W&S), Ports, Solid waste management (SWM) and Urban transport (Bus Rapid Transport Systems). The toolkit is a web-based resource that has been designed to help improve decision-making for infrastructure PPPs in India and to improve the quality of the PPPs that are developed. The toolkit can be accessed at http://toolkit.pppinindia.com/ The Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) has also developed The "PPP Post-Award Contract Management Toolkit", which is a web-based application that has been designed to help improve the contract management and project execution of the infrastructure sector related PPP projects in India. It aims to do so by serving as an efficient guide to the public sector entities involved in the execution of these projects. The toolkit covers three infrastructure sectors namely, Highways, Ports and Schools. The toolkit can be accessed at http://infrastructureindia.gov.in/toolkit/ Additionally, Compendium of Case Studies containing PPP initiatives in India has also been developed and can be accessed at https://www.pppinindia.gov.in/case-studies
- 16. Where can I get information for projects other than PPP projects?
-
www.infrastructureindia.gov.in is a repository of information on infrastructure projects being implemented in India by various Government Departments and Private Sector companies. This database has been developed by PPP Cell, Infrastructure Division, Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, Government of India. The database provides information on infrastructure projects through the functionality of viewing various standardized as well as customized reports across sectors, States, implementation status, year of award etc. The database captures information on: Government Infrastructure Projects (PPP) that were either under 'Pre-construction Stage', ‘Under Construction’ or ‘Operation and Maintenance Stage’ as on April 1, 2011 or ‘Awarded’ thereafter and with Project Cost > 5 crore. Government Infrastructure Projects (Traditional Procurement) that were under 'Pre-construction Stage', or ‘Under Construction’ as on April 1, 2012 or ‘Awarded’ thereafter and with Project Cost > 50 crore; and Private Sector Projects that were under 'Pre-construction Stage', or ‘Under Construction’ as on April 1, 2012 or ‘Awarded’ thereafter and with Project Cost > 50 crore.
- 17. What is the PPP model in education?
-
The PPP model proposed in the Eleventh Plan provides for no government or social control over education. It will lead to privatization.
- 18. Why use PPP?
-
PPPs offer the public sector potential cost, quality and scale advantages in achieving infrastructure service targets. However, PPPs are different to the traditional public sector route and these differences require adaptation of approach and capabilities in the public sector. There are also some new costs associated with PPPs. The advantages of PPP include:
- Access to private sector finance
- Efficiency advantages from using private sector skills and from transferring risk to the private sector
- Potentially increased transparency
- Enlargement of focus from only creating an asset to delivery of a service, including maintenance of the infrastructure asset during its operating lifetime
- This broadened focus creates incentives to reduce the full life-cycle costs (i.e., construction costs and operating costs)