Income Tax Audit under Section 44AB- An Introduction
The term ‘Audit’ means an official inspection of an organization’s accounts and production of report, typically by an independent body. It is also referred to as a systematic review or assessment of something. “Tax Audit” as the name suggests is an examination or review of accounts of any business or profession carried out by taxpayers from an income tax point of view. It makes the process of income computation for filing of return of income easier.
Objectives of tax auditTax audit is conducted to achieve the following objectives:
- Ensure proper maintenance and correctness of books of accounts and certification of the same by a tax auditor
- Reporting observations/discrepancies noted by tax auditor after a methodical examination of the books of account
- To report prescribed information such as tax depreciation, compliance of various provisions of income tax law, etc.
All these enable tax authorities in verifying the correctness of income tax returns filed by the taxpayer. Calculation and verification of total income, claim for deductions etc., also becomes easier.The core objective of an income tax audit is to ensure the taxpayer adheres to the income tax rules and provisions in a financial year. The transactions entered by the taxpayer w.r.t. Receipts, expenses, loan, deductions, etc are as per the provisions. The following are other objectives:
- To ascertain/derive/report the requirements of Form Nos. 3CA/3CB and 3CD.
- a proper audit for tax purposes would ensure that the books of account and other records are properly maintained
- Books of account truly reflect the income of the taxpayer and claims for deduction are correctly made by him
- Certification of books of accounts by an auditor
- A reporting of the discrepancies/ observations of the tax auditor on examination of books of accounts to the income tax department
- A check for fraud and malpractice by the taxpayer while filing income tax returns
- Reporting of essential details such as depreciation, loans and advances, deductions, and compliance with provisions of the income tax act. This reporting helps the income tax department in two ways. Firstly, facilitate the administration of tax laws by a proper presentation of accounts before the tax authorities. Secondly, calculation and verification of total income, expenditure, claim of deductions, and so on.
- Save the time of Assessing Officers in carrying out routine verifications, like checking the correctness of totals and verifying whether purchases and sales are properly vouched for or not. The time of the Assessing Officers saved could be utilized for attending to more important and investigational aspects of a case.
The income tax Department has enabled the tax audit utility form on its portal for financial year 2019-20 and 2020-21.Under the I-T Act, taxpayers are required to get their accounts audited if the sales, turnover or gross receipts of business exceed 10 crore, while in case of professionals; the limit was over 50 lakh in 2020-21 (AY 2021-22).
1. ITR filing due date extension:- (i). ITR filing by taxpayers not covered under audit is extended from 30th Sep 21 to 31st Dec 21
- (ii). ITR filing for tax audit cases is extended to 15th Feb 22
- (iii). ITR filing for transfer pricing is extended to 28th Feb 22
- (iv). ITR filing of belated or revised return for FY 20-21 is extended from 31st Dec 21 to 31st March 22
- (i). Due date to furnish the audit report is extended to 15th Jan 22
- (ii). Due date to furnish the audit report for transfer pricing cases is extended to 31st Jan 22
For fiscal 2019-20 i.e. AY 2020-21, limit was 5 crore for businesses and 50 lakh for professionals and due date for original tax audit report was January 15, 2021.
However, companies can still file the revised tax audit report for that year to rectify errors.
If a person is required to get his accounts audited under any other law for example, statutory audit of companies under company law provisions, in such cases, the taxpayer need not get his accounts audited again for income tax purposes. It is sufficient if accounts are audited under such other law before the due date of filing the return. The taxpayer can furnish this prescribed audit report under Income tax law.
Tax Audit & Section under which audit is required: An overview
There are total 5 clauses under which one might be required to get their books of accounts audited. It may happen that the assessee may fall under one more than one clause, in such case the taxpayers can select different option in the drop box menu.
Clause (a) of section 44AB
Read More...Clause (b) of Section 44AB
Read More...Clause (c) of Section 44AB
Read More...Clause (d) of Section 44AB
Read More...Clause (e) of Section 44AB
Read More...Revise Income Tax Audit Limits for FY 2021-22 AY 2022-23
Under section 44AB of the Act, every person carrying on business is required to get his accounts audited, if his total sales, turnover or gross receipts, in business exceed or exceeds one crore rupees in any previous year. In case of a person carrying on profession he is required to get his accounts audited, if his gross receipt in profession exceeds, fifty lakh rupees in any previous year. In order to reduce compliance burden on small and medium enterprises, through Finance Act 2020, the threshold limit for a person carrying on business was increased from one crore rupees to five crore rupees in cases where,-
- aggregate of all receipts in cash during the previous year does not exceed five per cent of such receipt; and
- aggregate of all payments in cash during the previous year does not exceed five per cent of such payment.
In order to incentivize non-cash transactions to promote digital economy and to further reduce compliance burden of small and medium enterprises, it is proposed to increase the threshold from five crore rupees to ten crore rupees in cases listed above.
In case of person engaged in business and opting for presumptive taxation under section 44AD:| Turnover limit for the previous year | Amount of profit with respect to turnover (in %) | Whether cash receipts less than 5% of the Turnover | Whether cash payment less than 5% of the total payment | Is Tax audit Applicable? |
| More than 10 Crores | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | Yes |
| More than 2 crore but | Not applicable | Yes | Yes | No |
| More than 2 crore but upto 10 Crore | Not applicable | No | No | Yes |
| More than 1 crore but upto 2 Crore | More than 8% or 6% of Turnover | Not applicable | Not applicable | Yes |
| More than 1 crore but upto 2 Crore | Less than 8% or 6% of Turnover | Not applicable | Not applicable | Yes |
| Less than 1 Crore | More than 8% or 6% of Turnover | Not applicable | Not applicable | Yes |
| Less than 1 Crore | Less than 8% or 6% of Turnover | Not applicable | Not applicable | Yes |
| Turnover limit for the previous year | Amount of profit with respect to turnover (in %) | Is audit Applicable? |
| More than 50 Lakhs | Not applicable | Yes 44AB(b) |
| Upto 50 Lakhs | More than 50% | No |
| Upto 50 Lakhs | less than 50% (sec 44ADA) | Yes 44AB(d) |
- If total income exceeds basic exemption limit only then tax audit is applicable.
- Where the assesse is covered under section 44AB then he is required to get the books of accounts audited by a Chartered Accountant.
- The tax audit report should be furnished in form 3CB CD, where the report of the tax audit conducted by the chartered accountant is to be furnished in Form No. 3CB and the details of audit are to be reported in Form No. 3CD.
Who is mandatorily subject to tax audit?
A taxpayer is required to have a tax audit carried out if the sales, turnover or gross receipts of business exceed 1 crore in the financial year. However, a taxpayer may be required to get their accounts audited in certain other circumstances.
Note: The threshold limit of 1 crore for a tax audit is proposed to be increased to 5 crore with effect from AY 2020-21 (FY 2019-20) if the taxpayer’s cash receipts are limited to 5% of the gross receipts or turnover, and if the taxpayer’s cash payments are limited to 5% of the aggregate payments.
| Category of person | Threshold |
| Business | |
| Carrying on business (not opting for presumptive taxation scheme*) | Total sales, turnover or gross receipts exceed 1 crore in the FY |
| Carrying on business eligible for presumptive taxation under Section 44AE, 44BB or 44BBB | Claims profits or gains lower than the prescribed limit under presumptive taxation scheme |
| Carrying on business eligible for presumptive taxation under Section 44AD | Declares taxable income below the limits prescribed under the presumptive tax scheme and has income exceeding the basic threshold limit. |
| Carrying on the business and is not eligible to claim presumptive taxation under Section 44AD due to opting out for presumptive taxation in any one financial year of the lock-in period i.e. 5 consecutive years from when the presumptive tax scheme was opted | If income exceeds the maximum amount not chargeable to tax in the subsequent 5 consecutive tax years from the financial year when the presumptive taxation was not opted for |
| Carrying on business which is declaring profits as per presumptive taxation scheme under Section 44AD | If income exceeds the maximum amount not chargeable to tax in the subsequent 5 consecutive tax years from the financial year when the presumptive taxation was not opted for |
| Carrying on business which is declaring profits as per presumptive taxation scheme under Section 44AD | If the total sales, turnover or gross receipts does not exceed 2 crore in the financial year, then tax audit will not apply to such businesses. |
| Profession | |
| Carrying on profession | Total gross receipts exceed 50 lakh in the FY |
| Carrying on the profession eligible for presumptive taxation under Section 44ADA | (1).Claims profits or gains lower than the prescribed limit under the presumptive taxation scheme Income exceeds the maximum amount not chargeable to income tax |
| Business loss | |
| In case of loss from carrying on of business and not opting for presumptive taxation scheme | Total sales, turnover or gross receipts exceed 1 crore |
| If taxpayer’s total income exceeds basic threshold limit but he has incurred a loss from carrying on a business (not opting for presumptive taxation scheme) | In case of loss from business when sales, turnover or gross receipts exceed 1 crore, the taxpayer is subject to tax audit under 44AB |
| Carrying on business (opting presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD) and having a business loss but with income below basic threshold limit | Tax audit not applicable |
| Carrying on business (presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD applicable) and having a business loss but with income exceeding basic threshold limit | Declares taxable income below the limits prescribed under the presumptive tax scheme and has income exceeding the basic threshold limit |
The Finance Act 2020 had increased the tax audit limit for a person carrying on business from 1 crore to 5 crore, subject to a condition that cash receipts and cash payments during the year do not exceed 5 per cent of the total receipts/payments. The Finance Act 2021 further increased this limit to 10 crore. Accordingly, any person carrying on business shall not be required to get his account audited by an accountant (and file tax audit report) if his total sales/turnover/gross receipts do not exceed 10 crore and cash payments during the year do not exceed 5 per cent of total receipts/payments. The payment or receipt, as the case may be, by a cheque drawn on a bank or by a bank draft, which is not account payee, shall be deemed to be the payment or receipt, as the case may be, in cash.

Tax Audit Report Filing Process

Due Date of Filing Tax Audit Report
The due date of filing the report depends on the due date of filing the income tax return. The taxpayer must file the report on or before the due date of filing the income tax return. The due date of filing ITR is 30th November of the subsequent assessment year for taxpayers who engage in an international transaction during the financial year. The due date of filing is 30th September of the subsequent assessment year for other taxpayers.
For all other assessee’s who are not liable to get their Tax Audit done under Section 44 AB – the Due Date of filing of Income Tax Return is 31st July.
Who will audit the books of accounts as per tax audit provisions?
A Chartered Accountant’ or ‘a firm of Chartered Accountants’ can conduct the audit as per tax audit provisions. An individual can conduct only 60 audits in a financial year. In the case of a partnership, this limit applies to each member of the partnership firm being a chartered accountant.
What constitutes an Audit Report?

The tax auditor shall furnish a tax audit report online by using his login details in the capacity of ‘Chartered Accountant’. Taxpayers shall also add CA details in their login portal.Once the tax auditor uploads the audit report, the same should either be accepted/ rejected by the taxpayer in their login portal. If rejected for any reason, all the procedures need to be followed again till the audit report is accepted by the taxpayer.You must file the tax audit report on or before the due date of filing the return of income. It is 30th November of the subsequent year in case the taxpayer has entered into an international transaction and 30th September (extended to 30th November for AY 2021-22) of the subsequent year for other taxpayers.
If any taxpayer who is required to get the tax audit done but fails to do so, the least of the following may be levied as a penalty:
- 0.5% of the total sales, turnover or gross receipts
- 1,50,000
However, if there is a reasonable cause of such failure, no penalty shall be levied under section 271B.So far, the reasonable causes that are accepted by Tribunals/Courts are:
Natural Calamities
Resignation of the Tax Auditor and Consequent Delay
Labor problems such as strikes, lock-outs for an extended period
Loss of Accounts because of situations beyond the control of the Assesses
Physical inability or death of the partner in charge of the accounts
In case of LLP should reporting for Tax Audit be in Form 3CA or 3CB?
In case of company, which follows April-March period as its financial year, the Tax Audit report would in Form No. 3CA, if the Tax Audit is applicable to it. However, in case of partnership firm or proprietary concern, which is not required to get their accounts audited under any other Law, Tax Audit report would be in Form No. 3CB.
In case of LLP following April-March as its financial year and if it is required to get its account audited under the LLP Rules, 2009, then the Tax Audit report would be in Form No. 3CA. However, if it is not required to get its accounts audited under the LLP Rules, 2009 then Form No. 3CB would be applicable. It may be noted that under rule 24 of the LLP Act, audit is mandatory in case the LLP whose turnover in the relevant financial year exceeds 40 lacs or whose contribution exceeds 25 lacs.
Consequences of late filing of Income tax returns
The penalties in India for not filing Tax Returns in time i.e. by 31st March following the taxable financial year which may range from 5,000 to 10,000 in addition to interest payable at 1% per month on the unpaid taxes.
- The most severe consequences of not filing a tax return on time is that one loses the benefit of carry forward of any losses that may have incurred which cannot be set off against the same year’s income. These losses can be in the nature of capital losses in case of individuals or it may also be losses incurred in the business or profession. Hence one loses the tax shield which they would have gained if they had recouped these losses to their portfolio through profits in the subsequent years. The taxes that you end up paying in the subsequent years on the profits are the real penalty in such a case.
- Further if you are entitled to a tax refund then normally you will get an interest of 6% per annum from 1st April before the due date till the issue of the refund. In case you file the return late you lose the opportunity of getting the interest for the period from April till the month in which you filed the return.
- If you have earned foreign income and have paid foreign taxes on such income, then the law requires you to file a form prior to return filing in India for claiming credit on such foreign taxes in order to avoid double taxation. If you forget to file that form in time, you may not get the credit of the foreign taxes paid by you.
- Charitable entities have to bear much harsher penalties for such delays in filing their returns as a charitable entity is entitled to exemption on its income (including donations received) if it spends such income on charity. However if it neither files income tax returns on time nor does its audit report, then it has to pay tax on its gross income without any deduction for the spending on charity. Even if it has spent its entire income on charity it ends up having to pay income tax over and above that.
- Businesses that are entitled to tax holidays also suffer consequences if they do not file relevant audit reports in time as they lose the benefit of tax holidays or deduction for the year
These penalties are therefore much harsher than a mere penalty. However, the High Courts have reduced the impact of consequences in relation of filing of annual reports by holding that what is important is the availability of audit report even though it is obtained late and as long as the reports are filed, the benefit of tax holiday or deduction cannot be denied. Unfortunately, there is no such relief granted by the court in relation to late filing of tax returns.
Points to be considered by the Tax Auditor
- The tax auditor should obtain from the assessee a letter of appointment for conducting the audit as mentioned in section 44AB.
- The tax auditor is required to upload the tax audit report directly in the e-filing portal. In case of joint auditors, management representation has to be obtained about responsibility of uploading Tax Audit Report & ITR by particular auditor.
- The appointment of the auditor for tax audit in the case of a company need not be made at the general meeting of the members. It can be made by the Board of Directors or even by any officer, if so authorized by the Board in this behalf.
- The appointment in the case of an assessee, being a firm or a proprietary concern, can be made by a partner or a person authorized by the assessee in the case of a firm or by the proprietor himself or a person authorized by him in the case of the assessee being a proprietary concern.
- It is possible for the assessee to appoint two or more chartered accountants as joint auditors for carrying out the tax audit, in which case, the audit report will have to be signed by all such chartered accountants. In case of disagreement, they can give their reports separately.
- The Act prohibits a relative or an employee of the assessee being appointed as a tax auditor under section 44AB, besides ICAI has also laid in the code of ethics that a Chartered Accountant should not express his opinion on financial statements of any business or enterprise in which he, his firm or a partner in his firm has a substantial interest.
- A chartered accountant who is responsible for writing or maintenance of the books of account of the assessee should not audit such accounts (including tax audits). This principle will apply and extend to any partner of such a chartered accountant as well as to the firm in which he is a partner.
- The audit of accounts of a Firm of chartered accountants, under section 44AB, cannot be conducted by any partner or employee of such a firm. Similarly, where such a firm is a proprietary one, the said audit cannot be conducted by the proprietor or his employee.
- A chartered accountant/ firm of chartered accountants, who is appointed as tax consultant of the assessee, can conduct tax audit under section 44AB. But an internal auditor of the assessee cannot conduct tax audit if he is an employee of the assessee.
- The tax auditor cannot be removed on the ground that he has given an adverse audit report or the assessee has an apprehension that the tax auditor is likely to give an adverse audit report. If there is any unjustified removal of tax auditors, the Ethical Standards Board constituted by the Council of the Institute if approached, may intervene in such cases. No chartered accountant should accept the audit assignment if the removal of his predecessor is not on valid grounds.
How many tax audit reports a Chartered accountant can Sign?
Specified Number of Tax Audit Assignments It is to be noted that a Chartered Accountant in practice can conduct 60 tax audits relating to an assessment year. The ICAI had clarified that audit prescribed under any statute which requires the assessee to furnish an audit report in the form as prescribed under section 44AB of the Income-tax Act, shall not be considered for the purpose of reckoning the specified number of tax audit assignments if the turnover of the assessee is below the turnover limit specified in section 44AB of the Income-tax Act. The ICAI has modified the guidelines on August 23, 2018 to provide that the audits conducted under Section 44AD, 44ADA and 44AE of the Income-tax Act (Presumptive Taxation Schemes) shall not be considered for the purpose of reckoning the ‘specified number of tax audit assignments’
Before accepting a tax audit, the chartered accountant should ensure that taking such audit will not exceed the specified number of tax audits assignments, which at present are 60 in a given financial year. This said specified number of 60 Needless to mention, A Chartered Accountant in practice, is deemed to be guilty of professional misconduct if, he accepts more than 60 tax audit assignments relating to an assessment year.
In case, a member is a partner in a firm of chartered accountants in practice, the ceiling of 60 tax audit assignments shall be computed with reference to each of the partners in the said firm. Where any partner of a firm of Chartered Accountants in practice, is also a partner of any other firm or firms of Chartered Accountants in practice, the ceiling limit of 60 shall apply with reference to all the firms together in relation to such a partner. Similarly, where any partner accepts one or more tax audit assignments in his individual capacity, the total number of such assignments under section 44AB which may be accepted by him whether directly in his individual capacity or as partner in one or more firms of chartered accountants in practice shall not exceed 60 tax audit assignments. If two chartered accountants already in practice or two of such chartered accountants are appointed as joint tax auditors, then the assignment will have to be included in the case of both the members and firms separately. It is, however, clarified that the audit of an assessee head office and branch offices shall be regarded as one tax audit assignment. The audit of one or more branches of the same concern by one Chartered Accountant in practice shall be construed as only one tax audit assignment.
Therefore, if there are 10 partners in a firm of Chartered Accountants in practice, then all the partners of the firm can collectively sign 600 tax audit reports. This maximum limit of 600 tax audit assignments may be distributed between the partners in any manner whatsoever. For instance, 1 partner can individually sign 600 tax audit reports in case remaining 9 partners are not signing any tax audit report.
- Tax Auditor is required to communicate with the previous Tax Auditor.
- No need to communicate with Statutory Auditor.
- A person is disqualified u/s. 288 from being appointment as an auditor if he or his relative is:
- Indebted to the Assessee. (Relative may be indebted up to 1,00,000/- )
- Holds security (Relative can hold up to 1,00,000/-)
- gives guarantee on behalf of third person (Relative can give guarantee up to 1,00,000/-)
Appointment of Tax Auditor in Company
The responsibility of appointing tax auditors in a company is vested with the Board of Directors. The Board may also delegate this responsibility to any other officer like CEO or CFO. Auditors in a firm or proprietorship can be appointed by a partner, proprietor or a person authorized by the assessee. Moreover, a taxpayer can also appoint two or more chartered accountants as joint auditors for performing the tax audit. In this case, the audit report must be signed by all the joint auditors, if all of them concur with the report. In case of any differences in opinion, the auditors must express their opinion separately through another report.
Letter of Appointment for Tax AuditThe tax auditor must obtain a letter of appointment from the concerned assessee before going forward with the tax audit. The appointment letter must be duly signed by the person competent to sign the return of income. The letter must mention the remuneration offered to the auditor. Further, the appointment letter should specify that no other auditor is entrusted with the task for the particular financial year, and could contain details of the previous auditor. The latter is mentioned to facilitate the communication between the appointed auditor and his predecessor.
Who cannot be tax auditor?There are certain prohibitions on the appointment of tax auditors, which are enumerated below:
- Any member in part-time practice is not eligible to perform tax audit.
- A chartered account cannot audit the accounts of a person to whom he is indebted for more than 10,000.
- A statutory auditor will be deemed to be guilty of professional misconduct if he/she accepts the appointment of Public Sector Undertaking/Government Company/Listed Company and other Public Company having turnover of 50 crores or more in a year and accepts any other work, assignment or service in regard to the same undertaking/company on a remuneration which in total exceeds the fee payable for carrying out the statutory audit of the same undertaking/company.
- The Chartered Accountant who is assigned with the task of writing and maintaining the books of account of the assessee should not audit such accounts.
- The audit of accounts of a professional firm of Chartered Accountants cannot be performed by any partner or employee belonging to such firm.
- An internal auditor of the assessee cannot be appointed as a tax auditor.
- An auditor cannot accept more than 60 tax audit assignments in a particular financial year.
Thus if a firm has 4 partners, the maximum no. of Tax Audits that can be taken by a firm in an assessment year would be 60*4=240. If the Firm undertakes all the 240 Tax Audit Assignments, the partners would not be in a position to undertake any tax audit assignment in their personal capacity. Now that tax audit e-filing is mandatory, the chartered accountant conducting the tax audit would also be required to prepare the tax audit report in electronic format.
Removal of Tax AuditorThe management is entitled to remove a tax auditor if the auditor has delayed the submission of the report to such an extent that it is not anymore possible to get the audit report uploaded before the specified due date. A tax auditor cannot be removed because he has submitted an adverse audit report or on the assesee’s apprehension that the tax auditor is likely to provide an adverse audit report. If a Chartered Accountant is removed on unfair grounds, the Ethical Standards Board, which was established by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is entitled to intervene. Moreover, if a Chartered Accountant is removed on invalid grounds, no other Chartered Accountant would be allowed to act as a replacement to the predecessor.
Applicability of Tax Audit in some cases:
Some cases may cover those assessees who are wholly outside the preview of income-tax law as well as those whose income is otherwise exempt under the Act. It is felt that neither section 44AB nor any other provisions of the Act stipulate exemption from the compulsory tax audit to any person whose income is exempt from tax. This section makes it mandatory for every person carrying on any business or profession to get his accounts audited where conditions laid down in the section are satisfied and to furnish the report of such audit in the prescribed form.
- A trust/association/institution carrying on business may enjoy exemptions as the case may be under sections 10(21), 10(23A), 10(23B) or section 10(23BB) or section 10(23C) or section 11.
- A co-operative society carrying on business may enjoy deduction under section 80P. Such institutions/associations of persons will have to get their accounts audited and to furnish such audit report for purposes of section 44AB if their turnover in business exceeds the prescribed limit.
- Only Agriculture Income (Tax Audit Not Applicable) But an agriculturist, who does not have any income under the head “Profits and gains of business or profession” chargeable to tax under the Act and who is not required to file any return under the said Act, need not get his accounts audited for purposes of section 44AB even though his total sales of agricultural products may exceed the prescribed limit.
- Non-Residents: –
The case of non-residents may be considered separately.
Section 44AB does not make any distinction between a resident and non-resident. Therefore, a non-resident assessee is also required to get his accounts audited and to furnish such report under section 44AB if his turnover/sales/gross receipts exceed the prescribed limits. This audit, however, would be confined only to the Indian operations carried out by the non-resident assessee since he is chargeable to income-tax in India only in respect of income accruing or arising or received in India.
Income below Taxable Limit:– It may be appreciated that the object of audit under section 44AB is only to assist the Assessing Officer in computing the total income of an assessee in accordance with different provisions of the Act. Therefore, even if the income of a person is below the taxable limit laid down in the relevant Finance Act of a particular year, he will have to get his accounts audited and to furnish such report under section 44AB, if his turnover in business exceeds the prescribed limit.
Whether a tax audit report can be revised?In certain cases, members are called upon to report on the accounts reopened and revised by the board of directors. The accounts of a company once adopted at its annual general meeting should not normally be reopened and revised. The Institute and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs have affirmed this position. In case of revision, the audit report should be given in the manner as required by the Institute in SA-560 (Revised), Subsequent Event. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs had also clarified that accounts can be revised to comply with technical requirements.
It may be pointed out that report under section 44AB should not normally be revised.
However, sometimes a member may be required to revise his tax audit report on grounds such as:
- Revision of accounts of a company after its adoption in annual general meeting.
- Change of law e.g., retrospective amendment.
- Change in interpretation, e.g. CBDT Circular, judgments, etc.
Clause 8A – Option u/s 115BA/115BAA/115BAB/115BAC/ 115BAD
Clause 8A has been modified to include if the assessee is exercising the of option u/s 115BAC or 115BAD (two new concessional rates introduced in Finance Act 2020) with already existing 115BA/ 115BAA/ 115BAB for companies.
- Taxpayer being an individual or HUF can go for new option u/s 115BAC when he opts to pay income tax under the new tax regime; wherein there are lower tax rates but does not allow certain deductions and exemptions; or
- Taxpayer being a Resident Co-operative Society can go for new option u/s 115BAD providing a benefit of a lower tax rate of 22% but subject to non-availing for certain deductions and exemptions and other conditions.
- Auditor should ensure to obtain a copy of Form 10-IB / 10-IC / 10-ID / 10-IE / 10-IF for opting to apply section 115BA / 115BAA / 115BAB / 115BAC / 115BAD respectively and report accordingly.
Computation of Total Turnover for the purpose of Tax Audit
ICAI has through a Guidance Note clarified the following points:-
- Where a person is carrying on 2 Business/2 Professions– the total turnover of both the businesses shall be clubbed together and tax audit shall be liable to be conducted if the Total Turnover exceeds 1 Crore/ 25 Lakhs as the case may be.
- Where a person is carrying on business as well as profession and the Turnover of the business is 1.2 Crore and the Gross Receipts of the profession is 22 Lakhs. In such a case, ICAI has clarified through a Guidance Note that the Assessee is liable to get the Tax Audit done of both the business as well as profession because the Gross Receipts from the business exceed the limit of 1 Crore. However, if his Total Turnover was 95 Lakhs and Gross Receipts from business was 22 Lakhs, he would not be required to get his Tax Audit done.
- In case where a person has a total turnover of 98 Lakhs and has sold a Car for 8 Lakhs- In such a case, the total amount on adding up becomes 1.06 Lakhs i.e. above 1 Crore. Confusion arose whether the person is liable to get an audit done in this case and ICAI has clarified that the turnover will not include any amount on the sale of the fixed asset as it was held by the person for business use and not for the purpose of sale.
ICAI has further clarified that the amount received from the following items shall not be included while computing the Total Sales/Total Turnover/ Gross Receipts:-
- Sale Proceeds of Fixed Assets
- Sale Proceeds of Assets held as Investments
- Rental Income
- Income by way of Interest unless assessable as Business Income
- Any expense which is reimbursable to the Agent by the Client
Inclusions and Exclusions from Turnover
The term ‘turnover’ for the purposes u/s. 44AB would mean the aggregate amount for which sales are affected or services rendered by an enterprise. The following should not be deducted from sales to arrive at turnover:
- Sale of scrap/ By product
- Sales proceeds of shares, securities, debentures etc. held as stock in trade by the assessee.
- Cash discount other than allowed in invoice
- Commission on sales
- If sales tax/ Excise duty was included in sale price while accounting (Inclusive method), then the same shall form part of Turnover.
- Advance received and forfeited from customers
- Cash assistance under the scheme of Government
- Liquidated damages
- Duty Drawbacks
- Export incentives
- Insurance claim (except relating to fixed assets)
- Profit on sale of import license
- Foreign exchange fluctuations on export sales
- Interest income (if it forms part of business income)
- Dividend income (in case of dealer of shares and securities)
- Commission, brokerage, service and other incidental charges received in the business of chit funds
- Reimbursement of expenses incurred (if credited to separate account then only to the extent of surplus)
- Hire charges and installments received
- Finance income in case of lessor
- Gross receipts including lease rent in the business of operating lease
- Hire charges of cold storage
- If sales tax/ Excise duty was not included in sale price while accounting (Exclusive method), then the same shall not form part of Turnover.
- Sale proceeds of Fixed Assets.
- Sale proceeds of Investment property i.e. asset held as investment.
- Sale proceeds of shares, securities, debentures held as an Investment.
- Discounts allowed in the Invoice.
- Turnover discount (even if allowed by way of separate credit note)
- Ancillary charges such as packing, freight and forwarding etc. provided they are separately mentioned in the Invoice. Otherwise they will form part of Turnover.
- Sales Returns
- Price adjustments.
- Special rebate (Excluding commission on sales)
- Interest income (if not included as business income)
- Dividend income except in case of dealer in shares
- Reimbursements of custom duty and other charges collected by clearing agent
- Share of profit of a partner of a firm/LLP excluded from total income u/s10(2A)
- Liabilities/ provisions of creditors, expenses or taxes written back
- Rental income (if not included as business income)
- Reimbursement of advertising charges by an advertising agent from the client
Complete List of considerations by the Tax Auditor in Tax Audit
The auditor should take care that:
- Taxpayer being an individual or HUF can go for new option u/s 115BAC when he opts to pay income tax under the new tax regime; wherein there are lower tax rates but does not allow certain deductions and exemptions; or
- Taxpayer being a Resident Co-operative Society can go for new option u/s 115BAD providing a benefit of a lower tax rate regime but subject to non-availing for certain deductions and exemptions and other conditions.
- Auditor should ensure to obtain a copy of Form 10-IC / 10-IE / 10-IF for opting to apply section 115BAA / 115BAC / 115BAD respectively.
- In such cases set off of carried forward loss (due to specified sections) or unabsorbed additional depreciation from any earlier assessment year is not allowed. Hence, such details need to be mentioned accordingly in this clause.
- Brought forward losses may pertain to different heads of income such as house property income, profits and gains in business or profession, speculation business or capital gains.
- Information about the pending assessment or appellate proceedings or about delay in filing loss returns should be given.
- The auditor should study the assessment records i.e. income-tax returns filed, assessment orders, appellate orders and rectification/ revision orders for the earlier years and ascertain if the figures / details given in the above clause are correct
- He should be also aware of section 78 regarding Carry Forward and Set Off of Losses in case of Change in Constitution of Firm or on Succession
- Any assessment, rectification, revision or appeal proceedings pending at the time of tax audit should be disclosed in the remarks column by way of information. If consequential orders for any revision/appellate order is yet to be passed, the same can be disclosed along with the impact thereof if Material
- Obtain suitable management representation regarding the carry forward losses and depreciation details.
- Carry forward of losses are restricted in case of firms / LLP u/s 78 and closely held companies u/s 79. Details should be given under this clause, with remarks regarding restriction of carry forward further. In next year the same would not be brought forward loss.
- Auditor should take note that section 78/79 restrictions do not affect the set off of unabsorbed depreciation as it is governed by section 32(2).
- Where change in shareholding of company has taken place in Previous Year due to which losses incurred in preceding Previous Years cannot be carried forward as per Section 79. The change would not affect carry forward of unabsorbed depreciation u/s 32(2). This provision shall not apply to a change in the voting power consequent upon:
- the death of a shareholder, or
- On account of transfer of shares by way of gifts to any relative of the shareholder making such gift.
- any change in the shareholding of an Indian company which is subsidiary of a foreign company arising as a result of amalgamation or demerger of a foreign company subject to the condition that 51 % of the shareholders of the amalgamating or demerged foreign company continue to remain the shareholders of the amalgamated or the resulting foreign company.
- Check whether the assessee has incurred any speculation loss referred to in section 73 during the previous year and any loss in respect of speculation business shall not be set off except against profits or gains of another speculation business. No loss shall be carried forward under this section for more than 4 AYs immediately succeeding the assessment year for which the loss was first computed. Speculative transaction does not include derivatives (futures & options) and commodity derivatives.
- Any loss, computed in respect of any specified business referred to in section 35AD and shall not be set off except against profits and gains, if any, of any other specified business.
- In case of a company, please state that whether the company is deemed to be carrying on a speculation business. The auditor should obtain information from the assessee and verify the same from the books of account, income tax returns of earlier years and other relevant documents.
- The admissibility of the aforesaid deductions/exemptions is dependent upon various conditions. It is, therefore, advised that while working out the amount of admissible deduction the tax auditor has to ascertain that those condition stand fulfilled or not.
- For ascertaining this, the auditor should obtain all necessary evidence which would enable him to express the opinion regarding the admissibility of deductions.
- In the case of a sole proprietor being an individual or HUF the auditor would be auditing the accounts of the business / profession and he may have other activities and other sources of income in respect of which tax audit is not mandatory. In such cases the particulars of deductions admissible under Chapter VIA has to be given with reference to the items appearing in the books of accounts of the business/profession which is subject to audit u/s 44AB
- There may be cases where there is difference between the amount claimed by the assessee and the amount computed by the auditor-
- In such cases it is quite possible that the client's claim is based on some judicial pronouncement on the subject. In such case the tax auditor should report the amount admissible with his comments in Form 3CA/ 3CB.
- If the claim of the assessee is well-founded and settled by judicial pronouncement the tax auditor may accept the claim but he has to record in his working papers that admissible amount has been reported on the basis of such judicial pronouncement. He may report the amount admissible with his comments in Form 3CA/ 3CB.
The auditor should take the following details from their clients to give a true and fair view about the company affairs:
- Quantitative details of raw material in case of trader and manufacturer. This clause is not applicable to service providers.
- In case of trading concern, quantitative details of principal items of goods traded is required to be disclosed, which are as follows:
- Opening Stock
- Purchases during the previous year
- Sales during the previous year
- Closing stock
- Shortage/ Excess, if any.
- Auditor should verify the stock details and also obtain certificates from the assessee in respect of the principal items of goods traded, the balance of opening stock, purchases, sales and closing stock and the extent of shortage/excess/damage and the reasons for the same.
- Principal items here would mean the items which constitute more than 10% of the aggregate value of purchases or sales.
- In case of Quantitative details of manufacturing concern, the auditor is required to verify the quantitative details of the principal items of raw materials, finished products and by-products, which are as follows:
(a). Raw Materials
- Opening stock
- Purchases during the previous year
- Consumption during the previous year
- Sales during the previous year
- Closing stock
- Yield of finished products
- Percentage of yield
- Shortage/excess, if any
(b). Finished products/By-products
- Opening stock
- Purchases during the previous year
- Quantity manufactured during the previous year
- Sales during the previous year
- Closing Stock
- Shortage/excess, if any.
- Auditor should check the details of purchase, consumption and production of principal items of raw materials and finished goods their yield including by-products.
- Information should be given only in respect of those items where it is practicable to do so, having regard to the records maintained by the Assessee.
- In case adequate records are not maintained / provided by the assessee, the auditor should report the same in Para 3 of Form 3CA or Para 5 of Form 3CB as the case may be. It could be as under:
- The assessee has not provided / maintained adequate records for our verification regarding the principal items of raw materials, finished products and by-products as required to be reported under clause 35(b) of Form 3CD or
- As explained by the assessee, keeping in view the nature, volume of the business and due to numerous items, it is not practically possible for the assessee to maintain any stock book to record quantities of each and every inward and outward of such goods on day-to-day basis, hence information under this clause is not feasible.
- Principal items here would mean the items which constitute more than 10% of the aggregate value of purchases, consumption or sales.
- The auditor should obtain the following certified documents for principal items of raw materials, finished products and by-products:
- Certificate from the assessee certifying the quantity and value of the opening stock, purchases, sales and closing stock.
- Certificate to the extent of shortage/excess/damage and the reasons for the same.
- Details of tax on distributed profits u/s 115-O which has been Omitted w.e.f. 01.04.2021.
- The auditor should check whether the assessee has received any amount in the nature of dividend u/ (22)(e)and if yes, the details need to be given:
(1). Payment should be made by closely held company i.e., a company in which public are not substantially interested (including unlisted public company).
(2). Payment should be by way of advance or loan or the payment should be on behalf, or for the individual benefit, of the shareholder.
(3). Shareholder must be a person who is the registered / beneficial owner of shares holding not less than 10% of the voting power or to a concern (Company / Firm / HUF / etc.) in which such shareholder is having substantial interest i.e., 20% or more. For this purpose, shareholder as an individual is to be considered and not along with his / her relatives.
(4). Dividend is deemed to the extent to which the company possesses accumulated profits on the date of giving loan / advance.
(5). The dividend taxable u/s 2(22) (e) is restricted to accumulated profits on the date of payment. Thus, the accumulated profits have to be determined as on the date of the payment. Further, if at any time earlier any amount has been taxed under any of the clauses of section 2(22) including clause (e), the accumulated profits will have to be reduced by the amount so taxed.
(6). Where the loan or advance is made by the closely held company to a concern, it is chargeable to tax in the hands of the shareholder and not in the hands of the concern till AY 2018-19. However, the position has been reverted back to be taxable in hands of the shareholder due to non-applicability of section 115-O from 1.4.2021.
(7). Section 2(22) (e) does not include any advance or loan made to a shareholder or the concern by a company in the ordinary course of its business, where the lending of money is a substantial part of the business of the company. Some of the decisions have held that `substantial part’ would indicate 20% i.e., where 20% or more funds have been deployed in the business of lending money the test of substantial part will be satisfied.
(8). Various courts have held that trade advances in the nature of commercial transactions would not fall within the ambit of the provisions of section 2(22)(e). Such cases need not be reported as 9. Few cases have also held that inter-corporate deposits are not loans.
(10). There are various cases in favor of assessee taking loan due to commercial expediency, etc. which the auditor should be aware of.
- The auditor should obtain list of all loans / advances received during the year by the assessee to test it for applicability of section 2(22)(e). In case the assessee has not received any such amount during the year, no reporting may be required under this clause.
- Where the assessee has received any loan or advance from any company, the auditor should obtain its list of shareholders to test 10% / 20% test as discussed above.
- The auditor should also obtain the financial statements of that company to ascertain its accumulated profits.
- The auditor may not be able to determine the accumulated profits of the closely held company making the payment for various reasons. He may not have access to the records of such closely held company, etc. In such a case the auditor should include appropriate remarks in clause (3) of Form No. 3CA or clause (5) of Form 3CB, as the case may be, about the methodology adopted by him, which could be as the assessee could not provide appropriate information / details to determine accumulated profits to enable us to report that the loan / advance received by the assessee is deemed dividend or not u/s 2(22) (e).
- He should also obtain from the assessee a certificate containing list of closely held companies in which he is beneficial owner of shares carrying not less than 10% of the voting power and list of concerns in which he has substantial interest.
- He should also obtain a certificate from the assessee giving particulars of any loans or advances received by any concern in which he has substantial interest from any closely held company in which he is beneficial owner of shares carrying not less than 10% voting power.
- If reliance has been placed on any judicial decision, a reference of the same may be given by the auditor as observations in clause (3) of Form No. 3CA or clause (5) of Form 3CB, as the case may be.
Amendment in Tax Audit Provisions
Finance Act, 2020 has introduced a proviso to sec 44AB (a) to encourage less-cash economy and to encourage digital transactions. If the turnover of the assessee is up to 5 crores and his cash receipts are up to 5% of total receipts and the cash payments are up to 5 % of total payments, then the assessee would not be required to get his books of accounts audited.The Finance Act, 2021 has increased the threshold limit of turnover for tax audit u/s 44AB from 5 crores to 10 crores where cash transactions do not exceed 5% of total transactions. This amendment will take effect from 1st April 2021 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year 2021-22. Thus, the higher limit of turnover will take effect from F.Y. 2020-21 itself.The Finance Act, 2021 has added a new second proviso to section 44AB (a) which is reproduced below-“Further it was provided that for the purposes of this clause, the payment or receipt, as the case may be, by a cheque drawn on a bank or by a bank draft, which is not account payee, shall be deemed to be the payment or receipt, as the case may be, in cash.”
As per provisions of section 44AB, turnover limit for tax audit has been increased from 1 crore to 10 crore if receipts and payment are within the permissible cash limit. The Finance Act, 2021 has introduced new proviso to section 44AB (a) wherein it has been stated that transactions through non account payee cheques shall be considered as deemed cash for this clause. This point is very important because large chunk of audit shall be governed on interpretation and adoption of this proviso. Here it is interesting to state that deeming provisions is with respect to only cheques and not for E-Payment or digital payment hence RTGS/NEFT etc. shall always be treated as non-cash. Now most important question is how to prove receipt and payment of cheque through account payee mode is a burning issue as assessee does not possess any documentary evidence thereof and only option left with the assessee to collect scanned copies of all cheques from the bank. After introduction of CTS clearing system, scanned copies all receipts and issued cheques remain with the banks but it is very cumbersome to get scanned copies of cheques from the bank looking to the magnitude of cheques. Though intention of the legislature is to ease the compliance burden of small assessee if they are dealing mostly through banking channel accordingly threshold limit for tax audit shall be 10 crore but
This will lead to a situation where the assessee has to prove that the transactions are indeed carried on through account payee cheques.
In the case of RTGS, NEFT or other digital modes of receipts or payments, there will not be any problem in proving that those transactions are carried on digitally in non-cash mode. The problem will be there in case of transactions carried on through cheques. Both the bearer/crossed and account payee cheques will be reflected as ‘cheque transactions’ in the bank statements. Thus it will not be possible for the assessee to prove that such cheque transactions are indeed account-payee cheque. It is also to be noted that, one needs to prove it for both the receipts of cheques and payments by cheques.Following observations can be made regarding the increased threshold limit for Tax Audit under section 44AB –
- The amendment is carried out only in section 44AB and no amendment has been made in section 44AD. Thus, the turnover limit of 2 crores for opting Section 44AD shall continue.
- The term aggregate of all receipts and aggregate of all payments‟ is very wide and covers not only receipts and payments on account of sale and purchase but also all other business transactions.
All the payments or receipts including capital introduction, drawings, receipt and repayment of loans, purchase of fixed assets, etc. shall be considered. Even taxes paid in cash shall be included for the calculation. In other words, all the receipts and payments made by the entity shall be considered for calculating total value of receipts and payments as well as the aggregate value of receipts or payments made in cash.
- It is not pointed out who will certify the margin of transactions in cash mode of 5%. It appears that assessee himself shall declare the percentage of receipts in cash and non-cash mode.
- This increased threshold limit for Tax Audit is applicable for a business entity only and the threshold limit for Tax Audit for a professional shall continue to be at 50 lacs even if more than 95% of the transactions are in digital mode.
- Any assessee whose turnover exceeds 10 crores (5 crores for A.Y. 2020-21), is required to get the books of accounts audited. The rate of profits declared, or method of receipt and payment is irrelevant.
Explanation of Deemed Cash for turnover purpose:
It is to be noted that cash receipts are to be compared with total receipts and cash payments are to be compared with total payments separately. Cash Receipts/Payments are not to be compared with aggregate of receipts and payments.
The expression “aggregate of all amounts received” denotes the Total Receipts of the assessee in cash and through banking channels. Total receipts invariably include receipt from sales or turnover of the business of the assessee. The words ‘in cash’ only includes receipts in cash mode only. In other words, the assessee must have received the amount in cash.
The words ‘said amount’ refers to “aggregate of all amounts received” (Total Receipts) and not to the turnover or sales amount.
Similarly, the expression “aggregate of all payments” denotes the Total Payments of the assessee in cash and through banking channels. Similarly, the words ‘said payment’ refer to the total payment which is invariably the “aggregate of all payments”.
In certain provisions, the law has used the words “an account payee cheque or an account payee bank draft or use of electronic clearing system through a bank account or through such other electronic mode as may be prescribed” and not the ‘cash’.
Hence transactions in the following modes will be regarded as transactions not carried on in cash-
- Account Payee Cheques
- Demand Draft/Pay Order
- Credit Card
- Debit Card
- Net Banking
- IMPS (Immediate Payment Service)
- UPI (Unified Payment Interface)
- RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement)
- NEFT (National Electronic Funds Transfer)
- BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money) Aadhaar Pay
CBDT has notified the ‘other electronic mode of payments’ by Notification No. 08/2020 dated 29.01.2020.
The limit of 5% receipt in cash or payments in cash is not limited to sale or purchase transactions. It rather covers all receipts and payments in cash including sales and purchases. In general receipts in cash of the following nature are included-
- Receipt on Sale of goods and services
- Receipt from debtors for the current year sales/outstanding receivables from earlier years
- Sale of fixed assets
- Sale of scrap
- Receipt of Loans and Advances
- Trade advances
- Receipt of deposits
- Sale of investments
- Some typical payments in cash of a business concern included are-
- Payments for Purchases
- Payment to Creditors for current year purchases/outstanding creditors
- Purchase of Fixed Assets and other Capital Expenditure
- Payments for salary, electricity, telephone charges, and other revenue expenditure
- Payments for Insurance
- Repayment of Loans and Advances
- Loans given
- Trade Advances given
- Deposits made, etc.
Issues while Computing the Limit of 5% Cash Transactions
Some of the issues in computing the limit of 5% cash transactions (receipts and payments) for the purpose of applicability of higher turnover limit of 5 crore u/s 44AB are discussed below-
1. Capital Contribution: When an Individual/sole proprietor introduces capital in his business in cash, then the same shall not be included in the total receipts in cash of the assessee. This is for the simple reason that one cannot transact with himself.However, the notified ITR forms do not follow this principle. It requires that all the cash receipt of the business including capital contribution should be considered in determining the 5% cash transactions limit.However, in case of partnership firms, the situation is different since a firm is assessed as a separate person under income tax law and is considered distinct from its partners. To clarify, if a firm receives any capital contribution in cash from any partner, it shall be counted towards the limit of 5%.
2. Direct cash deposit into bank account by customers: In this case, it will be included in cash transactions. Even if the assessee debits the bank account in his books, it will be regarded as a cash transaction since the account is ultimately settled in cash. It was held that depositing cash directly in the bank account of the supplier / beneficiary cannot be referred to as payment made through electronic clearing system, covered as an exception under Rule 6DD(c)(v); it was observed that the term use of electronic clearing system through bank account” as stipulated in Rule 6DD(c)(v) would necessarily include the transaction of funds by electronic mode through clearing system i.e. through electronic mode of transfer such as NEFT, RTGS, IMPS, etc.; thus it was opined that, such transaction by depositing cash directly in the bank account of the beneficiary is not routed through any clearing house nor is the money send through electronic mode and therefore such a transaction cannot be covered by Rule 6DD(c)(v) ”; Moreover it was noted that in the absence of adequate evidence to show that the assessee had deposited the amount on the instructions of the beneficiary or due to any business exigency there is no benefit of exemption.
3. Direct Cash deposit in creditors account: It will be included in computing cash payments of the assessee since the account is ultimately settled in cash.
4. Receipts/Payments in bearer cheques: In case the amount is received by a ‘bearer cheque’ and the same is used for withdrawing cash from the payer’s account, it will amount to a cash transaction.
5. Capital Expenditure: All the payments in cash are included whether it is paid for revenue expenditure or capital expenditure. There is no differentiation provided in the law.
6. Capital Receipt/Exempt Income- All receipts include receipts of capital nature and also the exempt income for e.g. Agricultural Income.
7. Adjustment by book entry: In a case where a person is a customer as well as vendor of the assessee. The debtors’ amount is set-off with the amount payable to the same person/vendor. Since no cash is involved in settling the due amount, this will be considered as non-cash transactions.
8. Cash deposited and Cash Withdrawals from bank account: Cash deposit and the cash withdrawals from the bank account amounts to contra entry or transactions with self and hence are excluded for computing the 5% cash limit.
Thus, any receipt of advance, receipt and repayment of loan, direct and indirect expenses, etc. – every transaction is covered in calculating the limit of 5% transactions in cash.
In order to compute the limit, the assessee should aggregate all the receipts from his cash ledger and bank ledger and then find out the percentage of cash receipts.
Similarly, the assessee should aggregate all the payments from his cash ledger and bank ledger and then find out the percentage of cash payments.
If both the cash receipts and cash payments is 5% or less, he shall get the benefit of higher turnover limit of 5 crore for tax audit. Otherwise, the limit of turnover for applicability of tax audit shall be 1 crore.
Conditions for the Applicability of New provisions of tax audit
Limit of 10 is crore applicable when following conditions are satisfied:
- aggregate of all amounts received in cash does not exceed 5% of the said amount; and
- aggregate of all payments made in cash does not exceed 5% of the said payment
The benefit of the increased threshold limit of 10 crores for the tax audit is entitled only when both cash receipts and cash payments does not exceed 5%. In case any of them exceeds 5%, entitlement to get benefit of threshold is cancelled.
The persons engaged in the profession aren’t entitled to claim enhanced turnover limit of 10 crore for the tax audit.
The following table shows the different situations under which the books of accounts are to be audited under section 44AB of the Act.
| Sr. No. | Person | When required to get accounts audited in terms of section 44AB | Clause of section 44AB |
| 1. | Every person carrying on profession referred to in section 44AA(1) profits from which are assessable on presumptive basis under section 44ADA | If he claims his profits and gains from such profession are lower than 50% of his gross receipts for the previous year in question and his total income exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax in any previous year | Clause (d) |
| 2. | Every person carrying on profession [other than those covered by clause (d) of section 44AB] | If his total gross receipts from profession exceed 50 lacs in any previous year | Clause (b) |
| 3. | Every person who derives income of the nature referred to in section 44B or section 44BBA | Section 44AB does not apply to such person & hence no need to get accounts audited u/s 44AB | 2ndproviso to section 44AB |
| 4. | Every person carrying on business profits of which are assessable on presumptive basis under section 44AE or section 44BB or section 44BBB | If he claims his profits and gains from such business are lower than the amount deemed to be profits and gains under the said section | Clause (c) |
| 5. | Every person carrying on business where the provisions of section 44AD(4) are applicable in his case | If his total income exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax in any previous year Section 44AB shall not apply to the person who declares profits and gains for the previous year in accordance with section 44AD(1) and his total sales, turnover or gross receipts, as the case may be, in business does not exceed 2 crore [first proviso to section 44AB] | Clause (e) first proviso |
| 6. | Every person carrying on any agency business | If his total sales, turnover or gross receipts , as the case may be, in business exceed or exceeds 1 crore in any previous year | Clause (a) |
| 7. | Every person carrying on business who is earning income in the nature or commission or brokerage | If his total sales, turnover or gross receipts , as the case may be, in business exceed or exceeds 1 crore in any previous year | Clause (a) |
| 8. | Every person carrying on profession referred to in section 44AA(1) who is also carrying on any business | Gross receipts of profession and business not to be clubbed for computing the limits of 1 crore [clause (a)] and/or 50 lacs [clause (b)]. Account of profession to be audited if clause (b) or (d) of | Clause (a) |
| section 44AB applies. Accounts of business to be audited if total sales, turnover or gross receipts, as the case may be, in business exceed or exceeds 1 crore in any previous year since section 44AD is not applicable to person carrying on profession referred to in section 44AA(1) | |||
| 9. | Every “eligible assessee” (as defined in section 44AD) carrying on “any eligible business” (as defined in section 44AD) turnover of which exceeds 2 crores in any previous year, and proviso to sec 44AB (a) not applicable.Both payment and receipt in cash does not exceed 5% of the total receipts and payment respectivelyEither payment or receipt in cash exceeds 5% of the total receipts and payment respectively | Assessee not eligible to opt for section 44AD. Therefore, he must get his accounts audited in terms of section 44AB(a) since his turnover exceeds 2 crores and thus exceeds 1 crore limit in clause (a) Audit u/s 44AD not applicable if total sales, turnover or gross receipt from business during the previous year does not exceed 10 crore If total sales, turnover or gross receipt from business during the previous year exceeds 1 crore |
Clause (a) Proviso to Clause (a) Clause (a) |
| 10. | Every assessee who is not an “eligible assessee” as defined in section 44AD i.e. LLPs, companies, AOPs, BOIs, AJPs | If total sales, turnover or gross receipts , as the case may be, in business exceed or exceeds 1 crore in any previous year | Clause (a) |
| 11. | Every non-resident assessee not covered by section 44AE or 44B or 44BB or 44BBA or 44BBB | If total sales, turnover or gross receipts , as the case may be, in business exceed or exceeds 1 crore in any previous year | Clause (a) |
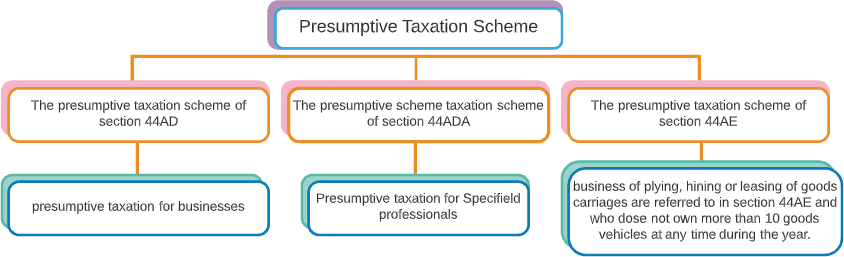
Presumptive Taxation
The presumptive scheme of taxation reduces compliance burden on small professions and facilitates ease of doing business. Under the presumptive scheme of taxation, profits are presumed at 50% of the gross receipts. The following Indian assessees are eligible: Individuals Hindu undivided families (HUFs) Partnership firms (note that limited liability partnerships are not eligible)Presumptive taxation for businesses is covered under section 44AD of the income tax act. Any business which has a turnover of less than 2 crore can opt to be taxed presumptively. They must declare profits of 8% for non-digital transactions or 6% for digital transactions, whichever one is applicable. The following businesses are excluded from presumptive taxation:
- Life insurance agents.
- Commission of any kind.
- Running the business of plying, hiring or leasing goods carriages.
- National Defense Fund set up by the Central Government.
- Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund.
- In presumptive taxation under Section 44AD, your net income is considered as 8% of your turnover and you will pay tax on that income.
- If your receipts are in digital (non-cash) form then only 6% of your receipts are your net income and you will pay tax on that income.
- You don’t have to maintain accounting records.
- You don’t have to get your accounting records audited.
- You have to pay advance tax – but instead of estimating income and paying tax each quarter, you can pay all your advance tax before March 31. Advance tax, for taxpayers having opted for the presumptive scheme, is to be paid by 15th March of the relevant financial year if you expect that your income tax liability will exceed 10,000 in the financial year.
A person who is carrying on any agency business and a person who is earning income in the nature of commission or brokerage cannot adopt the provisions of section 44AD.
Any person opting for the presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD is liable to pay whole amount of advance tax on or before 15th March of the previous year. If he fails to pay the advance tax by 15th March of previous year, he shall be liable to pay interest as per section 234C.
Note: Any amount paid by way of advance tax on or before 31st day of March shall also be treated as advance tax paid during the financial year ending on that day.
Eligible professionals under Section 44ADA
To reduce the burden of compliance of small taxpayers, the Government provides for a scheme of Presumptive Taxation which is very easy to understand and comply with. Under the scheme of Presumptive Taxation, the small taxpayers are not required to maintain any books of accounts and their profits are presumed to be a certain percentage of the Total Sales.To encourage businesses to receive payments digitally, the Government has also provided an incentive to Businesses who receive payments digitally. Profits on payment received digitally by businesses would be considered at 6% of the total amount received digitally. This incentive is applicable from Financial Year 2016-17 onwards.
For payments received in cash, the profits would continue to be considered at 8%. The above incentive is only provided to businesses under Section 44AD and not for Professionals or Transporters.After computing the Profits, the business would be required to pay Tax on such Profits as per the Income Tax Slab rates applicable. Any person opting for the presumptive taxation scheme under section 44ADA is liable to pay whole amount of advance tax on or before 15th March of the previous year. If he fails to pay the advance tax by 15th March of previous year, he shall be liable to pay interest as per section 234C.Earlier, the presumptive scheme of tax was applicable only for small business.Section 44ADA was introduced to extend the scheme of simplified presumptive taxation to specified professionals.
Professionals engaged in the following professions are eligible:
- Interior decorations
- Technical consulting
- Engineering
- Accounting
- Legal
- Medical
- Architecture
Other professionals, as mentioned below:
- Movie artists include a producer, editor, actor, director, music director, art director, dance director, cameraman, singer, lyricist, story writer, screenplay or dialogue writer and costume designers.
- Authorized representative means a person who represents another person for a fee before a tribunal or any authority constituted under any law. It does not include an employee of the person so represented or a person who is carrying on the profession of accountancy
- Any other notified professionals- certain sports-related persons, company secretaries and information technology.
Taxpayers should note that the facility of presumptive taxation is available exclusively for a resident who is an Individual, HUF or Partnership but not a Limited Liability Partnership Firm or Corporate assessees. With effect from Assessment Year 2021-22, the Finance Act, 2021 has restricted the benefit of section 44ADA only to a resident person being individual and partnership firm (other than LLP).Under the presumptive taxation schemes, the taxpayer can declare profits as a percentage of the total turnover (sales) or gross receipts. These declared profits are considered to be the business income of the assessee. A taxpayer who has opted for the scheme need not maintain detailed books of accounts. Similarly, under Section 44ADA, it is not necessary for small taxpayers to maintain books of accounts and the profits are calculated as a percentage of the total sales.
Presumptive Assessment Rate for ProfessionalsThe income of any professional under this section is considered to be 50% of the total gross receipts for the year, as they usually assumed that they do not incur many expenses. The professionals under this scheme are not required to maintain books of accounts. However, if they claim that their income is less than 50% of the total gross receipts and if the total income exceeds the basic exemption limit, they cannot be qualified to be classified under Section 44ADA. In such a case, they will have to maintain books of accounts to as per Section 44AA and these needs to be audited as per Section 44AB.
Opting out of the Scheme under Section 44ADAUnlike the restriction placed on businesses that have opted for the scheme under Section 44AD, the professionals under Section 44ADA can opt-in and opt-out at any time. The professionals can do so without the five-year restriction.
Conditions to Claim Deduction under Section 44ADA of Income Tax Act
The following are the conditions under which an assessee can claim a deduction under sec 44ADA:
- The assessee is a resident of India
- The assessee is an individual taxpayer, HUF, or a partnership firm excluding LLP
- Profession being carried on is prescribed under section 44AA of income tax act
- An assessee whose total gross receipts do not exceed fifty lakh rupees in a financial year
Under section 44ADA of the income tax act, the higher of the following is offered to tax:
- 50% of total gross receipts in a financial year
- Income offered by the assessee from the profession
For example-
| Particulars | Case I | Case II | ||
| FY 2019-20 | Under Normal Provisions | Under Presumptive Scheme | Under Normal Provisions | Under Presumptive Scheme |
| Gross Receipts | 20,00,000 | 20,00,000 | 30,00,000 | 30,00,000 |
| Less: Expenses | 7,00,000 | 10,00,000 | 17,00,000 | 15,00,000 |
| Taxable Income Chargeable To Tax | 13,00,000 | 10,00,000 | 13,00,000 | 15,00,000 |
Hence, in case I, the presumptive Scheme is beneficial but not for case II.
Maintenance of Books of Accounts and Tax Audit
An assessee opting for a presumptive income under section 44ADA will be exempt from the following:
- Maintaining the books of accounts under section 44AA
- Tax audit of books of accounts under section 44AB
However, if an assessee fulfills the following conditions then he/ she will be under the purview. Hence he/ she will be required to maintain books of accounts along with compliance of getting the books of accounts audited by a Chartered Accountant.
- an assessee claims that his/ her profits and gains from the profession are lower than 50% of the gross receipts
- An assessee whose total income exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax. The maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax is the basic slab exemption. For example- For a taxpayer, not being a senior citizen, the basic slab exemption is 2.5 lakh.
International Transaction
If you work for clients out of India, payments may be received by you via paypal or as a direct credit to your bank account. Mostly, the foreign client would deduct taxes before releasing the payment to you in accordance with the local tax laws there. You, as a resident of India, would anyway be liable to income tax on all your income. However, you can claim credit for taxes paid overseas, in your return of income.If you are paying taxes on your foreign income in that foreign country, then you can claim tax relief on taxed income (which was taxed twice), while filing return in India as per DTAA, entered between India and that particular foreign country.
TDS not deducted by the foreign clientIf no TDS has been deducted, there is nothing to worry. You need to include these receipts in your total income while making income calculations and pay applicable tax on them since you will be a tax resident of India. To meet advance tax requirements you may have to estimate your annual income from all sources.
Return of IncomeAn individual of HUF carrying on business will be bound to file his return of income in form ITR 3For a taxpayer who opts for presumptive tax is supposed to file his return in ITR 3.If you receive income from a foreign client in your foreign bank account, even then it will be taxed in India, if you are an Indian resident.
Presumptive Taxation for Business and Profession
Selecting the Legal Entity - Setting up a new venture one of the first questions you encounter when you begin your business is what legal entity it should be set up as. Depending on the nature and size of the business some of the legal entity options available are:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Limited Liability Partnership
- Private Company
- Public Company
- Joint Venture
As such, there is no legal rule that a ‘company’ must be formed to start a business. Incorporating a company has its own pros and cons. Forming a company, increases compliance work. If your business is growing rapidly and becomes unmanageable, it helps to separate it into a separate legal entity which will have its own PAN and will file a separate tax return. Else you may choose to carry on your business as a sole proprietor.
Maintaining Books of AccountsIf as a business any of the following criteria are met, then maintaining the books of accounts as per the income tax act is mandatory:
- Income is more the 1,20,000; or
- Total sales, turnover or gross receipts are more than 10,00,000. In any of the three immediately preceding previous years. This condition has further been relaxed for individuals and HUF where they will be bound by the mandate of maintaining books of accounts only if :
- Income is more than 2.5 lakhs or
- Total sales, turnover or gross receipts are greater than 25 lakhs in any of the three immediately preceding previous years.
The penalty for non-maintenance of books of accounts:
If you have not maintained the accounting records which you should have maintained as per law, you would be liable for a penalty of up to 25,000.
For businesses having gross receipts of more than 1 crore in a financial year are liable for tax audit. The due date of filing the tax audit report is 30th September of the assessment year. The tax audit report must be filed electronically via Form 3CD. For taxpayers subject to tax audit, the due date for filing of return of income is also 30th September of the assessment year. Under normal circumstances, revision of a tax audit report is not possible. However, in cases where the accounts have been revised it is possible to revise the tax audit report.
Due Date- Due date for filing of tax audit report– 30th September of the assessment year
- Due date for return filing (if tax audit is applicable)– 30th September of the assessment year
- Due date for return filing (if tax audit is not applicable)– 31st July of the assessment year
Professions for the purpose of Indian tax laws are:
- Engineering
- Legal
- Architectural profession
- Accountant
- Medical
- Technical consultant
- Interior decoration
- Maintenance of books of accounts
- Professionals carrying on specified professions
Professionals carrying on the above mentioned specified professions are required to maintain books of accounts in accordance with Rule 6F of the Income tax Rules. Such professionals will be required to maintain accounting records if gross receipts exceed 1.5 lakhs in any of the 3 immediately preceding years. In case he has started off with his profession in a particular year and his receipts exceed 1.5 lakhs for that year, he is again supposed to maintain accounting records for that year.
- Cash Book– A book to record all the cash receipts and payments which helps you know your cash balance at the end of the day or end of the month.
- Journal– You have to maintain a log of all your day to day transactions. In accounting terms, you have to record all the debits and credits, when you are following the mercantile system of accounting.
- Ledger– A book where all your entries flow from journal, has details of all the accounts and simplifies the preparation of your financial statements at the end of a year.
- You have to maintain photocopies of all the bills or receipts if the value is more than 25.
- Lastly, you have to maintain the original bills or receipts if the value is more than 50. If you are into the medical professions, you must maintain these additional records too.
- Daily case registers with details of patients, fees received, services provided and date of receipt.
- Stock details of the medicines and other consumable items on the daily basis.
Professionals carrying on non-specified professions
If you are carrying on any profession other than those discussed above, you would need to maintain such books of accounts so as to enable an assessing officer to calculate your taxable income as per Income tax laws. However, this mandate would arise only when income, if you are an individual, exceeds 2.5 lakhs or gross receipts are more than 25 lakhs in any one of the immediately 3 preceding years.
Computation of Taxable Income
A professional could easily arrive at his taxable “Income under the head Profits and Gains from Business or Profession” by reducing all his profession related expenses from this gross receipts out of the profession. The profession related expenses could be salary (if you have engaged someone), rent for the premises from where you are carrying out your profession, internet expenses, mobile expenses, official travel, lunch expenses (met officially) etc.
Tax Filing
As a professional, the form applicable to you is ITR 3. You will be liable to file your return on or before 31st July of the Assessment Year unless you are subject to an audit under the Income-tax Act.
Applicability of Tax Audit
You would be liable for carrying out a tax audit if your gross revenue from profession exceeds 25 lakhs during any given financial year, Failure to get your books audited can attract a penalty of upto 0.5% of your gross revenue of 1.5 lakhs whichever is lower.
Presumptive Taxation
A professional having a gross revenue upto 50 lakhs can opt for the presumptive scheme of tax wherein he can straightaway offer 50% of the gross revenue as his taxable income and pay taxes as per his slab rates on such income. Once he opts for this scheme, he cannot claim any of the profession related expenses as a deduction again.
Further, anyone opting for this scheme is not bound by the mandate of maintaining books of accounts too. While he is also liable to file his return by 31st July of the assessment year, he must file his return in ITR 4.Further, he will be liable for tax audit in a scenario where he offers income lesser than the income arrived at on presumptive basis and also his income exceeds the basic exemption limit.
Freelancers Income
Freelancers who are into any of the specified or non-specified professions, get covered under the same rules as applicable to any other full-time specified or non-specified professional be it rules of computation of taxable income and tax liability, maintenance of books of accounts, presumptive tax, return filing etc.
The presumptive taxation scheme of section 44AE
The presumptive taxation scheme of section 44AE can be adopted by a person who is engaged in the business of plying, hiring or leasing of goods carriages and who does not own more than 10 goods vehicles at any time during the year.
In case of a person who is willing to opt for the presumptive taxation scheme of section 44AE, for Heavy Goods Vehicle, income will be computed at the rate of 1,000 per ton of gross vehicle weight for every month or part of a month during which the heavy goods vehicle is owned by taxpayer. In case of vehicles other than heavy goods vehicle, income will be computed at the rate of 7,500 for every month or part of a month during which the goods carriage is owned by taxpayer. Part of the month would be considered as full month.
A partnership firm adopting the provisions of section 44AE can claim further deduction on account of remuneration and interest paid to partners (computed as per the Income-tax Act) from the income computed at the presumptive rate.For provisions of presumptive taxation for Transporters under Section 44AE, Tax @ 7500 per vehicle for Transporters.
Amendments introduced in Section 44AD vide Various Finance Acts
- The Salary/ Remuneration/ Interest paid to Partners would also not be allowed to be claimed as a deduction.
- Businesses claiming benefit of Section 44AD would also be required to comply with the provisions of Advance Tax. However, to keep the compliance at minimum in such cases – the business would be required to pay 100% of the tax applicable by 15th March of the Financial Year. No other provisions of Advance Tax would apply in this case.
To encourage business to receive payments digitally, the Govt. has also decided to give several incentives to businesses who receive the payments digitally. One such incentive is that if a business receives payments digitally, he can claim his Income to be 6% of the total payments received digitally i.e. through Cheque/ Demand Draft/ Debit Cards/ Credit Cards/ NEFT/ RTGS or any other Cashless mode.For all payments received digitally, the profits would be assumed at 6% of such payments provided the payment is received during the year or before the due date of filing of Income Tax Return under Section 139(1).For all payments received in cash, the assumed profit percentage would be remaining the same i.e. 8%.
- Section 44AD applies to all businesses except the business of plying, hiring or leasing goods. Section 44AD won’t apply in case of plying, hiring or leasing of goods as these have already been covered under section 44AE.
- Section 44AD won’t apply in case of Agency Business as well as in case of a business earning income from Commission or Brokerage.
- As Section 44AD specifically mentions the word business, therefore section cannot be applied in case of professionals.
- Section 44AD only applies in case of Individuals; Partnership & HUF provided they are Resident in India. This section does not apply in case of Limited Liability Partnerships as they have been specifically excluded from this section.
In case a person opts out of the provisions of Section 44AD – he would also be required to get his accounts audited under Section 44AB by a Chartered Accountant.
- In case an assessee is carrying on more than 1 business, the total turnover of all the businesses should be taken into account.
- However, if the assessee is carrying on business as well as profession, Section 44AD can be applied on the income earned from business. Computation of Income earned from Profession would be computed as per the normal provisions of the Income Tax Act.
- An assessee declaring his income as per presumptive taxation under section 44AD can also claim tax benefit of deductions under chapter VI-A
- In case an assessee is applying presumptive taxation under section 44AD, he should file his income tax return in ITR Form 4 – Sugam
Budget 2021 also announced an increase in the limit for tax audit for persons who are undertaking 95% of their transactions digitally from 5 crore to 10 crore under section 44AB.
Applicability of tax audit provisions in a nutshell
The applicability of tax audit provisions from Assessment Year 2020-21 can be understood with the help of following table:
| Nature of Business or Profession | Category of Taxpayer | When audit is Mandatory? |
| Any Professions (Specified or Non-specified) | Any | If Gross Receipts from Profession during the relevant previous year exceeds 50 lakhs |
| Business | Both the Payment and Receipt in case does not exceed 5% of the Total Receipts and Payments respectively. | If total Sales, Turnover or Gross Receipts from Business during the previous year exceeds 5 Crore. |
| Either payment or receipt in cash exceeds 5% of the total receipts and payment respectively | If total sales, turnover or gross receipt from business during the previous year exceeds 1 crore | |
| Business eligible for Presumptive Tax Scheme under Section 44AD | Resident Individual or HUF | If income of assessee exceeds the maximum exemption limit and he has opted for the scheme in any of the last 5 previous years but does not opt for the same in current year. |
| Business eligible for Presumptive Tax Scheme under Section 44AD | Resident Partnership Firm | Taxpayer has opted for the scheme in any of the last 5 previous years but does not opt for the same in current year. |
| Profession eligible for Presumptive Tax Scheme under Section 44ADA | Resident Assessee | Taxpayer claims that his profits from profession are lower than the profits computed under Section 44ADA and total income exceeds the maximum exemption limit |
| Business eligible for Presumptive Tax Scheme under Section 44AE | Any Assessee engaged in plying, hiring or leasing of goods carriage | Taxpayer claims that his profits from business are lower than the profit computed under Section 44AE |
| Business eligible for Presumptive Tax Scheme under Section 44BB | Non-resident assessee engaged in exploration of mineral oil | Taxpayer claims that his profits from business are lower than the profit computed under Section 44BB |
| Business eligible for Presumptive Tax Scheme under Section 44BBB | Foreign Company engaged in civil construction | Taxpayer claims that his profits from business are lower than the profit computed under Section 44BBB |
How is advance tax calculated and paid?
Advance tax is to be calculated on the basis of expected tax liability of the year. Advance tax is to be paid in installments as given below:
- In case of all the assessees (other than the eligible assessees as referred to in section 44AD and 44ADA) :
- Atleast to 15 per cent – On or before 15th June
- Atleast to 45 per cent – On or before 15th September
- Atleast to 75 per cent – On or before 15th December
- Atleast to 100 per cent –On or before 15th March
- In case of eligible assessee as referred to in section 44AD and 44ADA: 100 per cent – On or before 15th March
Note: Any tax paid on or before 31st day of March shall also be treated as advance tax paid during the same financial year.The deposit of advance tax is made through Challan ITNS 280 by ticking the relevant column, i.e., advance tax.
Tax Audit and ITR date Extension
It is important for all taxpayers to remember the due date of filing income tax returns. The due date varies on the basis of taxpayers. For instance, salaried individuals are usually required to file their income tax returns by the 31st of July whereas corporates covered under audit can file their returns by 31st September of the assessment year (unless extended by the government). Income tax filing due dates for FY 2020-21 (AY 2021-22)
| Category of Taxpayer | Due Date for Tax Filing –FY 2020-21 | Due Date for Tax Filing-FY 2021-22*(unless extended) |
| Individual / HUF/ AOP/ BOI (books of accounts not required to be audited) | 31st December 2021 (extended from 31st July) | 31st July 2022 |
| Businesses (Requiring Audit) | 15th February 2022 (extended from 31st October 2021) | 31st October 2022 |
| Businesses (Requiring TP Report) | 28th Feb 2022 (extended from 30th Nov 2021) | 30th November 2022 |
| Due Date | Tax Due |
| 15th June 2021 | Due date for the first installment of advance tax for the FY 2021-22 |
| 15th September 2021 | Due date for the second installment of advance tax for the FY 2021-22 |
| 15th December 2020 | Due date for the third installment of advance tax for the FY 2021-22 |
| 31st December 2021 | Income tax return filing for FY 2020-21 for individuals and entities not liable for tax audit and who have not entered into any international or specified domestic transaction |
| 15th January 2022 | Submission of audit report (Section 44AB) for AY 2021-22 for taxpayers liable for audit under the Income Tax Act. |
| 31st January 2022 | Submission of audit report for AY 2021-22 for taxpayers having transfer pricing and specified domestic transactions |
| 15th February 2022 | ITR filing for taxpayers requiring audit (not having international or specified domestic transactions). |
| 28th February 2022 | ITR filing for TP cases (for taxpayers having international and specified domestic transactions). |
| 15th March 2022 | (i).The fourth installment of advance tax due for the FY 2021-22 (ii).The due date for the whole amount of advance tax for FY 2020-21 for taxpayers covered under the presumptive scheme of Section 44AD and 44ADA |
| 31st March 2022 | Last date for filing a belated return or revised return for FY 2020-21. |
If the due date for filing the original return of income is missed, one can file a return later after the due date, called a belated return. The income tax department also specifies the due date of filing the belated return. This date is now reduced by three months to 31st December of the assessment year (unless extended by the government).
However, the CBDT has extended the due date for filing the revised or belated return for FY 2020-21 from 31st December 2021 to 31st March 2022.Filing returns beyond the deadline can attract a penalty of up to 10,000. Hence, it is advisable for timely filing of income tax returns unless in exceptional circumstances.If the taxpayer wants to revise the original return due to some amendments, the same can be done using revised return u/s 139 (5). You can file a belated return on or before 31st December of the assessment year. For A.Y. 2021-22, CBDT has extended the due date for filing a belated return from 31st December 2021 to 31st March 2022.Taxpayers cannot file any return once this date is passed. However, if the return was missed due to an extreme situation, you can lodge a request to your A.O. seeking permission to file past returns u/s 119.
The due date of Audit Report and ITR Filing by Trust & NGO
Section 139 is a complete code in itself and it provides the persons who are required to file the return, categories of persons who are required to file, different situations in which the return may be required even without income, due date within which the return should be filed by the taxpayers, etc. Section 139 read with section 119 further empowers the CBDT to further relax the due date if the circumstances or situation so demands.
The assessee other than an assessee referred to in clause (aa) is —
- a company; or
- a person (other than a company) whose accounts are required to be audited under this Act or under any other law for the time being in force; or
- a partner of a firm whose accounts are required to be audited under this Act or under any other law for the time being in force or the spouse of such partner if the provisions of section 5A applies to such spouse]
The 1st day of October of the assessment year; It may be noted that the due date is 31st October for certain categories of person specified therein. In clause (ii), it includes “a person (other than a company) whose accounts are required to be audited under this Act or under any other law for the time being in force;”One may note that the trusts are required to get the books of accounts audited under the relevant Act also wherein it is registered. Normally, trusts are registered either under the Society Act, Companies Act, Trust Act etc. All such Act throughout the country stipulates to get the books of accounts of trust audited as a mandatory condition.
Further, the Income Tax Act also provides for the audit of the trust if the income (i.e., gross receipts in general) of such trust exceeds the amount which is not chargeable to tax (i.e., 2.50 Lakh for most of the trust as this is the basic exemption limit which is applicable to individual assessee).In short, the trusts are required to get the books of accounts audited under the Respective Act of their registration as well as under the Income Tax Law.The due date of filing the income tax return is often relaxed / extended by the CBDT to take care of special situations & problems in filing the income tax return. This date of 31st October for the FY 2020-21 was extended to 15th February 2022 by the CBDT vide Circular No.9/2021 dated 20.05.2021 and Circular No.17/2021 dated 09.09.2021. This date is further extended to 15th March 2022 now by Circular NO. 1/2022 dated 11.02.2021.
In short, the due date of filing the audit report by the trust shall be 15th February 2022 now for the FY 2020-21. It may be noted that there is no special or separate due date for FCRA registered NGO. The date applicable to normal trust would be applicable even to the FCRA registered NGO.
Section 139(1) - Return of incomeEvery person,—
- being a company or a firm; or
- being a person other than a company or a firm, if his total income or the total income of any other person in respect of which he is assessable under this Act during the previous year exceeded the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax,
shall, on or before the due date, furnish a return of his income or the income of such other person during the previous year, in the prescribed38 form and verified in the prescribed manner and setting forth such other particulars as may be prescribed : Provided that a person referred to in clause (b), who is not required to furnish a return under this sub-section and residing in such area as may be specified by the Board in this behalf by notification in the Official Gazette, and who during the previous year incurs an expenditure of fifty thousand rupees or more towards consumption of electricity or at any time during the previous year fulfils any one of the following conditions, namely :—
- is in occupation of an immovable property exceeding a specified floor area, whether by way of ownership, tenancy or otherwise, as may be specified by the Board in this behalf; or
- is the owner or the lessee of a motor vehicle other than a two-wheeled motor vehicle, whether having any detachable side car having extra wheel attached to such two-wheeled motor vehicle or not; or
- has incurred expenditure for himself or any other person on travel to any foreign country; or
- is the holder of a credit card, not being an “add-on” card, issued by any bank or institution; or
- is a member of a club where entrance fee charged is twenty-five thousand rupees or more,
shall furnish a return, of his income during any previous year ending before the 1st day of April, on or before the due date in the prescribed form and verified in the prescribed manner and setting forth such other particulars as may be prescribed : Provided further that the Central Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, specify the class or classes of persons to whom the provisions of the first proviso shall not apply and that every company or a firm shall furnish on or before the due date the return in respect of its income or loss in every previous year.
A person, being a resident other than not ordinarily resident in India within the meaning of clause (6) of section 6, who is not required to furnish a return under this sub-section and who at any time during the previous year,—
- holds, as a beneficial owner or otherwise, any asset (including any financial interest in any entity) located outside India or has signing authority in any account located outside India; or
- is a beneficiary of any asset (including any financial interest in any entity) located outside India,
shall furnish, on or before the due date, a return in respect of his income or loss for the previous year in such form and verified in such manner and setting forth such other particulars as may be prescribed: Provided also that nothing contained in the fourth proviso shall apply to an individual, being a beneficiary of any asset (including any financial interest in any entity) located outside India where, income, if any, arising from such asset is includible in the income of the person referred to in clause (a) of that proviso in accordance with the provisions of this Act: Provided that every person, being an individual or a Hindu undivided family or an association of persons or a body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, or an artificial juridical person, if his total income or the total income of any other person in respect of which he is assessable under this Act during the previous year, without giving effect to the provisions of clause (38) of section 10 or section 10A or section 10B or section 10BA or section 54 or section 54B or section 54D or section 54EC or section 54F or section 54G or section 54GA or section 54GB or Chapter VI-A exceeded the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax, shall, on or before the due date, furnish a return of his income or the income of such other person during the previous year, in the prescribed form and verified in the prescribed manner and setting forth such other particulars as may be prescribed:
Provided also that a person referred to in clause (b), who is not required to furnish a return under this sub-section, and who during the previous year—
- has deposited an amount or aggregate of the amounts exceeding one crore rupees in one or more current accounts maintained with a banking company or a co-operative bank; or
- has incurred expenditure of an amount or aggregate of the amounts exceeding two lakh rupees for himself or any other person for travel to a foreign country; or
- has incurred expenditure of an amount or aggregate of the amounts exceeding one lakh rupees towards consumption of electricity; or
- fulfils such other conditions as may be prescribed,
shall furnish a return of his income on or before the due date in such form and verified in such manner and setting forth such other particulars, as may be prescribed.]
Every person in receipt of income derived from property held under trust or other legal obligation wholly for charitable or religious purposes or in part only for such purposes, or of income being voluntary contributions referred to in sub-clause (iia) of clause (24) of section 2, shall, if the total income in respect of which he is assessable as a representative assessee (the total income for this purpose being computed under this Act without giving effect to the provisions of sections 11 and 12) exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax, furnish a return of such income of the previous year in the prescribed form and verified in the prescribed manner and setting forth such other particulars as may be prescribed and all the provisions of this Act shall, so far as may be, apply as if it were a return required to be furnished under sub-section (1).
If the total income in respect of which such research association, news agency, association or institution, person or fund or trust or university or other educational institution or any hospital or other medical institution or trade union or body or authority or Board or Trust or Commission or infrastructure debt fund or Mutual Fund or securitization trust or venture capital company or venture capital fund is assessable, without giving effect to the provisions of section 10, exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax, furnish a return of such income of the previous year in the prescribed form47 and verified in the prescribed manner and setting forth such other particulars as may be prescribed and all the provisions of this Act shall, so far as may be, apply as if it were a return required to be furnished under sub-section (1).
The assessee shall be liable to pay simple interest at fifteen per cent per annum, where the return under sub-section (1) or sub-section (2) or sub-section (4) for an assessment year is furnished after the specified date, or is not furnished.
Specified date”, in relation to a return for an assessment year, means,—
- in the case of every assessee whose total income, or the total income of any person in respect of which he is assessable under this Act, includes any income from business or profession, the date of the expiry of four months from the end of the previous year or where there is more than one previous year, from the end of the previous year which expired last before the commencement of the assessment year or the 30th day of June of the assessment year, whichever is later;
- in the case of every other assessee, the 30th day of June of the assessment year.
Where the Assessing Officer considers that the return of income furnished by the assessee is defective, he may intimate the defect to the assessee and give him an opportunity to rectify the defect within a period of fifteen days from the date of such intimation or within such further period which, on an application made in this behalf, the Assessing Officer may, in his discretion, allow; and if the defect is not rectified within the said period of fifteen days or, as the case may be, the further period so allowed, then, notwithstanding anything contained in any other provision of this Act, the return shall be treated as an invalid return and the provisions of this Act shall apply as if the assessee had failed to furnish the return : Providedthat where the assessee rectifies the defect after the expiry of the said period of fifteen days or the further period allowed, but before the assessment is made, the Assessing Officer may condone the delay and treat the return as a valid return.
A return of income shall be regarded as defective unless all the following conditions are fulfilled, namely:—
- (a). the annexures, statements and columns in the return of income relating to computation of income chargeable under each head of income, computation of gross total income and total income have been duly filled in;
- (b). the return is accompanied by a statement showing the computation of the tax payable on the basis of the return;
- (c). the return is accompanied by the report of the audit referred to in section 44AB, or, where the report has been furnished prior to the furnishing of the return, by a copy of such report together with proof of furnishing the report;
- (d). the return is accompanied by proof of—
- (i). the tax, if any, claimed to have been deducted or collected at source and the advance tax and tax on self-assessment, if any, claimed to have been paid : Provided that where the return is not accompanied by proof of the tax, if any, claimed to have been deducted or collected at source, the return of income shall not be regarded as defective if—
- a certificate for tax deducted or collected was not furnished under section 203 or section 206C to the person furnishing his return of income;
- such certificate is produced within a period of two years specified under sub-section (14) of section 155;
- the amount of compulsory deposit, if any, claimed to have been made under the Compulsory Deposit Scheme (Income-tax Payers) Act, 1974 (38 of 1974);
- where regular books of account are maintained by the assessee, the return is accompanied by copies of—
- manufacturing account, trading account, profit and loss account or, as the case may be, income and expenditure account or any other similar account and balance sheet;
- (ii). in the case of a proprietary business or profession, the personal account of the proprietor; in the case of a firm, association of persons or body of individuals, personal accounts of the partners or members; and in the case of a partner or member of a firm, association of persons or body of individuals, also his personal account in the firm, association of persons or body of individuals;
- (iii). where the accounts of the assessee have been audited, the return is accompanied by copies of the audited profit and loss account and balance sheet and the auditor’s report and, where an audit of cost accounts of the assessee has been conducted, under section 233B 51 of the Companies Act, 1956 (1 of 1956), also the report under that section;
- (iv). where regular books of account are not maintained by the assessee, the return is accompanied by a statement indicating the amounts of turnover or, as the case may be, gross receipts, gross profit, expenses and net profit of the business or profession and the basis on which such amounts have been computed, and also disclosing the amounts of total sundry debtors, sundry creditors, stock-in-trade and cash balance as at the end of the previous year:
Conclusion
Tax audit is a review of your financial records by a Chartered Accountant. Your books must be audited if:
- You are a professional earning gross receipts exceeding 50 lakhs
- A Business owner with an annual revenue of over 10 crores where cash transactions do not exceed 5% of total transactions
You have opted for presumptive taxation, you declare your income below the prescribed percentage but your total income exceeds the basic exemption limit of 250,000
a. Where accounts are audited under companies Act: Then it will be sufficient if the accounts are audited under such law before the specified date and assessee obtains a report from a chartered accountant in the prescribed form under Income Tax Act, 1961.Under section 141 of Companies Act, 2013, only a Chartered Accountant is qualified to conduct audit of companies.A question often arises whether the audit under section 44AB is required to be conducted by the statutory auditor? In this connection, it may be stated that Section 44AB stipulates that only Chartered Accountants should perform the tax audit. This section does not stipulate that only the statutory auditor appointed under the Companies Act, 2013 or other similar Statute should perform the tax audit. As such the tax audit can be conducted either by the statutory auditor or by any other chartered accountant in full time practice.In a case where statutory auditor is not appointed, where such appointment is required by a statute the chartered accountant appointed to conduct audit under section 44AB can commence and complete his audit without waiting for the appointment of statutory auditor and report on the accounts audited by the statutory auditors. The tax auditor in such cases will, however, have to conduct the financial audit as well in order to enable him to certify whether or not the accounts reported upon by him give a true and fair view of the state of affairs of the assessee whose accounts are audited by him under section 44AB and the tax auditor provides his report in Form No. 3CB and to furnishes/certifies the relevant particulars in Form No.3CD.
b. Where accounts are audited under any other provisions of the Income Tax Act 1961: Where a person is required to get his accounts audited under any other law, then it shall be sufficient compliance with the provisions of this section if such person gets the accounts audited under such other law before the specified date and furnish by that date the report of the audit as required under such other law and a further report by an accountant in the form prescribed under this section.
c. Report of audit of accounts to be furnished under section 44AB: Rule 6G.
- 1. The report of audit of the accounts of a person required to be furnished under section 44AB shall,
- in the case of a person who carries on business or profession and who is required by or under any other law to get his accounts audited, be in Form No. 3CA:
- in the case of a person who carries on business or profession, but not being a person referred to in clause (a), be in Form No.3CB.
Submission of Audit Report in Form 3CB instead of Form 3CA along with Form 3CD is sufficient compliance of Tax Audit u/s 44AB hence no penalty u/s 44AB.
- (2). The particulars which are required to be furnished under section 44AB shall be in Form No. 3CD.
Tax auditor shall furnish tax audit report online by using his login details in the capacity of ‘chartered accountant’. Taxpayer shall also add CA details in their login portal. Once audit report is uploaded by tax auditor, same should either be accepted/ rejected by taxpayer in their login portal. If rejected for any reason, all the procedures need to be followed again till the audit report is accepted by the taxpayer.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is tax audit?
-
The dictionary meaning of the term "audit" is check, review, inspection, etc. There are various types of audits prescribed under different laws like company law requires a company audit; cost accounting law requires a cost audit, etc. The Income-tax Law requires the taxpayer to get the audit of the accounts of his business/ profession from the view point of Income-tax Law.Section 44AB gives the provisions relating to the class of taxpayers who are required to get their accounts audited from a chartered accountant. The audit under section 44AB aims to ascertain the compliance of various provisions of the Income-tax Law and the fulfillment of other requirements of the Income-tax Law. The audit conducted by the chartered accountant of the accounts of the taxpayer in pursuance of the requirement of section 44AB is called tax audit.The chartered accountant conducting the tax audit is required to give his findings, observation, etc., in the form of audit report. The report of tax audit is to be given by the chartered accountant in Form Nos. 3CA/3CB and 3CD.
- 2. What is the objective of tax audit?
-
One of the objectives of tax audit is to ascertain/ derive/ report the requirements of Form Nos. 3CA/ 3CB and 3CD. Apart from reporting requirements of Form Nos. 3CA/ 3CB and 3CD, a proper audit for tax purposes would ensure that the books of account and other records are properly maintained, that they truly reflect the income of the taxpayer and claims for deduction are correctly made by him. Such audit would also help in checking fraudulent practices. It can also facilitate the administration of tax laws by a proper presentation of accounts before the tax authorities and considerably save the time of Assessing Officers in carrying out routine verifications, like checking correctness of totals and verifying whether purchases and sales are properly vouched for or not. The time of the Assessing Officers saved could be utilized for attending to more important and investigational aspects of a case.
- 3. As per section 44AB, who is compulsorily required to get his accounts audited, i.e., who is covered by tax audit?
-
As per section 44AB, following persons are compulsorily required to get their accounts audited:
- A person carrying on business, if his total sales, turnover or gross receipts (as the case may be) in business for the year exceed or exceeds 1 crore. This provision is not applicable to the person, who opts for presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD and his total sales or turnover doesn't exceeds 2 crores.
Note: The threshold limit, for a person carrying on business, is increased from 1 Crore to 10 crore in case when cash receipt and payment made during the year does not exceed 5% of total receipt or payment, as the case may be. In other words, more than 95% of the business transactions should be done through banking channels.
- A person carrying on profession, if his gross receipts in profession for the year exceed 50 lakhs.
- An assessee who declare profit for any previous year in accordance with section 44AD and he decreases profit for any of one 5 assessment year relevant to the previous year succeeding such previous year lower than the profit computed as per section 44AD and his income exceeds the amount which is not chargeable to tax.
- If an eligible assessee opts out of the presumptive taxation scheme, within the aforesaid period, he cannot choose to revert back to the presumptive taxation scheme for a period of five assessment years thereafter.
- A person who is eligible to opt for the presumptive taxation scheme of section 44ADA but he claims the profits or gains for such profession to be lower than the profit and gains computed as per the presumptive taxation scheme and his income exceeds the amount which is not chargeable to tax.
- This provision is not applicable to the person, who opts for presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD and his total sales or turnover does not exceeds 2 crores.
- A person who is eligible to opt for the presumptive taxation scheme of sections 44AE but he claims the profits or gains for such business to be lower than the profits and gains computed as per the presumptive taxation scheme of sections 44AE.
- A person who is eligible to opt for the taxation scheme prescribed under section 44BB or section 44BBB but he claims the profits or gains for such business to be lower than the profits and gains computed as per the taxation scheme of these sections.
Note: Section 44BB is applicable to non-resident taxpayers engaged in the business of providing services or facilities in connection with, or supplying plant and machinery on hire basis to be used in exploration of mineral oils. Section 44BBB is applicable to foreign companies engaged in the business of civil construction or erection of plant or machinery or testing or commissioning thereof, in connection with a turnkey power project.
- 4. If a person is required by or under any other law to get his accounts audited, then is it compulsory for him to once again get his accounts audited to comply with the requirement of section 44AB?
-
Persons like company or co-operative society are required to get their accounts audited under their respective law. Section 44AB provides that, if a person is required by or under any other law to get his accounts audited, then he need not again get his accounts audited to comply with the requirement of section 44AB. Is such a case, it shall be sufficient if such person gets the accounts of such business or profession audited under such law and obtains the report of the audit as required under such other law and also a report by the chartered accountant in the form prescribed under section 44AB, i.e., Form No. 3CA and Form 3CD.
- 5. What are Form Nos. 3CA/3CB and 3CD?
-
The report of the tax audit conducted by the chartered accountant is to be furnished in the prescribed form. The form prescribed for audit report in respect of audit conducted under section 44AB is Form No. 3CB and the prescribed particulars are to be reported in Form No. 3CD.In case of persons covered under previous FAQ, i.e., who are required to get their accounts audited by or under any other law, the form prescribed for audit report is Form No. 3CA and the prescribed particulars are to be reported in Form No. 3CD.
- 6. What is the due date by which a taxpayer should get his accounts audited?
-
A person covered by section 44AB should get his accounts audited and should obtain the audit report on or before 30th September of the relevant assessment year, e.g., Tax audit report for the financial year 2021-22 corresponding to the assessment year 2022-23 should be obtained on or before 30th September, 2022.The tax audit report is to be electronically filed by the chartered accountant to the Income-tax Department. After filing of report by the chartered accountant, the taxpayer has to approve the report from his e-fling account with Income-tax Department.
- 7. What is the penalty for not getting the accounts audited as required by section 44AB?
-
According to section 271B, if any person who is required to comply with section 44AB fails to get his accounts audited in respect of any year or years as required under section 44AB or furnish such report as required under section 44AB, the Assessing Officer may impose a penalty. The penalty shall be lower of the following amounts:
- 0.5% of the total sales, turnover or gross receipts, as the case may be, in business, or of the gross receipts in profession, in such year or years.
- 1,50,000.
However, according to section 271B, no penalty shall be imposed if reasonable cause for such failure is proved.
- 8. Who can use ITR – 4 (SUGAM)?
-
Form ITR – 4 (SUGAM) can be u sed by an Individual/HUF/Firm (Other than LLP) whose total income for the year includes:
- Business income computed as per the provisions of section 44AD or 44AE; or;
- Income from Profession as computed as per the provisions of 44ADA; or
- Income from salary/pension; or
- Income from one house property (excluding cases where loss is brought forward from previous years); or
- Income from other sources (excluding winnings from lottery and income from race horses dividend income in excess of 10 lakhs or unexplained Income, etc. as referred to in section 115BBE)
Further, in a case where the income of another person like spouse, minor child, etc., is to be clubbed with the income of the taxpayer, this return form can be used where income to be clubbed falls in any of the above categories.
- 9. Who cannot use ITR – 4 (SUGAM)?
-
Form ITR – 4 (SUGAM) cannot be used by an individual/HUF:
- Who is a Non-resident or Not Ordinarily Resident
- Who is a Director of a company
- Whose total income exceeds 50 lakhs
- Who has income from more than one House Property
- Who has held unlisted equity shares at any time during the previous year
- Who claims deduction under section 80QQB or section 80RRB in respect of royalty from patent or books
- Who claims deduction under section 10AA or Part-C of Chapter VI-A
- Who has brought forward loss or losses to be carried forward under any head
- Who has income of the nature specified in section 17(2)(vi) on which tax is payable or deductible under section 191(2) or section 192(1C).
- Person claiming deduction under section 57 from income taxable under the head 'Other Sources' (other than deduction allowed from family pension)
- Who wants to claim relief under section 90 and section 91
- Who wants to claim credit of tax deducted at source in the hands of any other person.
- Who has any assets (including Financial Interest in an entity) located outside India.
- Who has signing authority in any account outside India
- Who has any income to be apportioned in accordance with provisions of section 5A
- Who has any of the following income:
- (a). Income from Business or Profession
- (b). Income from Business or Profession- Capital Gains or Loss
- (c). Income from Business or Profession- Income taxable under the head 'Other sources' which is taxable at special rate
- (d). Income from Business or Profession- Dividend income exceeding 10 lakhs taxable under Section 115BBDA
- (e). Income from Business or Profession- Unexplained income (i.e., cash credit, unexplained investment, etc.) taxable at 60% under section 115BBE
- (f). Income from Business or Profession- Agricultural Income exceeding 5,000
- (g). Income from Business or Profession- Income from any source outside India
- (h). Income from Business or Profession- Income from speculative business and other special incomes.
- (i). Income from Business or Profession- Income from agency business or commission or brokerage
In case the assesse keeps and maintains all books of accounts and other documents referred to in section 44AA, and also gets his accounts audited and obtains an audit report as per section 44AB, filling up the Form ITR – 4 (SUGAM) is not mandatory. In such a case, other regular return forms viz. Form ITR – 3 or Form ITR – 5, as applicable, should be used.
- 10. What is the due date for filing of return of income by an individual carrying out a business or a profession?
-
An individual carrying on a business or profession must file his return of income on or before 31st July of an assessment year. If he is subject to tax audit, he can file his return anytime on or before 30th September of the assessment year. These due dates apply in the normal course unless there is an extension of due dates announced by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT).
- 11. When will a businessman or a professional be subject to tax audit?
-
In the case of a businessman, if his total turnover from business exceeds 1 crore, he is liable to an audit under the Income-tax Act under Section 44AB. In case he is a professional, if his gross receipts exceed 25 lakhs, he is liable for a tax audit.
- 12. I run a small business with a turnover of about 30 lakhs on an average every year. Do I have to maintain accounting records?
-
Yes. If your turnover from business exceeds 25 lakhs in any one of the immediately 3 preceding years, you must maintain books of accounts. Not doing so can attract a penalty of 25,000.
- 13. I have opted for the presumptive scheme of tax. Should I still pay advance tax?
-
If you have opted for the presumptive scheme of tax, you may not be liable to pay advance tax every quarter but you must ensure you are paying all your advance taxes on or before 15th March of the concerned financial year. Further, any taxes paid before the 31st March will be considered as advance taxes only.
- 14. Can a person opting for presumptive scheme of tax claim any further expenses from his gross income?
-
No. Once a person declares the prescribed percentage of his gross receipts or turnover as income, he cannot once again claim any other expenses as a deduction.
- 15. Should a person offering income presumptively maintain books of accounts?
-
No. A person opting for presumptive income scheme under Section 44AD, 44ADA, 44AE etc, need not maintain any books of accounts.
- 16. Can I opt out of the presumptive scheme if I feel it does not work well for me?
-
Once you opt for this scheme, you must follow it for the next 5 years. Opting out of it for any 1 year during these 5 years will make you ineligible to again opt for it the 5 years immediately following the year when you opted out of it.For example, an assessee claims to be taxed on presumptive basis under Section 44AD for AY 2016-17. For AY 2017-17 and 2018-19 also he offers income on basis of presumptive taxation scheme. However, for AY 2019-20, he did not opt for presumptive taxation Scheme. In this case, he will not be eligible to claim benefit of presumptive taxation scheme for next five AYs, i.e. from AY 2020-21 to 2024-25.
- 17. When shall an assessee maintain books and get the accounts audited?
-
If an assessee meets the following criteria, then he/she must maintain books and get accounts audited under section 44AB:
- Income from the profession is offered at a lower rate than 50% of the gross receipts
- Total income of the assessee is more than the basic exemption
- 18. Can a person use 44AD and 44ADA simultaneously if he has income from both businesses, as well as a profession?
-
Yes, a person can use 44AD and 44ADA simultaneously if he has income from both businesses, as well as a profession.
- 19. Section 44AE - can I file the ITR without having any goods carriage in the presumptive scheme? As the section says, 'should own no more than 10 goods carriage vehicles'?
-
You need to have at least one goods carriage vehicle in order to be eligible to show income u/s 44E while filing return. Otherwise, without a single goods carriage vehicle, an individual cannot be said to be engaged in the business of goods carriage and hence would not be eligible for showing presumptive income u/s 44E.
- 20. My status is RNOR, can I file returns under 44ADA (Presumptive Scheme)?
-
Section 44ADA applies to resident assesses. Since, an RNOR is also a resident assessee; it applies to you as well. Hence, you can file returns under 44ADA.
- 21. Can a management consultant avail presumptive taxation under Section 44AD of the Income Tax Act?
-
Yes, a management consultant can avail presumptive taxation under section 44AD, since a management consultant is not covered under the persons excluded from applicability of Section 44AD.
- 22. Can I file the ITR 4 under 44ADA if I filed the ITR 3 last year which was the first year of filing? The 5 years limit is for 44ADA as well.
-
Yes, the limit of 5 years also applies to Section 44ADA.
- 23. Can we use section 44AD and show 8% even if profit is 20%?
-
Section 44AD is applicable to small business to provide them ease of compliance and save them from requirement of maintenance of detailed books and getting them audited annually. Hence, small business can avail the benefit of showing 8% profit even if it is 20%. However, ethically, they should show the actual amount of profit as 8% is the minimum profit to be shown.
- 24. Section 44AD or 44ADA, which taxation is better to save tax when filing income through Google Adsense earnings?
-
Google adsense earnings are of the nature of commission income as they are received for display of advertisements on the person’s page, video or other online content. Since commission and brokerage income have been specifically excluded from applicability of section 44AD and neither are they included in the applicability of Section 44 ADA which applies only to certain specified professions.
- 25. Can I file ITR 4 if a person earns income from brokerage for A.Y. 2018-19?
-
No, you cannot file ITR 4 if a person earns income from brokerage for A.Y. 2018-19, since ITR 4 is for individuals showing business income u/s 44 AD and brokerage has been specifically excluded from the scope of Section 44AD.
- 26. While submitting Form 3CB-3CD, “Unique Document Identification Number (UDIN)” page is displayed. Though we have duly taken UDIN before uploading the tax audit report, I am not able to add the UDIN details. Should I select “I do not have UDIN / I will update later” instead?
-
This feature is presently not available and will be enabled shortly. You may still go ahead and file the form by selecting “I do not have UDIN / I will update later”. Once the UDIN feature made available for all the forms, you can update the same in the portal.
- 27. I am trying to file and submit Form 10B. However, upon submission, the page displays the following error "INVALID FORMAT FOR ARN". What should I do?
-
Before filing Form 10B, please update your profile from the “My Profile” section and ensure that all mandatory fields (Mobile Number with country code, Email and Designation of the person to whom it belongs, Country, Flat/Door/Building, Pin code/Zip code, Post office, Area/Locality, District/City, State) are filled. Try not to use special characters while filling the address section. Also ensure that that the key person who will be appointed as principal contact and authorized to e-verify are chosen correctly. Ensure all the details such as PAN, Name, designation, DIN, Residential status, mobile number along with country code, email id and other mandatory details are updated. Also, verify whether the status of the DSC registered is appearing as ‘Yes’ (if the mode of filing is through DSC). After updating your profile details, you can re-login and try again.
- 28. I am not able to upload the Form 29B. How can I file and submit Form 29B?
-
Form 29B is available on the e-Filing portal. Form 29B is required to be assigned by Taxpayer to their Chartered Accountant (CA). You can assign the Form after initiating the Form through file Form functionality or My CA functionality available at the portal.
Once the taxpayer assigns the Form, the CA can access this Form in his / her worklist. Once uploaded by CA, Taxpayer can access and accept the Form under his Worklist. - 29. I am unable to file form 29B for the Assessment Year 2021-22. The page is displaying the following error “Submission Failed: Invalid Input”. What should I do?
-
You might have missed filling Part 3 of “Report of an accountant”. In case the field is not applicable, you can enter “NA” in the text box provided below para 3 of “Report for an Accountant” and try resubmitting the form.
- 30. I am unable to file form 29B for the assessment year 2021-22. The page is displaying the following error “INVALID FORMAT FOR ARN”. What should I do?
-
This is observed when “Profile” of the User is not updated correctly. Please ensure that there is no mismatch in the information filled in the Form and your profile. After updating your profile, re-login to the e-Filing portal and try again.
- 31. While filing form 29B, Part C (Details of the amount required to be increased or decreased in accordance with sub-section (2C) of section 115JB), I am trying to enter the amounts by which the book profit needs to be increased or decreased. However, the form is not accepting negative value. What should I do?
-
It is likely that you are working on old drafts of the Form 29B. Please delete the draft and file a fresh form.
- 32. I am unable to submit form 10DA as the following error message appears ‘Submission failed’. How should I proceed?
-
You should withdraw/delete old form which is already saved in “File Income-tax Forms” and start the fresh filing of the Form. Ensure that all fields including address fields are fully updated in the verification panel and retry submitting the form.
- 33. Based on a notification on 29th December, 56F is removed and replaced by 56FF (only for reinvestment details). However, there is no change in section 10AA read with 10A. Do I need to file 56F?
-
Both the forms are available to users in the e-Filing portal.
- 34. I am unable to add income details while filing Form 10E for the FY 2019-20. What should I do?
-
Ensure that you are filing Form 10E for Assessment year 2021-22. In order to file Form 10E for Assessment year 2021-22, click e-File>Income-tax Forms>File Income-tax Forms. Scroll down to find the tab “Persons without Business/Professional Income” Click on File now. Select Assessment Year as 2021-22 and click on Continue.
- 35. While filing Form 10E, I am unable to view the taxes applicable in the Assessment year. How should I proceed?
-
Ensure that you have filled in all income details (including previous year income details in Table A). The taxes will be automatically displayed based on the slab rate. Verify if the income as per the details available on the portal matches with your calculation and insert the amount of tax in the respective table.
- 36. Is Form 10-IE mandatory to file?
-
Yes, it is mandatory to file Form 10-IE only in case, you want to opt for new tax regime and have Income under the Head “Profits and Gains of Business and Profession.
- 37. What will happen if Form 10-IE is applicable to me and I fail to file before filing ITR?
-
In case you do not file form 10-IE before filing your ITR, you cannot opt for new tax regime.
- 38. While submitting the form 10-IE, displays “Invalid Input” or “Submission Failed!” What should I do?
-
Before, filing Form 10-IE please update “Contact Details” (or “Key Person Details” in case you are an HUF) under “My Profile” and ensure that all mandatory fields are filled.
After updating your Contact details from your profile, you can re-login and try again. - 39. While filing Form 10-IE, the AO details or Date of Birth/ Incorporation is getting pre-filled. What should I do?
-
Please delete the old draft of the form by clicking on “Delete Draft” and try re-submitting Form 10-IE.
- 40. While submitting the form 10-IE, designation of Karta of HUF is not getting pre-filled under Verification tab. What should I do?
-
You are requested to update the “Key Person Details” under “My Profile” section. Re-login to the e-Filing portal and try again.
- 41. I do not have any business income. While filing Form 10-IE, I am unable to select “No” under “Basic Information” tab. What should I do?
-
In case you don’t have any business, income and are required to file ITR 1/ ITR 2, there is no need to file Form 10-IE in order to opt for the new tax regime under Section 115BAC of the Income-tax Act, 1961. The option to exercise the benefit under Section 115BAC, in case you do not have business income, can be claimed while filing the respective ITR form (ITR 1/ ITR 2).
- 42. When I am trying to upload attachments while filing statutory forms, certain errors are being displayed on the page. What should I keep in mind while uploading attachments on the e-Filing portal?
-
The error might be due to naming convention used in the file. Please avoid using any special characters in the file name and keep the file name small. In addition, the size of the attachment should be less than 5 MB and the attachment should be in PDF or Zip format only.
- 43. While submitting Form 10BA, the page displays the error: “Error: Please enter valid values”. What should I do?
-
In case you are facing such issue while submitting the form, ensure that steps mentioned for updating profile are completed. Additionally, delete the old draft of the form by clicking on “Delete Draft”. Re-log in to the e-Filing portal and try again.
- 44. While submitting Form 35, the page displays the error “Appeal fees paid should be either of 250, 500 or 1000 as the case may be” while entering the appeal fees challan details. What should I do?
-
Open the 4th panel, i.e., "Appeal details”
- Please ensure that the mandatory fields like “Amount of income assessed” etc. are updated.
- In case of TDS appeal, it may be selected as “Not Applicable”.
Once these fields are updated, go to 7th panel i.e., “Appeal filing details” and try deleting and re-entering the challan details.
- 45. While filing Form 10IC, I had selected “Yes” for “Whether option under sub-section (4) of section 115BA has been exercised in Form 10-IB?” Even then, the pre-filled “Previous Year” and “Date of filing of Form 10-IB” fields were missing. What should I do?
-
You should delete the ‘Draft’ Form 10-IC which is already saved in “File Income-tax Forms” and start the fresh filing of the Form.
- 46. While filing Form 10IC, one I have selected “Yes” for “Whether option under sub-section (4) of section 115BA has been exercised in Form 10-IB?” the check box for “I do hereby withdraw the option under sub-section (4) of section 115BA exercised on….” is not getting saved. What should I do?
-
You should delete the ‘Draft’ Form 10-IC which is already saved in “File Income-tax Forms” and start the fresh filing of the Form.
- 47. While filing Form 10-IB, the Basic details of the Company were not auto-populated correctly from “My Profile”. What should I do?
-
You should delete the ‘Draft’ Form 10-IB which is already saved in “File Income-tax Forms” and start the fresh filing of the Form.
- 48. While filing Form 10-ID, the “Assessing Officer” details were not getting auto-populated from “My Profile”. What should I do?
-
You should delete the ‘Draft’ Form 10-ID which is already saved in “File Income-tax Forms” and start the fresh filing of the Form.